* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Greeks
Athenian democracy wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Economic history of Greece and the Greek world wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek medicine wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek literature wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek religion wikipedia , lookup
History of science in classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
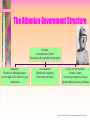
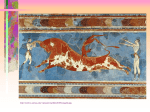
http://ccwf.cc.utexas.edu/~tjmoore/myth4web/05troygold.jpg. Minoans + Mycenaeans = The Greeks Origins of the Greeks: Minoans & Mycenaeans 2800 B.C.E. - 1500 B.C.E. Minoans (2800-1400 BCE) • • • • • • • • • http://ccwf.cc.utexas.edu/~tjmoore/Myth3web/05atheseusmincan.jpg. Lived on island of Crete Existed during Egypt’s Old Kingdom Government: Priest-kings Religion: Polytheists Cities NOT surrounded by walls Ship Builders & Traders Farming Fishing Overpowered by Mycenaeans by 1400 BCE Minoan Art Sculptures, Pottery, and Frescoes Minoans created and traded pottery, leather, bronze armor, and metal jewelry. They also enjoyed sports such as boxing and bull leaping. http://ccwf.cc.utexas.edu/~tjmoore/Myth3web/05atheseusmincan.jpg Minoan Fresco at the Palace of Knossos http://ccwf.cc.utexas.edu/~tjmoore/myth.html. Minoan fresco: Prince of Knossos http://www.graeco-roman.com/items/G4310.htm Minoan Religion Polytheists Main god: Great Goddess, Mother Earth) Minoan Religion • Built shrines on housetops, hilltops, and in caves – Why hilltops? – Why caves? • Offerings included: – – – – – Human hair fruit flowers jewels gold Mother Earth The fall of Minoan civilization is described in the legendary fight of Theseus, a young Greek prince and the Minotaur. Relief Sculpture of Theseus and defeated Minotaur http://ccwf.cc.utexas.edu/~tjmoore/Myth3web/05atheseusmincan.jpg Mycenaeans (2000 - 900 BCE)• • • • • • • • • Lower Greece (lowlands) Built fortress-palaces on hilltops Engaged in farming, herding, olive growing. Traded: gold & bronze Learned from Minoans: Shipbuilding, navigation, gold & bronze work, fashions, art, writing. Better warriors than traders (pirates) Became most powerful people in Aegean world by 1400 BCE Trojan War (1200s BCE) Conquered by Dorians (late 1200’s) The “Dark Age” (1100 -800 BCE) • Civil wars broke out following Trojan War • Dorians conquered Mycenaeans • Aegean world began era of “wandering and killing” • Independent communities developed Layered view of nine major settlements of Troy by Christopher Haussner based on archaelogical excavation. http://ccwf.cc.utexas.edu/~tjmoore/myth4web/05troygold.jpg Greek City-States (700 - 338 BCE) Greek City-States • The Hellenes, or Greeks emerge from the Dark Age • The Polis, or city-state was the center of Greek life • Polis structure: – Acropolis (fortified hill) – Agora (marketplace at foot of acropolis) – Polis included homes, farming villages, fields, and orchards http://www.indiana.edu/~kglowack/athens/acropolis.html Greek Civics and Politics • Civic and personal honor is one and the same • The Polis (city-state) is above everything else Greenblatt, Lemmo. Human Heritage. Glencoe, McGraw-Hill 1995. A New Government • Solon created 1st Constitution (594 BCE) – Set of principles and rules for governing • Purpose: To end oligarchy and to prevent uprising against government by middle and lower class http://www.indiana.edu/~kglowack/athens/images/07.017.JPG The First Democratic Constitution • Created by Cleisthenes in 508 BCE (lasted 300 yrs.) • Limits power of rich & land ownership • All male landowners could vote • All debts were erased • All enslaved due to debt, were freed • All Athenians became citizens and able to participate in government • Assembly created to make laws Representation of Cleisthenes http://www.bbc.co.uk/history/ancient/greeks/greekdemocracy_2.shtml The Athenian Government Structure Pericles Commander-in-Chief Selected by the elected ten generals Assembly Elected by Athenian males over the age of 20; Served 1 year Made laws Ten Generals Elected by Assembly Run Army and Navy Coucil of Five Hundred Served 2 years Chosen by lot among citizens Handled daily business of Athens http://norfacad.pvt.k12.va.us/project/pericles/Pericles.htm Greek Religion The most popular priestess was a priestess in the temple of Delphi. The Delphi was the center of the world for Greeks. http://ccwf.cc.utexas.edu/~tjmoore/mythslides1/27delphiview.jpg Gods with human qualities (anthropomorphism) Poseiden The Courtship of Venus and Mars http://ccwf.cc.utexas.edu/~tjmoore/mythslides1/mythslides1.html Aphrodite Greek Theater • Began during festivals honoring the god Dionysus (600 BCE) • Types of Plays – Tragedies • Aeschylus • Sophocles • Euripides – Comedies • Only men could act in plays • A civic responsibility http://ccwf.cc.utexas.edu/~tjmoore/mythslides1/28feastofgods.jpg The Great Greek Philosophers • Socrates • Plato • Aristotle http://www.arts.uwaterloo.ca/PHIL/cpshelle/Gallery/Greek/aristotle.jpg Socrates (469-399 BCE) Greenblatt, Lemmo. Human Heritage. Glencoe, McGraw-Hill 1995 http://www.btinternet.com/~socratic/ • Stonemason, spent time arguing with assembly • Taught: Question everything, use stepby-step questioning to final conclusion (Socaratic Method) • Executed for denying gods, corrupting youth, and trying to overthrow gov. Plato (427-347 BCE) • Pupil of Socrates • Recorded speeches of Socrates • Father of Political Science • Founded The Academy to train government leaders • Wrote The Republic & The Dialogues http://plato.evansville.edu/ Aristotle (384-322 BCE) Plato Aristotle http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/history/aristotle.html • Pupil of Plato at The Academy • Trained in Medicine • “Master of Them That Know” • First to classify plants & animals • Developed final steps in scientific method (Hypothesis and Test)