* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Management and Organisational Behaviour
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
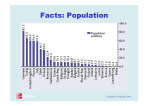
The Economics of European Integration Chapter 7 Growth Effects and Factor Market Integration © Baldwin & Wyplosz 2003 Growth Effects • European leaders have long emphasised a different the pro-growth aspects of European integration. • These operate in a way that is fundamentally different from the way allocation effects operate. • They operate by changing the rate at which new factors of production – mainly capital – are accumulated, i.e. the name ‘accumulation effects’. © Baldwin & Wyplosz 2003 Verbal Logic of Growth • Growth in income per worker requires more output per worker. • Nation’s labour force can produce more goods and services year after year only if they have more/better ‘tools’ year after year: – ‘tools’ means capital broadly defined: • physical capital (machines, etc.) • human capital (skills, training, experience, etc.) • knowledge capital (technology). © Baldwin & Wyplosz 2003 Verbal Logic of Growth • ERGO, rate of output growth linked to rate of physical, human and knowledge capital accumulation. • Most capital accumulation is intentional and it is called investment: – thus: European integration affects growth mainly via its effect on investment in human capital, physical capital and knowledge capital. © Baldwin & Wyplosz 2003 Verbal Logic of Growth: Summary • European integration (or any other policy) → Allocation effect → Improved efficiency → Better investment climate → More investment in machines, skills and/or technology → Higher output per person. • Medium run effects eventually peter out – Growth returns to its long-run rate. • Long-run effects raise long-run rate forever. © Baldwin & Wyplosz 2003 Some Facts European Growth Phases, 1890-1992 © Baldwin & Wyplosz 2003 Some Facts Growth in the WWII Reconstruction Phase © Baldwin & Wyplosz 2003 Some Facts GDP per capita & rankings, 1950 and 1973 (1990 international dollars) 1950 GDP (1990 $) European Rank 1950 Change in Rank 19501973 GDP Growth Rate EEC average 4,825 8.0 + 1.2 4.2 EFTA average 6,835 3.6 -1.4 3.0 France 5,221 7 +2 4.0 Germany 4,281 9 +5 5.0 Italy 3,425 13 +2 4.9 UK 6,847 2 -5 2.4 © Baldwin & Wyplosz 2003 Some Facts GDP per capita & rankings, 1950 and 1973 (1990 international dollars) – full list © Baldwin & Wyplosz 2003 Some Facts GDP per capita & rankings, 1950 and 1973 (1990 international dollars) – full list, cont. © Baldwin & Wyplosz 2003 Solow Diagram • Show medium run growth effects in simple diagram. • To simplify, start with whole EU as a single, closed economy with fully integrated capital and labour markets and the same technology everywhere. © Baldwin & Wyplosz 2003 Solow Diagram © Baldwin & Wyplosz 2003 Induced Capital Formation © Baldwin & Wyplosz 2003 Integration Induced Investment Rate Rise © Baldwin & Wyplosz 2003 Integration-induced investment in Spain and Portugal © Baldwin & Wyplosz 2003 Integration-induced investment in Ireland © Baldwin & Wyplosz 2003 Integration-induced investment in Greece © Baldwin & Wyplosz 2003 Long-Term Growth in Solow-Like Diagram © Baldwin & Wyplosz 2003 Long-Term Growth Impact of Integration euros/L Integration improves efficiency → improves investment climate → higher investment rate (s rises to s’) → faster growth (knowledge capital accumulates more rapidly) GDP/L s’(GDP/L) Y/L* s(GDP/L) C A d(K/L) B K/L* K/L =Knowledge/L © Baldwin & Wyplosz 2003 Microeconomics of Capital Market Integration © Baldwin & Wyplosz 2003 Welfare Effects of Capital ‘Migration’ • ‘Native’ capital-owners in home lose area ‘A’; home labour gains area A+B; Total economic impact on home citizens equal to area B. • Foreign capital still employed in foreign gains F; foreign labour loses D+F; total impact on foreignbased factors is -D: – if we count the welfare of foreign capital owners whose capital now works in home (gains C+D), so overall foreign welfare gain is C. © Baldwin & Wyplosz 2003 Welfare Effects of Capital ‘Migration’ © Baldwin & Wyplosz 2003 Labour Market Integration: Simplest Framework • Just like capital migration analysis © Baldwin & Wyplosz 2003 Immigration: Facts © Baldwin & Wyplosz 2003 Immigration: Facts (cont.) © Baldwin & Wyplosz 2003 Unemployment © Baldwin & Wyplosz 2003