* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Analog audiotape editing
Audio crossover wikipedia , lookup
Stage monitor system wikipedia , lookup
Stereophonic sound wikipedia , lookup
Fade (audio engineering) wikipedia , lookup
Mixing console wikipedia , lookup
Music technology (electronic and digital) wikipedia , lookup
Sound recording and reproduction wikipedia , lookup
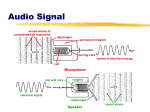
RTV 440 Sound and Miking Sound in an environment • Sound wave – Compression / rarefaction • Frequency / Measured in hertz • Amplitude / Measured in decibels (db-spl) – AM/FM, kHz / MHz (r.f.) • Attack/sustain (internal dynamics)/decay -- sound envelope • Acoustics / Psychoacoustics / binaural hearing • Absorbed / Reflected • Direct / Indirect (echo & reverberation) Some issues with sound • Equal loudness principle--depending on loudness we don’t hear low and high frequencies as well as we hear middle • Masking--Hiding of some sounds by other sounds by other sounds when each is a different frequency and they are presented together. Loud over soft / lower-pitched over higher • Acoustical phase--the time relationship between two or more sound waves at a given point in their cycles • Timbre--a sound’s unique tone quality or tone color Acoustical issues • • • • • Ergonomics – human element in designing room Sound Absorption and Reflection Diffusion--scattering of sound waves Diffraction--spreading or bending Resonance--vibration of an object at the same frequency as the original body’s frequency • Lively or Dead Room • Isolation Sound Frequency Spectrum • Bass – Low bass, 1st & 2nd octaves, 16-64 Hz – Upper bass, 3rd& 4th octaves, 64-256 Hz • Midrange – 5th, 6th & 7th octaves, 256 - 2,048 Hz – Upper midrange: 8th octave, 2,048 - 4,096 Hz • Treble – 9th & 10th octaves, 4,096 - 16,384 Hz • 20 to 20,000 Hz, sort of (plus outline) ‘Hearing Test’ • • • • • High frequency test Range of frequencies (oscillator) 10 – 200 Hz 22 kHz down to 8 kHz C Scale notes Mics -- Converting Sound • Sound Frequency Spectrum – Bass, midrange, treble • • • • Frequency / Hertz Amplitude / decibels Acoustics Direct / indirect sound – Echo / reverberations Microphone Directional Patterns • Omnidirectional / nondirectional • Unidirectional / Directional/ cardioid – Super, hyper, ultra • Bidirectional • (see reading for diagrams) Applications of polar patterns • • • • • • Football miking News live shot Basketball game Studio interview News anchor In audio recording studio • Shotgun boom pole Cardioid range • • • • Cardioid Supercardioid Hypercardioid Ultradirectional – Shotgun mic Professional Mic types • Moving coil/dynamic • Ribbon • Capacitor/condensor (power source) – Electret condensor • Transducer – changes energy from one form to another – in this case sound waves into an electrical current Mics on cameras • +48v ONLY for mics that require phantom power (some of the shotguns) • Line vs. mic input • XA 20 cameras – Audio Technica mini plug mics • Always use lavalier for close up audio More about mics and sound • Common audio connectors – RCA (phono), ¼” (phone), mini-plug, XLR – Jack (‘female’) vs. plug (‘male’) – Firewire, HDMI, etc. • Close vs. distant miking – Cross-pair, mid-side, coincident (stereo) • Wide – range of frequencies • Flat – accurately recreates frequencies • Colored response – changes frequencies (lavaliere boosts high frequencies, for example Close miking when you can’t get close • Visible mics – What kinds of productions – ‘dressing the mic’ • Hidden mics – Under clothing, in set pieces – Wired vs. wireless • Boom pole – Fishpole, giraffe, perambulator • Looping / ADR – High percentage of TV and movie content Common mic types • • • • • lavaliere headset handheld studio/boom mounted TV boom – Perambulator boom, giraffes, fishpole • PZM (boundary mic) Audio Mixing • Three things you mix – Sources, techniques, aesthetics • ProTools or Adobe Audition (DAW) • Stereo or multi-track recording • 5 console functions – Amplify, switch, route, mix, balance • Various console inputs • Layering, in moviemaking Other console terms • • • • • • • • • Program / Audition Monitor vs. cue Master pot VU meter / PPM (analog / LED) Muting system Foldback (IFB note) Pad / trim / gain / AGC Pan Pot Submixer & pre-amp Other audio mixing terms • • • • Compressor Limiter Equalizer (EQ) Filters – High pass, low pass, band pass, notch • Stereo vs. multi-track recording – Basics of multi-track / mixdown Three things you mix... • Music – – – – Production library, royalty-free loops BMI, ASCAP, SESAC blanket license vs. ‘needle drop’ SoundExchange fees • SFX -- Production library, Foley • Voice – Narration vs. dialogue – Straight voice, VO/music, donut, jingle • Teams go record sounds, due before 5:00 --> ###