* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Relational Database Management System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
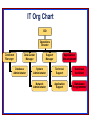
Database Management Data in organizations and the data management environment Managing Data All the value of this company is in its people. If you burned down all our plants, and we just kept our people and our information files, we should soon be as strong as ever. Thomas Watson, Jr. Former chairman of IBM Data, Information, & Knowledge Data Watson: “raw, unsummarized, and unanalyzed facts.” Information Watson: “data that have been processed into a meaningful form.” Knowledge Watson: “the capacity to use information… the expertise to make sense of… information… to interpret information and use it in decision making.” Information is created from streams of data through the application of knowledge. Data – functions and impact through time… o Data facilitate business events, such as transactions, in the present. o Data produced during prior events constitute an historical record of the past that can be summarized, explored, and analyzed for insights... o … which, in turn, informs decision-making that shapes the future. Management of data Desirable attributes: Typical problems: o o o o o o o o o o shareable transportable secure accurate timely relevant o o redundancy inconsistency lack of control access problems - poor interfaces - long delays lack of richness lack of integration Individual data management • Internal memory is limited • External memory extends internal memory Calendar • Organizing principles – Set amount of space – Ordering – Rapid access December 25, 1852 9 10 11 12 Staff Meeting Email Communication Project Planning Check lunch preparations 1 Meeting with directory 2 Vendor presentation 3 4 Process paperwork 5 6 Drive home 7 Dinner 8 9 Reading and relaxation © 1803, The Expeditioner, London Address book • Organizing principles – Pre-formatted storage space – Ordering – Rapid access K-L Name Address Rudyard Kipling PO Kyhber Pass Northwest Frontier India Name Address Jack London PO Klondike Alaska Name Address Name Address © 1815, The Expeditioner, London K L To do list • Organizing principles – Structure – Rapid scan support To Be Done This Week Action List √ Explore Nile Shoot crocodile Write journal √ Unwrap mummy © 1823, The Expeditioner, London (In data management, computer databases are just part of the picture… ) Organizational memory is supported by: o o o o o o o o relational databases other “database” technology - DBs based on older technology (our focus) - object databases - spreadsheets - PDAs and cell phones - voicemail, email, groupware - on-line documents paper records multi-media artifacts formal decision models employees’ brains organizational procedures and routines systems applications Data management systems timeline Object-oriented DBMS Relational DBMS Network DBMS Hierarchical DBMS File systems 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 Flat File Database Name Address Course Grade Mark Freeman 123 Main St English 101 B Mark Freeman 123 Main St Data Structure A Mark Freeman 123 Main St Psych 101 C Mary Smith 413 Elm Dr Chemistry 200 A Mary Smith 413 Elm Dr French 205 B David Cole 1009 10th Apt B Accounting 102 A Hierarchical Database Network Database Network and Hierarchical • Redundant • Difficult to maintain – Required system-level understanding of underlying data structures to access data • Costly – Labor – Computer resources – Time Relational Databases • E F Codd, 1970 • Relational – Relations = Grouping of related data (tables) – Data stored only once – Query language for accessing data – Analysts no longer need know how data is stored! • RDBMS (Relational Database Management System) IT Org Chart CIO Operations Director Database Manager Data Center Manager Database Administrator Support Manager Application Development System Administrator Technical Support Database Architect Network Administrator Application Support Database Programmer Information Technology Roles • Database Administrator – Manages day-to-day operations, install, upgrade, data backup recovery • Data Architect – Designs the database – Works with a business analyst to choose what data to store and how to organize it • Database Programmer – Develops database applications: computer programs that allow users to retrieve and process data Data Modeling – Top-down approach Data Model Data Definition Database Table The database development lifecycle (DDLC)… and the Term Project Assignments Completed by Instructor PROJECT PLANNING Assignment 1: Database Dictionary REQUIREMENTS DEFINITION Assignment 3: SQL Queries DESIGN CONSTRUCTION IMPLEMENTATION Assignment 1: Data Model USE Assignment 2: Database Prototype EVOLUTION Database Management Systems • OLTP (Online Transaction Processing) – Many transactions – Short transactions – Volatile data • Decision Support – Data Warehouse, Data Mining – Fewer transactions – Longer transactions – Static data Database Management System Design Design decisions have significant future impact Reliability Scalability Security