* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Sun - rosedalegrade9astronomy
Survey
Document related concepts
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial atmosphere wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Energetic neutral atom wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
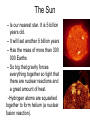
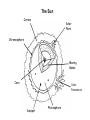
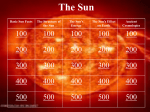
The Sun – Is our nearest star. It is 5 billion years old. – It will last another 5 billion years – Has the mass of more than 300 000 Earths – So big that gravity forces everything together so tight that there are nuclear reactions and a great amount of heat. -Hydrogen atoms are squashed together to form helium (a nuclear fusion reaction). The Sun Corona Solar Flare Chromosphere Moving Gases Core Solar Prominence Sunspot Photosphere Interactions of Earth and Sun – – – – – Our distance from the sun is just right for light – it’s not too hot or too cold. Solar wind – high energy particles – these are DEADLY!!!! Earth is like a big magnet – the force around the EARTH is called the MAGNETOSPHERE Both the magnetosphere and atmosphere protect us from the Sun’s Radiation When solar winds react with nitrogen and oxygen at the Earth’s poles, we get the AURORA – the NORTHERN LIGHTS or SOUTHERN LIGHTS. http://www.designer-daily.com/northern-lights-by-norio-matsumoto-756 Aurora Borealis (Northern Lights) Interactions of Earth and Sun • Energy emitted by the Sun: • Stars and other celestial objects emit energy consisting of electromagnetic waves that travel at the speed of light, known as electromagnetic radiation. • Most of the Sun’s energy will be absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere, but some will be reflected back into space. Aurora Borealis (Northern Lights) The Atmosphere Allows for LIFE – Our atmosphere traps heat from the Sun (otherwise it would be VERY cold!) – Ozone layer protects us from UV rays from the sun (otherwise we would all get sunburn!) http://www.kidsgeo.com/geography-for-kids/0040-introduction-to-ouratmosphere.php