* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download May 2016 Article 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
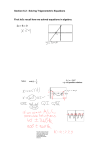
INSTRUCTION Kumon vs. High School Math Curriculum Chart Kumon is pleased to announce a comparison chart between the Kumon Math Curriculum and the National Math Curriculum (for math subjects: Algebra I, Algebra II, Geometry, Trigonometry, Math Analysis, Linear Algebra, and Calculus). As each state creates its own curriculum, we have compiled the curriculum of eight states (California, Florida, Hawaii, Illinois, Michigan, New York, New Jersey, and Texas) to create our view of the National Math Curriculum. This chart may be used to motivate the students in your Center in a variety of ways, including: 1. Showing to students and parents how the Kumon Math Worksheets compare to what they are currently learning, and what they will learn, in school. 2. Increasing your knowledge and understanding of the general topics that are taught in the general high school math courses. One point to remember is that, as each state sets its own curriculum (and there are even differences between districts and schools), there may be some differences between exactly what your students are learning in school and what is displayed on this chart. Some points to remember about the Kumon Curriculum are: • 24 It is a Global Curriculum that is based on the performances of all countries. VOICES: A QUARTERLY MAGAZINE FOR INSTRUCTORS • It is also structurally different from the “spiral curriculum” implemented in American schools. • It thoroughly prepares students to be successful in life, not just in school. • It will assist students in their school math studies. Following are some examples of standards from each of the High School Math Curriculum subjects along with Kumon problems related to that standard. School Topic – Algebra I 1. Solve linear equations and inequalities. o Kumon Examples: 8x + 3y = • H 41a (1) 30 5x + 3y = 21 • H 132a (1) 3x + 4 < 5x + 8 4x − 8 < x + 1 2. Solve quadratic equations by factoring, completing the square, or using the quadratic formula. o Kumon Examples: 2 • I 112a (2) x + 5x + 6 = 0 (factor) • I 125a (3) x the square) 2 − 6x − 5 = 0 (complete INST R U C T I O N • I 132a (2) 2x − 7x + 1 = (Quadratic Formula) 2 0 School Topic – Algebra II 1. Perform basic four operations on complex numbers. o Kumon Examples: • J 112b (13) −9 × −16 = • J 113a (4) • J 113b (9) • J 114a (2) 9 ÷ −25 = (2 + 2i )(3 + 2i ) = (2 − 5 2i )(3 + 4 2i ) = 2. Determine a quadratic function from its roots or graph. o Kumon Example: • K 36b (4) Find the equation of the parabola which intersects the x-axis at 2 points (1, 0), (3, 0) and passes through point (4, – 6). 3. Solve problems dealing with absolute value. o Kumon Examples: • L 32b (2) x x + 3 = ( ) • L 33b (3) Graph the function • L 38b (1) Find the point of intersection of the two functions y = 2x − 3 School Topic – Geometry 1. Know and use angle and side relationships in special triangles (30-60-90, 45-45-90) o Kumon Examples: • I 180a Find the value of x and y in each figure using the following theorems: • (1) In a right triangle with 30° and 60° angles, the ratio of the length of each side to each other is • 1: 3 : 2 . (2) In a right triangle with 45° angles, the ratio of the length of each side to each other is 1:1: 2 . 2. Find equations of parallel and perpendicular lines. o Kumon Examples: • M 165a (1) Given point P(1,1) and the line l: 3x + 4 y = 12 , obtain the equation of a line m which passes through point P and is perpendicular to l. • M 180b (3) Obtain the equation of the line that passes through the point of intersection of lines 4x − y = −1 and x + 6 y = −3 , and is parallel to line 6x − 3y = 2 . y = x 2 − 2x − 3 , y = x + 3 VOICES: A QUARTERLY MAGAZINE FOR INSTRUCTORS 25 INSTRUCTION School Topic – Trigonometry School Topic – Calculus 1. Know the sine and cosine graph. o Kumon Examples: • M 72a 1. Draw the graph of from 0 to 2π. • M 78a 1. Draw the graph of 1. Find the derivative of a function. o Kumon Examples: • Differentiate the following functions: 2 • L 48a (8) y = ax • L 50a (2) from π − 2 y = sin x , y = cos x , to 3π. 2. Use addition formulas for sines and cosines to prove or simplify trigonometric identities. o Kumon Example: • M 114a (1) Prove the following equality using the Addition Theorem: sin 2α = 2sinα cosα School Topic – Mathematical Analysis 1. Derive equations using locus of points. o Kumon Example: • N 2b 4. Obtain the equation of the locus of point P x, y such that the distance ( ) from P to A (5,4 ) is 2. 2. Find the maximum and minimum of a function o Kumon Example: • K 70a 1. Given the quadratic function 2 () ( ) f x = x−a +2 (0 ≤ x ≤ 1) find the maximum and minimum values. School Topic – Linear Algebra 1. Add and multiply matrices. o Kumon Example: • *XM 7b 2.(3) Perform the following calculations of matrices. 1 2 −4 2 4 −4 + − = 2 −3 1 4 −3 1 2. Compute the dot product of 2 vectors. o Kumon Example: r • *XV 7a 1. Given that a ( ), r r b = ( 2,3) , and c = ( 3,4 ) , evaluate the = 1,2 following expressions, and determine whether each result is a vector or a scalar. r r • (1) a g b = 26 VOICES: A QUARTERLY MAGAZINE FOR INSTRUCTORS ( )( y = x 2 3x 2 + 1 3x + 2 ) 2. Solve definite and indefinite integrals. o Kumon Examples: • Evaluate the following integrals: • L 120b (1) ∫ 2 1 • ( 4x 3 ) − 6x 2 dx = L 113b (9) ∫ ( x + 1) 2 ( ) 2 dx − ∫ x − 1 dx = We hope that you find this comparison chart useful in motivating your students. *XM and XV are sections of Level X, to be released later this year, which contains Elective Course material including: Triangles, Vectors, Matrices, Probability, and Statistics.