* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Astronomy PowerPoint - Effingham County Schools
Impact event wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy on Mars wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
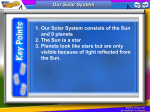
ASTRONOMY Astronomy = the study of space • The big bang theory proposes that about 14 billion years ago the entire universe was in a bubble smaller than the head of a pin. It was hotter and denser than anything we can imagine…then it EXPLODED and the universe was born!!! Time, space and matter all started with the big bang. The universe grew from being smaller than an atom to larger than a galaxy. The universe continues to expand. • The Nebular theory tells us how solar systems and stars are created. Gaseous clouds (nebulae) slowly rotate, gradually collapse & flatten due to gravity and eventually form stars and planets. • No one knows the size or shape of the universe but there are billions of galaxies spread throughout the universe. • Gravity or gravitational forces are forces of attraction. • Every object that has mass exerts a gravitational force on every other object. •Planetary Gravity – the Sun’s gravitational pull keeps the planets orbiting the sun. •The motion of the moon is affected by the earth and the Sun. • The amount of gravitational pull depends on the amount of mass & the distance between the two objects. Mass is the amount of matter and object has. Gravity is a force caused by mass. Weight is a measure of how much force is applied due to mass. Distance also plays a role in the amount of gravity: if the distance between objects is increases then gravity decreases, and conversely if the distance between the objects is decreases then the gravity will increase. • Gravity gives objects weight. No one knows the mechanism by which gravity works. 110 110 110 110 110 110 X X X X X X 110 110 X X • The universe is made up of two things – matter and energy. • Matter examples – planets and stars. • Energy examples – light and heat • The universe is made up of galaxies. There are 2,000,000,000,000,000,000 stars in the universe and each of these stars makes up a galaxies. • The universe has a diameter of 150 billion light years! The universe is more than 13.7 billion years old! • • • • • • • • • • County Planet Street Solar System Country Home Galaxy Hemisphere State Continent Town • Universe • A galaxy is a group of millions of stars relatively near each other. Most stars seem to be in one or another galaxy. Earth’s own star - the Sun – is in the Milky Way Galaxy. Small galaxies have about 10 million stars – Big galaxies have a trillion stars. • There are three types of galaxies: spiral, elliptical, and irregular. • Spiral Galaxies have a bulge, disk and halo. The bulge is a round structure in the center. The disk is made up of dust and gas. The disk forms “arms” of our galaxy. Our galaxy the Milky Way is located in an arm of our galaxy. • Elliptical galaxies are shaped like an elongated sphere. These galaxies are older and therefore have very little dust or gas. • Irregular galaxies have no shape. Spiral • turns like a pinwheel. • This the type of our galaxies shape “The Milky Way” • Our star, the sun, is located on the arm and the planets travel around the sun • Sun takes 250 million years to make a complete trip • Arms Are Stars • Contains Gas and Dust Elliptical • Ellipse or Sphere shape (Oval) • Thought to contain older stars. • Contains almost no gas or dust Irregular • no definite shape • Contains lots of dust and fewer stars Picture of the Galaxies Spiral Galaxy Irregular Galaxy Elliptical Comets • Comets are sometimes called “dirty snowballs” because they are a mixture of ice and dust, and so they look like dirty snowballs. The ices contained by comets include: water, methane, ammonia and carbon dioxide. The ices sublimate off the nucleus when the comet nears the sun. A dust tail – which is the part of the comet easiest to see – is made of dust particles driven off the nucleus by escaping gases. As the sun vaporizes the gases a coma is formed which is a cloud around the nucleus. • Comets are leftovers from the formation of the universe. Meteoroids, Meteor and Meteorite • Meteors or meteorites are bits of rock (like granite) and ice – from out in space that get pulled in by Earth’s gravity and fall through the atmosphere and sometimes land on earth’s surface. Many meteors are from comet pieces. • Meteors are sometimes called “shooting stars” but they are not stars. They glow in the sky like stars because when they hit the earth’s atmosphere the friction of the rock rubbing against the atmosphere causes heat and light – and look like a fire. • Most meteors are tiny, the size of pebbles, and most fall in the ocean. • Remember! • Meteor – flash of light • Meteorite – space rock that hits earth’s surface • Meteoroid – piece of an interplanetary matter smaller than a kilometer. Asteroids • Asteroids are generally larger chunks of rock that come from the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. • Asteroids are metallic, rocky bodies without atmosphere that orbit the Sun, but are too small to be classified as planets. • Asteroids are thought to be primordial material which has been prevented from forming planets – accretion. • Known asteroids can range in size from 1000 km to the size of pebbles. THE COMPONENTS OF OUR SOLAR SYSTEM • The solar system is made up of all the planets that orbit our sun. The solar system also consists of moons, comets, asteroids, minor planets dust and gases. • Everything in the solar system orbits (revolves) around the sun. The sun contains 98% of all the matter (mass) in the solar system. The sun is so massive it has more gravitational pull that any other objects in the solar system & attracts all other objects to it. These objects are moving quickly away from the sun and so are not pulled into the sun. • The sun is the center, then Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and finally Neptune. There is a band of asteroids between Mars and Jupiter. The Kuiper Belt exists beyond Pluto – most all items in the Kuiper Belt are comets. • The Oort cloud is even farther out and consists of comets buzzing around in random directions. Inner Planets - Terrestrial Planets • Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars • Closest to the Sun • Have Rocky Crust • Small in Size • Dense in mantle and core • Temperature depends on the sun Outer Planets - Gas Giants • • • • • • • Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune Farthest from the Sun Made of Mainly of Gases Small Solid Core Most have Rings Around Them Most have Many Moons Most have much more mass that gravity pull objects in close Geocentric Theory Geocentric – Geo = earth, centric = center • The geocentric model states that the earth is the center of the solar system and universe. The Catholic Church supported this model because the church taught that God put earth at the center of the solar system/universe. Aristotle and Ptolemy were two supporters of geo-centricity. The idea that the earth was moving seemed silly, because if the earth was moving we should be able to feel the movement. •The order of the planets in the Geocentric model is: Earth, moon, Mercury, Venus, Sun, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, and the stars. Heliocentric Theory Heliocentric – Helio = sun, centric = center • The heliocentric model states that the sun is the center of the solar system and the earth and other planets revolve around the sun. The geocentric model had been accepted for 1000 years. A scientist named Copernicus proposed that the sun was the center of the solar system. The church felt as though this idea went against the teaching of the church. Galileo wrote a book that supported Copernican ideas –later he was arrested and found guilty of heresy and sentenced to house arrest for the remainder of his life. Galileo was pardoned 350 years after his death. THE MOON SEEM TO CHANGE SHAPE • What you see as moon light is really light from the sun reflecting on the moon’s surface. Areas where sunlight doesn’t reach look dark. Areas on the surface move into and out of sunlight. • The moon’s position in its monthly orbit determines how it appears form earth. • Phases of the Moon – • 1st Week – Moon starts to Wax (starts looking larger) • New Moon – unlit portion of moon faces earth, the moon looks dark • Waxing Crescent – A small portion of moon can be seen • 2nd Week • 1st Quarter – 50% of the near side is in sunlight and can be seen • Waxing Gibbous – near side of moon is more than 50% lit, but not 100% lit • 3rd Week • Full Moon – Half way through the cycle the whole near side of moon is lit • Moon Starts to Wane (starts looking smaller) • Waning Gibbous – near side is less than 100% lit but more than 50% lit • 4th Week • 3rd Quarter – 50% of the near side is in sunlight and can be seen. • Waning Crescent – A small portion of the moon can be seen. • Cycle then repeats with a New Moon Moon Phase Song (To the tune of “If You’re Happy and You Know It”) If it’s waxing you’ll be seeing much more light. It’ll be getting so much brighter on the right. If it’s waxing then you’ll know. For you will see more of a glow. Soon a full moon will light up your darkest night. When it’s waning there’s less light for you and me. Don’t go whining ‘bout the darkness that you see. Though the cycle’s going to end It will soon begin again For a cycle goes around and ‘round you see. Eclipses • 2 types of Eclipses: Solar and Lunar Lunar Eclipses • Sunlight streams past earth and the moon, lighting one side of each. Beyond each is a long thin cone of darkness where no sunlight reaches - a shadow in space. If the moon, the sun, and earth line up exactly a shadow crosses the Earth or moon. An eclipse occurs when a shadow makes the sun or moon appear to grow dark, remember if it is dark we cannot see it. • Lunar Eclipse – the moon becomes dark during a lunar eclipse because it passes through Earth’s shadow. There are two parts of Earth’s shadow – the umbra- which is the darkest part of the shadow, and the penumbra which is a lighter cone of shadow. Just before lunar eclipse sunlight streaming past earth produces a full moon then the moon moves into the umbra. Earth’s dark shadow seems to creep across the moon. The moon is small enough to fit completely in earth shadow, and so cannot be seen. • • Total lunar eclipse – moon passes completely into the earth’s shadow and no part of the moon can be seen. • Partial lunar eclipse – if the moon misses part or all of the umbra, only part of the moon is in shadow cannot be seen. Solar Eclipses In a solar eclipse the sun appears to darken (and we can’t see it) because the moon’s shadow falls onto part of the earth. A solar eclipse occurs when the moon passes directly between the earth and the sun. Only locations in the path of the moon’s shadow experience a solar eclipse. Solar eclipses are rarer than lunar eclipses. Bright light from the sun disk can damage your eyes if you look directly at it. Annular Eclipse Earth’s Tilt And Seasons • The seasons are the result of the Earth’s tilt on it axis. The earth’s axis is tilted at 23.45 degrees. This tilting is what gives us four seasons of the year – spring, summer, autumn and winter. Since the axis is tilted, different parts of the globe are pointed toward the sun at different times of the year. • Summer is warmer than winter because the sun’s rays strike the Earth at an angle with is more direct during the summer than in winter. In addition to the angle of the sun’s rays, it is warmer in summer because the days are longer than the nights during the summer, allowing a longer time for the warming to occur. • Quick Vocab: Solstices (sol = sun; stice from stit = stopped) • When the sun reaches the highest or lowest point in the sky at noon a solstice occurs and marks the longest day (in daylight hours) in the summer, and the shortest day (in daylight hours) in the winter. The winter solstice occurs on 12/21 or 12/22, the summer solstice occurs on 6/21 or 6/22. • Quick Vocab: Equinox: (equi = night; nox = night) • Equinox – The day and night are equal in length. Vernal equinox – happens in March 20th and is the beginning of spring. Autumnal equinox – happens in September 22 and is the beginning of fall. NH = Spring Equinox SH = Autumn Equinox Rotation and Revolution PAGE 45 - 48 Rotation • Rotation means to spin on an axis. All celestial bodies rotate. Once started spinning objects in space tend to keep spinning. If an object decreases in size it will spin faster. The fact that most objects from galaxies to planets spin in nearly the same way is a clue that they have a common origin. • The earth’s rotation takes 23 hours and 56 minutes. • The earth and moon rotate about their axes at the same rate so the same side of the moon always faces the earth. • Rotation is responsible for the length of the day and night. Rotation is responsible for the apparent movement of the moon, stars, and planet. Mercury • 58 days 16 hours --rotation Venus • Rotation = 243 days Earth • Rotation 23 hours 56 minutes Mars • Rotation 24 hours 37 minutes Jupiter • Rotation 9 hours 50 min Saturn • Rotation 10 hours 14 minutes Uranus • Rotation 20 hours Neptune • Rotation 21 hours • The earth moves in an almost circular but slightly elliptical motion around the sun – this is called revolution. • One revolution around the sun is equal to 365.25 days – or one year. • The moon revolves around the earth in 27.322 days. • Orbit is a regular repeating path that one object in space takes around another object in space. Venus 225 Earth days Mars 1.9 Earth years Earth 365.25 days Mercury 88 Earth days Jupiter 12 Earth years Saturn 29 Earth years Uranus 84 Earth years Neptune 164 Earth Years