* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Accessory Organs
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
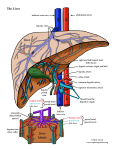
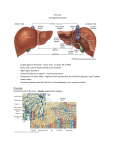
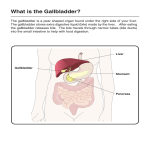
Accessory Organs Liver Pancreas spleen Gall bladder The Liver • • • The largest gland in the body Weighs about 1.5kg Location – under the diaphragm on the right Found in the upper abdominal cavity: extends from right upper quadrant to left upper quadrant of the abdomen Attached to diaphragm by Falciform and coronary ligaments Left and right triangular ligaments Functions: Bile production and secretion Detoxification Storage of glycogen Protein synthesis Production of heparin and bile pigments Erythropoiesis (in fetus) The Liver Anatomically has four lobes – right, left, caudate, and quadrate The falciform ligament: Separates the right and left lobes Separate the subphrenic recess made by the peritoneum Suspends the liver from the diaphragm and anterior abdominal wall The ligamentum teres: Is a remnant of the fetal umbilical vein Round ligament in the inferior surface Runs along the free edge of the falciform ligament Ligamentum venosum inferior surface remnant of fetal ductus venosus Functional lobes Rt and Lt lobes Portal lobes are two equal lobes (sagittal plan) Further divided in 8 segments based on principal branches of Hepatic art. Vien, and bile duct Divided into 4 anatomical lobes Left Right Caudate Post Quadrate nt Surfaces of the Liver Figure 24.19b, c 1.Diaphragmatic surface Posterior surface The Liver Superior surface 2. Visceral surface • Covered by visceral peritoneum except porta hepatis and gall bladder bed. The visceral surface is related to: Right side of the stomach i.e. gastric and pyloric areas Superior part of the duodenum i.e. duodenal area Lesser omentum Gall bladder Right colic flexor and right transverse area ; colic area Right kidney and suprarenal gland; Renal area The Liver Inferior surface 1. 2. 3. The round ligament(ligamentum teres) – obliterated umbilical vein The ligamentum venosum – fibrous remnant of fetal ductus vein The Porta hepatis (hepatic potal; portal fissure) transverse fissure on the visceral surface of the liver. It gives passage to the: 1. Portal vein 2. Hepatic artery 3. Hepatic nerve plexus 4. Hepatic ducts 5. Lymphatic vessels Peritoneal relations of the Liver The Lesser omentum Encloses the portal triad (bile duct, hepatic artery and portal vein ) Passes from the liver to lesser curvature of the stomach + 2 cm of duodenum Thick free edge -- hepatoduodenal ligament Sheet like remainder – hepatogastric ligament Microscopic Anatomy of the Liver Hexagonal-shaped liver lobules are the structural and functional units of the liver Composed of hepatocyte (liver cell) plates radiating outward from a central vein Portal triads are found at each of the six corners of each liver lobule Portal triads consist of a bile duct and Hepatic artery – supplies oxygen-rich blood to the liver Hepatic portal vein – carries venous blood with nutrients from digestive viscera Figure 23.14d Microscopic Anatomy of the Liver Liver sinusoids – enlarged, leaky capillaries located between hepatic plates Kupffer cells – hepatic macrophages found in liver sinusoids Hepatocytes’ functions include: Production of bile Processing bloodborne nutrients Storage of fat-soluble vitamins Detoxification Secreted bile flows between hepatocytes toward the bile ducts in the portal triads Figure 23.14b Figure 23.14c Blood Supply of Liver Hepatic artery provides oxygenated blood Hepatic portal vein provides deoxygenated blood Nutrients, drugs, toxins, microbes Hepatic artery and vein carry blood to sinusoids Substances exchanged by hepatocytes Blood drains to central vein and eventually hepatic vein Portal triad Hepatic portal vein Hepatic artery Bile duct Histology and Blood Supply of the Liver Fig. 24.20 Liver: Associated Structures The lesser omentum anchors the liver to the stomach The hepatic blood vessels enter the liver at the porta hepatis The gallbladder rests in a recess on the inferior surface of the right lobe Bile leaves the liver via Bile ducts which fuse into the common hepatic duct The common hepatic duct fuses with the cystic duct These two ducts form the bile duct Bile Duct System Bile secreted by hepatocytes Bile canaliculi Bile ducts Right and left hepatic ducts Common hepatic duct Common bile duct Gallbladder for temporary storage of bile Cystic duct Figure 23.13a Figure 23.13c The cystic duct is about 2.5 cm in length. Internal projections of circular Location – underside of the muscle fibers account for the right lobe of the liver Connected to the liver by the spiral valve of Heister, which makes the passage of calculi hepatic duct difficult. Connected to the duodenum The common hepatic duct is by the common bile duct usually less than 2.5 cm The functions of the long, and is formed by the gallbladder is to concentrate union of the right and left and store bile hepatic ducts. Gallstones The common bile duct, about 7.5 cm long, is formed by the junction of the cystic and the common hepatic ducts. The Gallbladder The anatomical subdivisions are, a fundus, a body, and a neck which terminates in the narrow infundibulum. The angulated distal part of the neck forms a pouch, called Hartmann’s pouch, a common site for a solitary gall-stone to lodge. The muscle fibers in the wall of the gall-bladder are arranged in a criss-cross manner, being particularly well developed in the neck. The mucous membrane contains indentations of the mucosa that sink into the muscle coat - these are the crypts of Luschka. The wall of the gallbladder is composed of three layers: mucosa ; muscularis and serosa. There is no muscularis mucosae or submucosa. There are different sized branching folds lined by single layer of columnar cells with a pale cytoplasm and basally located nuclei. The lamina propria is composed of loose connective tissue, blood vessels, nerves and some plasma cells. The muscle layer is composed of haphazardly distributed bundles of smooth muscle fibers. Pancreas Mixed endocrine and exocrine gland Exocrine compound acinar gland, similar in structure to parotid gland. Distinction between 2 glands can be made based on absence of striated ducts and presence of islets of Langerhans. Initial portions of intercalated ducts penetrate lumens of acini. Centroacinar cells constitude interacinar portion of intercalated duct. Pancreas –all flesh Introduction… • • • Soft, lobulated elongated gland with both exocrine and endocrine functions Exocrine –pancreatic juice Endocrine-insulin Location…. epigastric & left hypochondriac regions behind the stomach in the lesser sac Transversely across the posterior abdominal wall at the level of the L2 & L3 Size and shape… Parts … J shaped or retort shaped. Length-15-20 cm Thickness1.2-1.8 cm Breadth-2.5 -3.8 cm Wt-90 gm Head … Enlarged part C shaped, lying within the concavity of duodenum, consist of 3 borders-superior ,inferior & right lateral 2 surfaces-anterior & posterior uncinate process Posterior surface relation: IVC Right Renal veins Right crus of diaphragm Bile duct Stomach Lesser omentum Head … Superior border-1st part of duodenum -Sup. pancreaticodudenal A. Inferior border-3rd part of duodenum -Inf. pancreaticodudenal A. Rt. lateral border-2nd part of duodenum -Terminal part of bile duct -Anastomosis betn 2 arteries. Uncinate process… Triangular projection which arises from lower and left part off the body. Relations: • Anterior: -Superior mesenteric vessels. • Posterior -Aorta • Above -Left renal vein Neck… Relations: Anterior surface Peritoneum covering lesser sac Pylorus Posterior surface is related to superior mesenteric vein portal vein Body… Elongated part. Extends from neck to the tail. Passes toward the left with slight upward and backward inclination Triangular in cross section • 3 borders-Anterior -superior -Inferior • Tuber omentale -small projection on superior border little to the left of the neck Body-Relations… Borders: • Anterior attach to root of the tranverse mesocolon . • Superior related to coeliac trunk, hepatic artery & splenic artery • Inferior is related to superior mesenteric artery. Surfaces: • Anterior is convex covered by the peritoneum related to the lesser sac & stomach. • Inferior surface covered by the peritoneum related the DJ flexure coils of jejunum & Lt. colic flexure. Body –relations… Posterior surface -Aorta -Left crus of the diaphragm -Left kidney -Left Suprarenal gland -Left renal vessels -Splenic vein Tail … • • • Left end of the pancreas Lies in the lienorenal ligament ,together with the splenic vessels Related to the lower part of the spleen (gastric surface. Ducts system… Exocrine part of pancreas is drained by the 2 ducts Main Lies near posterior surface ,3 mm in diam.white in colour Begins at the tail, runs throughout the body ,bends at the neck to run downwards backwards in the head. Herring bone pattern Accessory. The accessory duct Begins in the lower part of head, crosses the main duct with which it communicates Opens as minor duodenal papilla in the 2nd part of duodenum (6-8 cm distal to pylorus) • • In the head of the pancreas, it is related to the bile duct(on rt. side) Two ducts open in the wall of the 2nd part of the duodenum and join to form hepatopancreatic ampulla of vater which open as major duodenal papilla,8-10 cm distal to pylorus. Arterial supply… -Splenic A. -Superior pancreaticoduodenal artery (from coeliac trunk) -Inferior pancreaticoduodenal A.(from superior mesenteric A) Nerve supply… • • • Parasympathetic by the vagus nerve controlling secretion . Sympathetic from coeliac & superior mesenteric plx. Secretion is also controlled by harmone secretinpancreozymine. Lymphatic drainage… Head & neck –ventral & dorsal pancreaticodudenal grp LN. Body &tail by pancreatico-splenic LN. Efferents to Coeliac & sup.mesenteric LN Pancreas Figure 24.26a