* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Neck and back muscles
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
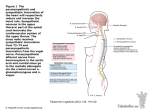
Neck and back muscles Erector Spinae / Multifidus / Rectus Abdominus / Transversus Abdominus / Internal Obliques / External Obliques / Splenius / Quadratus Lumborum Erector Spinae The erector spinae (sometimes known as sacrospinalis) is often described as a group of different muscles called iliocostalis, longissimus and spinalis. Origin Posterior crest of the ilium Lower posterior surface of the sacrum Lower 7 ribs Spinous processes of T9-L5 Transverse processes of T1-12 Insertion Angles of the ribs Transverse processes of all vertebrae Base of the skull Actions Extension of the spine Lateral flexion (side-bending) of the spine Maintains correct curvature of the spine Innervation Dorsal rami of cervical, thoracic and lumbar spinal nerves Daily uses Maintaining good posture Multifidus Multifidus is a series of small muscles which travel up the length of the spine. It is an important muscle in the rehabilitation of Gilmore's Groin. Origin Posterior surface of the sacrum Articular processes of the lumbar vertebrae Transverse processes of the thoracic vertebrae Articular processes of C3-7 Insertion Each part of the muscle inserts into the spinous process 2-4 vertebrae higher than its origin Actions Extension, lateral flexion and rotation of the spine Innervation Dorsal rami of the spinal nerves Daily uses Maintaining good posture of the spine Rectus Abdominus Rectus Abdominus is the most superficial of the abdominal muscles. It is this muscle which forms the six-pack shape! Origin Crest of the pubis Pubic symphesis Insertion Xiphoid process (base of the sternum) 5th,6th and 7th costal cartilages Actions Flexes lumbar spine Innervation Ventral rami of thoracic nerves Daily uses Moving from lying to sitting Transversus Abdominus Muscle Transversus Abdominus is often abbreviated to TVA. This is a very important core muscle which is vital in maintaining good posture. Activities such as Pilates focus on contraction of the TVA. Origin Front of the iliac crest Inguinal ligament Costal cartilages of the lower 6 ribs Thoracolumbar fascia Insertion Linea alba Actions Compresses the abdomen and supports the abdominal visera Innervation Ventral rami of thoracic nerves Ilioinguinal nerve Iliohypgastric nerve Daily uses Maintaining good posture Internal Obliques Origin Iliac crest Inguinal ligament Thoracolumbar fascia Insertion Lower 3-4 ribs Linea alba Actions Contraction of one side alone laterally bends the trunk to that side and rotates the trunk to the other side Compresses the abdomen and supports the abdominal viscera Innervation Ventral rami of thoracic nerves Ilioinguinal nerve Iliohypgastric nerve Daily uses Raking leaves External Obliques Origin Lowest 8 ribs Insertion Front 1/2 of the iliac crest Linea alba Actions Contraction of one side alone laterally bends the trunk to that side and rotates the trunk to the other side Compresses the abdomen and supports the abdominal viscera Innervation Ventral rami of thoracic nerves Daily uses Raking leaves Quadratus Lumborum The quadratus lumborum muscle is a common muscle involved in lower back pain. Origin Posterior iliac crest Iliolumbar ligament Insertion Twelfth rib Transerve processes of L1-L4 Actions Laterally flexes (side-bends) trunk Innervation Ventral rami of the subcostal nerve Lumbar nerves Daily uses Bending sideways to pick something up