* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 5 PowerPoint
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Standby power wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
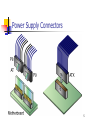
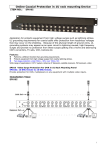
Chapter Overview Power Supplies Power Supply Problems 1 Overview of Power Supplies The standard power supply Converts AC to DC “Conditions” power by evening out fluctuations Requires a fan Standard power in U.S. is 110 volts alternating current (VAC) oscillating at 60 hertz (Hz). You must consider physical size, wattage, and connector types when replacing a power supply. 2 Power Supply Sizes Power supply sizes are based on the type of case and motherboard connections. The AT-style is found on older computers and earlier Pentium systems. The ATX-style (current technology) is found on Pentium II and later systems. You should compare the existing power supply with the new one before replacing it. 3 Power Supply Wattage A watt is a unit of electrical power equivalent to one volt-ampere. Total wattage needs are determined by adding the power required for each device, plus more power for startup. General-use computers require 130–205 watts. Servers and high-performance workstations require 350–500 watts. 4 Power Supply Connectors 5 Connections to Peripheral Hardware 6 Extenders and Splitters An extender lengthens the reach of a power connector. A splitter increases the number of connections. 7 Power Failures Power failures can have internal or external causes. External failures, which are more common, include Surges Spikes Sags Brownouts Blackouts 8 Power Protection Devices A surge suppressor Filters the effects of voltage spikes and surges Smoothes out power variations An uninterruptible power supply (UPS) is an inline battery backup. 9 Power Supply Problems 10 Chapter Summary The AT-style power supply is used for older motherboards and the ATX-style power supply is used for newer motherboards. Peripheral devices use Molex connectors and mini connectors. Different types of power failures can cause computer problems and can damage computer equipment. Surge suppressors and UPS devices can protect computer equipment. 11