* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Anticipated Problem: What are the main parts of a plant?
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
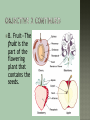
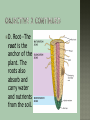
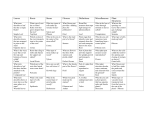
Briefly talk with students about how humans use plants to protect the soil, provide fresh air, and create visual interest. Ask the students if they have thought about plant parts that they eat. As a class, brainstorm edible plant parts. List them either on the chalkboard or on an overhead transparency. After the students have either exhausted their ideas or you think the list is long enough, give each student a copy of WS–A. Have them work in pairs or small groups to identify which category (flowers, fruits, leaves, roots, seeds, or stems) they think each of the foods belong. 1 Identify the parts of a plant. 2 Understand the function of each plant part. 3 Identify the plant parts that are used for human consumption. Flower Fruit Leaf Root Seed Stem Anticipated Problem: What are the main parts of a plant? I. There are six main parts of a plant. Each part is important to the plant’s survival. A. Flower B. Fruit C. Leaf D. Root E. Seed F. Stem Anticipated Problem: What is the function of each part of a plant? II. Each part of the plant has a specific job to do. Without even one of these parts, the plant, as a whole, would not be able to survive. A. Flower—The flower is the reproductive organ of the plant that produces seeds. The flower may also attract insects for pollination, if necessary. B. Fruit—The fruit is the part of the flowering plant that contains the seeds. C. Leaf—The leaf is the food factory of the plant. The leaves use chlorophyll, water, sunlight, and carbon dioxide to make food. D. Root—The root is the anchor of the plant. The roots also absorb and carry water and nutrients from the soil. E. Seed—The seed contains an embryo that provides food and water until the plant is able to make food for itself. F. Stem—The stem holds the leaves and flowers of the plant. Tubes in the stem transport food and water from the roots. Anticipated Problem: What plant parts do humans eat? III. The fruits, vegetables, and spices that we eat are parts of plants. Many times people incorrectly identify the part of the plant they are eating. A. Some examples of flowers that humans eat are broccoli, cauliflower, artichokes, and whole cloves. B. Some examples of fruits that humans eat are apples, grapes, avocados, pumpkins, cucumbers, tomatoes, and eggplants. C. Some examples of leaves that humans eat are cabbage, lettuce, Brussels sprouts, spinach, oregano, and basil. D. Some examples of roots that humans eat are beets, carrots, radishes, turnips, and rutabagas. E. Some examples of seeds that humans eat are peas, beans, corn, sunflower seeds, nuts, rice, peanuts, and popcorn. F. Some examples of stems that humans eat are celery, mushrooms, onions, potatoes, asparagus, cinnamon, and yams. 1. What are the main parts of a plant? 2. What is the function of each part of a plant? 3. What plant parts do humans eat?