* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3APPT09MAINe
Microsoft SQL Server wikipedia , lookup
Oracle Database wikipedia , lookup
Open Database Connectivity wikipedia , lookup
Entity–attribute–value model wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Access wikipedia , lookup
Functional Database Model wikipedia , lookup
Concurrency control wikipedia , lookup
Ingres (database) wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Storage Engine wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Jet Database Engine wikipedia , lookup
Relational model wikipedia , lookup
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
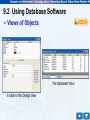
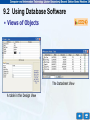
9.1 Basic Concepts of Database • The Structure of a Database – A database is a structured collection of data and consists of one or more tables. – A table in turn contains records and fields. A record is a row which contains a set of properties related to a particular item while a field is a column which contains a specific property for all items. – A well-designed database enables huge data storage and efficient data retrieval. 9.1 Basic Concepts of Database • The Structure of a Database Structure of a database 9.1 Basic Concepts of Database • Primary Key – A primary key is a field or a set of fields in a table. – Each record’s primary key is a unique value for identifying itself among all the records in the same table. – Primary keys can be used to establish relationships among tables. – In the following table, the field ‘Student ID’ can be used as a primary key since all the students are assigned a unique student identity number. 9.1 Basic Concepts of Database • Primary Key Primary key Student ID Student name Class Class number Age Sex 010101 Chan Tai Man 3A 3 15 M 010112 Cheung Siu Ming 3A 6 14 M 010215 Fok Wing Sze 3B 10 15 F 010231 Leung Hon Cheung 3B 18 15 M 010345 Wong Fung Yi 3C 33 16 F A table of students’ information 9.1 Basic Concepts of Database • Primary Key Primary key Student ID Student name Class Class number Age Sex 010101 Chan Tai Man 3A 3 15 M 010112 Cheung Siu Ming 3A 6 14 M 010215 Fok Wing Sze 3B 10 15 F 010231 Leung Hon Cheung 3B 18 15 M 010345 Wong Fung Yi 3C 33 16 F A table of students’ information 9.2 Using Database Software – When we manipulate a large amount of data, manual processing is proved to be both tedious and inefficient. – Therefore, we need to use database software to process database records. – With database software, relevant information can be accessed and updated efficiently with built-in functions – sorting – searching – report generation 9.2 Using Database Software – Common database software – – – – Microsoft Access FoxPro Oracle MySQL – They have different processing capacities that fit into different scales of applications. 9.2 Using Database Software • Working Environment of Microsoft Access – In Microsoft Access, the database window enables users to create various objects in the database. – After an object is created, it can be accessed in this window. Title bar Toolbar Creation mode Objects column Existing objects The working environment of Microsoft Access 9.2 Using Database Software • Tables – A database can consist of multiple tables which are structured collections of records. – Each record is one single row in a table and each record consists of many fields. An example of a table 9.2 Using Database Software • Query – A set of user-defined criteria for retrieving the relevant information from the database – It must be written in a specific format. Microsoft Access provides different tools to help users compose a query. – After a query is submitted, the requested data will be retrieved and the result will be displayed to users. A query in design (left) and its executed result (right) 9.2 Using Database Software • Form – An interface created by users to manipulate and display data – It can also serve other purposes such as user menus and message display. An example of a form 9.2 Using Database Software • Report – Present information in a user-defined format. – It can be viewed on screen or printed on paper. An example of a report in the Print Preview 9.2 Using Database Software • Views of Objects – In Microsoft Access, each object can be displayed in different ways with different views. Objects Views Tables Design View, Datasheet View, Pivot Table View and Pivot Chart View Queries Design View, Datasheet View, SQL View, Pivot Table View and Pivot Chart View Forms Design View, Datasheet View, Form View, Pivot Table View and Pivot Chart View Reports Design View and Print Preview List of different views for different objects 9.2 Using Database Software • Views of Objects The Datasheet View A table in the Design View 9.2 Using Database Software • Views of Objects The Datasheet View A table in the Design View 9.3 Creating a Table in Microsoft Access • Methods of Creating a Table – In Microsoft Access, there are three ways to create a table in a database. • By using the Design View; • By using the Table Wizard; • By entering data into Datasheet. – Using the Design View is the most preferred method to create a table since it allows users to define precisely the properties of each field such as name, data type and size. 9.3 Creating a Table in Microsoft Access • Methods of Creating a Table – The other two methods only allow users to create tables of rough designs and sooner or later, the table structures will probably need to be refined in the Design View anyway. – It is always a good practice to design thoroughly first before implementation and therefore the latter two methods are not recommended to build a robust database. 9.3 Creating a Table in Microsoft Access • Creating a Table in Design View – The Design View window is divided into two parts • Top pane – Enter the field names, data types and an optional description of the fields. • Bottom pane – Specify field properties. Top pane Bottom pane Working environment in Design View 9.3 Creating a Table in Microsoft Access • Creating a Table in Design View – The Design View window is divided into two parts • Top pane – Enter the field names, data types and an optional description of the fields. • Bottom pane – Specify field properties. Top pane Bottom pane Working environment in Design View