* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ASPERGILLOSIS (BROODER PNEUMONIA)
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
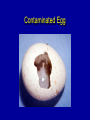
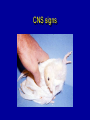
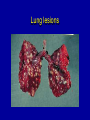
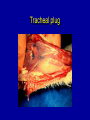
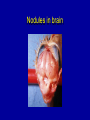
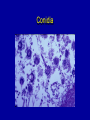
ASPERGILLOSIS (BROODER PNEUMONIA) • • • Affects most avian species Important in poults, chicks, and quail. Is a serious problem in penguins in zoos. ETIOLOGY Aspergillus fumigatus • • • Spores from contaminated incubators, feed, litter can penetrate broken shells. Large dose to infect Probably not bird to bird. INCUBATION PERIOD 8 to 12 days in vivo 48 hrs in vitro COURSE OF DISEASE 2 to 3 weeks may linger MORTALITY • Depends on age • Up to 100% under brooder • Other diseases aggravate METHOD OF SPREAD • Inhalation of spores 1. Contaminated eggs in incubator 2. Dusty litter and ranges. Spreads readily under brooder If clinical signs occur after 7 days of age, consider farm rather than hatchery exposure. Contaminated egg Contaminated Egg Contaminated Egg Contaminated Egg Contaminated Litter COMMENT • Usually a young bird disease: • Exposure in the hatchery or because they are so close to new litter material, they inhale spores. CLINICAL SIGNS 1. Rapid gasping respiration (without rales) 2. "Starve outs", emaciated 3. Blepharoconjunctivitis yellow caseous pellet in eye 4. Encephalitis common in turkey poults but rare in chickens Affected chicks Gasping chick Gasping chick Nervous signs CNS Signs CNS signs POSTMORTEM FINDINGS 1. Round yellow caseous granulomas on air sac, throughout lungs. “Pearl disease” 2. Occlusion of trachea 3. Occasionally green mold growth on air sacs or in lungs Air sac lesions Nodules in air sacs Air sac lesions Lung lesions Lung lesions Blocked bronchi Tracheal plug Tracheal plug Brain lesion Nodules in brain Ocular lesions DIAGNOSIS • Typical lesions • Culture on Sabouraud's dextrose agar w/added chloramphenicol. • Identify and classify fungal growth (Light microscope). Colonies on Sabaraud’s agar Conidia DIAGNOSIS (CON’T.) • Histopathology to demonstrate fungal hyphae in tissue. • Hyphae brownish and have outgrowths in "y" branches. Histo 10 x Branched, septate hyphae Branched, septate hyphae TREATMENT • None specific • Stress prevention PREVENTION • Remove source of infection – – – – • • • • Use high quality litter with little bark Collect eggs often to prevent cracks Keep clean litter in nests Do not set cracked eggs Fumigate incubators and hatchers Add antifungal agents to feed Treat litter w/ fungistatic/cidal agents (TBZ (Folatech), propronic acid, Clinafarm in the hatchery) General clean up - disinfection between grow out.