* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SQL Server 2005 -CLR
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
SQL Server 2005
The Common Language Runtime (CLR) Integration
Presented by Tarek Ghazali
IT Technical Specialist
Microsoft SQL Server MVP
Web Development MCP
LebDev Vice President
© 2006 Tarek Ghazali. All rights reserved.
CLR Integration
CLR Introduction
Highlights
– Common type system (CTS)
Mapping of data types. Programming language Framework
– Just-in-time (JIT) compilers
–
–
–
–
–
JIT compiles intermediary language (MSIL) into native code
Highly optimized for platform or device
Garbage collector
Permission and policy-based security
Exceptions
Threading
Diagnostics and profiling
CLR Integration
CLR Diagram
Class Library Support
CommonBase
Language
Runtime Diagram
Thread Support
COM Marshaler
Type Checker
Exception Manager
Security Engine
Debug Engine
MSIL to Native
Compilers (JIT)
Code
Manager
Class Loader
Garbage
Collector (GC)
CLR Integration
SQL Server 2005 – CLR
Run managed code within a database by
using in-process assemblies
Create managed stored procedures,
triggers, user-defined functions, userdefined types, and aggregates
Integration benefits:
–
–
–
–
Enhanced programming model
Enhanced safety and security
Common development environment
Performance and scalability
CLR Integration
Deep Integration with the Database
SQL Engine
CLR
Hosting
Layer
SQL OS Layer
Windows OS
CLR Hosting layer
provides coordination
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
Assembly Loading
Memory management
Security Model
Reliability
Threads & Fibers
Deadlock detection
Execution context
The Developer Experience
VB,C#,C++ VS .NET
Project
Build
Runtime
hosted by SQL
(in-proc)
SQL Queries:
select
sum(tax(sal,state))
from Emp where county
= ‘King’
Assembly:
“TaxLib.dll”
SQL Data Definition:
create assembly …
create function …
create procedure …
create trigger …
create type …
SQL Server
CLR Integration
Available Classes
Even in supported assemblies, some APIs are not
available in SQL
– Environment.Exit(), Console, etc.
Potentially unreliable constructs disabled
–
–
–
–
No
No
No
No
thread creation
shared state or synchronization
listening on sockets in server
finalizers
Eliminate functionality N/A to database
– System.Windows.Forms
– System.Drawing
– System.Web, …
CLR Integration
SQL Server Projects in Visual Studio 2005
Project for creating managed database objects
Automatically includes necessary references
– System
– System.Data.dll
Includes templates for each object type
–
–
–
–
–
Stored procedure
Trigger
User-defined function
User-defined type
Aggregate
Allows immediate deployment and debugging
CLR Integration
The System.Data.SqlServer Namespace
Class
Description
SqlContext
Provides access to other objects, like a connection
SqlConnection
An open connection to a SQL Server database
SqlCommand
Used to send a command to the database server
SqlParameter
Supplies a parameter for a SqlCommand object
SqlPipe
Used to send results or information to the client
SqlDataReader
Reads the data one row at a time, forward only
SqlResultSet
For working with flexible server-side cursors
SqlTransaction
For providing transactional behavior
SqlTriggerContext
Provides information about the trigger action
CLR Integration
Registering an assembly
CREATE ASSEMBLY assembly_name
– [ AUTHORIZATION owner_name ]
– FROM { < client_assembly_specifier > | < assembly_bits
> [,...n] }
– [ WITH PERMISSION_SET = { SAFE | EXTERNAL_ACCESS
| UNSAFE } ]
– < client_assembly_specifier > :: =
–
'[\\machine_name\]share_name\[path\]manifest_file_nam
e'
– < assembly_bits > :: =
–
{ varbinary_literal | varbinary_expression }
CLR Integration
Assembly Security -PERMISSION_SET
SAFE
– May not access external resources: registry, file system, or network
– May access data using the current context but not via SQLClient or any
other data provider
– No thread processing
EXTERNAL_ACCESS
– May access external resources:
registry, file system, network, environment variables
UNSAFE
–
–
–
–
May access external resources
Can use SQLClient and other data providers
Can use thread constructs
(No restrictions; similar to extended stored procedures)
CLR Integration
Assembly
Create
Meta Data of Assemblies
Details of Assembly: Assembly source code:
Sys.assembly_files
Sys.assemblies
Other meta data information
•SYS.OBJECTS
•SYS.ASSEMBLY_MODULES
•SYS.ASSEMBLY_TYPES
Assembly references:
Sys.assembly_references
CLR Integration
User Defined Functions
Similar to T-SQL function
Written in CLR language
– Decorated with [SqlFunction] attribute in code
– Assembly loaded into the database
– Function defined from assembly
Limits on functions
– must be in public class
– cannot be in nested class
– method must be public and static
CLR Integration
User Defined Functions -Example
public class MyFunctions
{
[SqlFunction]
public static SqlString GetLongDate(SqlDateTime
DateVal)
{
// Return the date as a long string
return DateVal.Value.ToLongDateString();
}
}
CLR Integration
User Defined Functions
Properties have impact on whether or not computed column
that use these functions can be indexed.
– IsDeterministic = true
(it always produces the same output values given the same input
values and the same database state.)
– DataAccess
DataAccessKind.None: Does not access data.
DataAccessKind.Read: Only reads data.
– SystemDataAccess
SystemDataAccessKind.None: Does not access system data.
SystemDataAccessKind.Read: Only reads system data.
– IsPrecise = { true | false }
(that indicates whether the routine involves imprecise computations
such as floating point operations. )
CLR Integration
.Net Stored Procedures (1)
Capable of doing everything a T-SQL
proc can do.
Uses a Shared method (static in C#)
Pass parameters both ways
– OUTPUT parameters should be byref (ref
in C#)
Return multiple result sets
CLR Integration
.Net Stored Proc Can Return (2)
Numeric return code
Count of rows affected by the
command
Scalar value
Single row
One or more multi row result sets
A stream of XML
CLR Integration
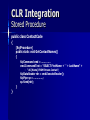
Stored Procedure
public class ContactCode
{
[SqlProcedure]
public static void GetContactNames()
{
SqlCommand cmd = ……. ……
cmd.CommandText = "SELECT FirstName + ' ' + LastName" +
– " AS [Name] FROM Person.Contact";
}
}
SqlDataReader rdr = cmd.ExecuteReader();
SqlPipe sp = …………..;
sp.Send(rdr);
CLR Integration
Create Sql Server Proc.
Syntax :
create procedure ProcName
as external name
<assemblyname>.<classname>.<methodn
ame>
Example :
create procedure GetContactsName as
external name assemblyname.ContactCode.
GetContactNames
CLR Integration
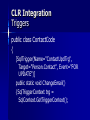
Triggers
public class ContactCode
{
[SqlTrigger(Name="ContactUpdTrg",
Target="Person.Contact", Event="FOR
UPDATE")]
public static void ChangeEmail()
{SqlTriggerContext trg =
SqlContext.GetTriggerContext();
DEMO
CLR Integration
When to use T-SQL
T-SQL better used for data access
– All pre-SQL Server 2005 code is written in T-SQL
– SQL Server 2005 adds exception handling to TSQL
T-SQL can be faster for data access
– Direct access to SQL Server's internal buffers
– Rich, data-centric library of functions
– No conversion of types
CLR Integration
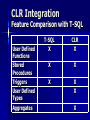
Feature Comparison with T-SQL
User Defined
Functions
Stored
Procedures
Triggers
User Defined
Types
Aggregates
T-SQL
X
CLR
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
CLR Integration
Best uses of SQLCLR
Computational functions are always faster
Streaming table valued functions
User defined aggregates
– Orders magnitude faster than server or client cursor
solutions
Scalar functions
– Function body is compiled to native code
Use managed code for:
– Procedures that feature complex logic
– Access to the .NET Framework class library
– CPU intensive functions
SQLCLR Guidance
Mid Tier vs. Data Tier
SQLCLR support does not mean move
all business logic to server
Candidates for moving to server
– Centralized data validation
– Process large amount of data while
needing a small portion of it for
application use
Resources & Questions
Microsoft Resources:
– msdn.microsoft.com/sqlserver/
– www.microsoft.com/sql/community
Contact me:
– [email protected]
– www.sqlmvp.com (will be available soon)
Download Presentation :
– www.lebdev.net
Thanks.