* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
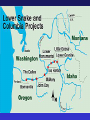
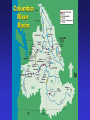
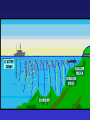
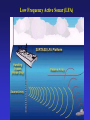
Fisheries Conservation • Important vertebrate animal – commercial & sport fisheries • Indicators of environmental health • Poor track record – pollution & sustainable mgt • Mgt relies on understanding responses to changes in environmental conditions Freshwater Fishery • Primarily recreation – small commercial • Sport fishery – resident & anadromous fish Freshwater Fishery Habitat – influence on fish life cycle 1) Temperature – influence on reproduction 2) Water Depth & Velocity – reproduction & growth 3) Turbidity – sedimentation 4) Dissolved Oxygen – streams & lakes (oxygen depletion) – relation to organics Freshwater Fishery Habitat – influence on fish life cycle 5) Substrate – material on bottom of water body redd: substrate nest for eggs 6) Cover – “in-water” & terrestrial shelter Environmental Limits to Reproduction 1) Natural Limitations 2) Human-Caused Limitations Environmental Limits to Reproduction 1) Natural Limitations * Storms * Soil Mass Movements * Activities of other Animals * Natural Barriers * Natural Disturbance to Vegetation * Predation * Winterkill Thermal Stratification (temperate lakes) dimictic vs. monomictic Winter cool water less dense Spring/Fall turnover (“mixing”) Summer epilimnion metalimnion thermocline hypolimnion Some Fisheries Legislation • 1950 Sportfish Restoration Act (Dingle-Johnson Act) - tax on sportfish equipment • ESA, etc… • 1984 Wallop-Breaux Amendment - new taxes (e.g., boat fuel) - new trust fund - aquatic education, marine fisheries Pacific Salmonid Fishery • State of Washington has 4 federally listed species -Snake & Columbia River drainages • sockeye (red) salmon, steelhead, chinook salmon, bull trout • Estimated 435 separate stocks in WA • 1 extinct • 113 unknown status • 134 depressed • 187 healthy • Harvest of chinook salmon 500,000 to 0 to 2,000+ (1970s to 1994 to 1996) • Harvest of coho salmon 2.5 M to 1,000+ Pacific Salmonid Fishery • 75% of steelhead stocks = unhealthy • 68% of chum salmon = healthy • 60% of sockeye salmon = unhealthy • Average size (age) of chinook & chum salmon declined 50% since 1920’s due to: - modified habitat - selective harvest - genetic change (hatchery vs. wild fish) Pacific Salmonid Fishery • Goal of fish hatcheries = replenish fish stocks to meet harvest demands (~125 federal/state/tribal) • Dramatic increase in hatchery fish can (~200 M salmon/steelhead): - lead to overfishing of remaining wild fish - spread disease to wild fish (e.g., whirling disease) - reduce genetic diversity (homogenize unique salmon stocks) Marine Fisheries: Conservation Topics MSY vs. optimum yield Marine Fisheries: Conservation Topics • Trawling & Turtle Exclusion Devices (TEDs) • Trawling & Marine Benthos 150,000 turtles annually in shrimp nets Marine Fisheries: Conservation Topics • Tropical Fish Industry • Low Frequency Active Sonar (US Navy) • High resolution detection (monitoring) • National Security • Invasive • Sonar waves cause disorientation • Sonar waves shatter tympanic bullae (“ear drums”) Passive Sonar Active Sonar Low Frequency Active Sonar (LFA) Low Frequency Active Sonar (LFA) Low Frequency Active Sonar (LFA)