* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Edmund Phelps wikipedia , lookup
Full employment wikipedia , lookup
Fear of floating wikipedia , lookup
Money supply wikipedia , lookup
Interest rate wikipedia , lookup
Greg Mankiw wikipedia , lookup
Early 1980s recession wikipedia , lookup
Monetary policy wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
Stagflation wikipedia , lookup
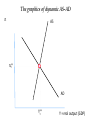
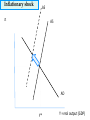
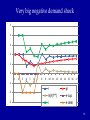
The full dynamic short-run model 1 The Dynamic Model A nice new addition to Mankiw. Combines - IS - LM (changed to reflect central bank targeting) - Phillips curve Closed economy Short-run of business cycles Keynesian rather than classical 2 Monetary policy rule Taylor rule: i t = πt + θ π (πt - π*) +θY (Yt - Y* ) Rationale: a rule that incorporates both real and inflation targets But, also one that has good stability properties Derived from minimizing loss function such as L = θ π (πt - π*) 2 +θY (lnYt - lnY* ) 2 [This version has loss function the same as the Taylor run. It seems more likely that the optimal Y* would be above potential output.] 3 20 Federal funds rate Taylor rule rate 16 12 8 4 0 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Fedfunds* = pi +2 + .5*(pi – 2) - .25*(u – nairu) pi = 4 quarter PCE core inflation Why is rate below target today? 4 Algebra of Dynamic AS-AD analysis Key equations: 1. Demand for goods and services: 2. Cost of capital: 3. Phillips curve: 4. Inflation expectations: 5. Monetary policy: Yt = Y* - α (rt –r*) + μG + εt rt = it – π e t + risk premium π t = π e t + φ(Yt - Y* ) + vt π e t = π t-1 i t = πt + θ π (πt - π*) +θY (Yt - Y* ) Notes: • Equation (1) is just our IS-LM solution • Phillips curve substitutes output by Okun’s Law • Mankiw uses slightly different version of (4) • Mankiw doesn’t consider risk premium, so ignore for now • We have added “G” to show the impact of fiscal policy 5 Solve for AS and AD AD: Y t = -[α θ π /(1+ α θ Y )] π t + μ /(1+ α θ Y )] G +… AS: π t = π t-1 + φ(Yt - Y* ) + vt NOTE: AD is like IS-LM equilibrium except is substitutes the Fed response for a fixed money supply AS is Phillips curve with substituting for expected inflation Note that we have moved up one derivative from intro AD-AD because of Phillips curve. 6 The graphics of dynamic AS-AD π AS πt* AD Yt* Y = real output (GDP) 7 Inflationary shock AS π AS AD Y* Y = real output (GDP) 8 Example by simulation model This will be available on course web page. You might download and do some experiments to see how it works. New kind of economics: computerized modeling. [The screen shots are ones that were used in class. The model posted on the course web site is slightly changed from that version.] 9 10 Parameters Parameters alpha phi= Taylor rule: pi*= r*= coef(i,pi)= coef(i,Y)= 1 dY/dr 0.25 d(pi)/dY 2 Inflation target 2 Natural rate of interest 0.5 Taylor coeff on inflation 0.5 Taylor coeff on output Shocks to system e-sup 1 Supply (inflation) shocks eps-d 0 Demand (G, NX, I) shocks shock r 0 Financial crisis shocks (+ is financial crisis) 11 Numerical simulation in base run t r -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 pi 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 Y-Y* 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 e-s 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 i 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 e-d 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 e-r 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 12 Graph of base case 4.5 4 3.5 r ln(Y/Y*) i 3 pi e-sup e-dem 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 13 Very big negative demand shock 5 4 3 2 1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 -1 -2 -3 r ln(Y/Y*) i pi e-sup e-dem 14 Other examples 1. Supply shocks (e-sup = 1) 2. Financial crisis (shock r = 1) 3. Inflation targeting without output targets: much deeper recessions with demand shocks (ECB) 4. Unstable monetary policy where insufficient response to shocks (Great Inflation discussion) 5. Liquidity trap 15 Summary This now finishes our treatment of closed-economy business cycles. Key elements are - IS elements in I, C, fiscal policy, and trade - Financial markets and monetary policy - Inflation dynamics Can we abolish the business cycle? 16