* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Speech and Language Disorders
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
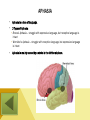
SPEECH AND LANGUAGE DISORDERS Written By: Emily Moyer SPEECH AND LANGUAGE DISORDERS Click on each of the pictures to learn more about each speech or language disorder. Then, continue to the next slide to learn about a few more disorders. Articulation Disorders Aphasia Stuttering Dysarthria Voice Disorders Apraxia SPEECH AND LANGUAGE DISORDERS CONTINUED… Continue clicking on each disorder to find out more information. When you are finished with this slide, click the arrow to continue to the multiple choice question. Hearing Disorders Balance Disorders ARTICULATION DISORDERS • An articulation disorder involves the disruption of speech sounds. • This is a disorder that usually affects children more than adults, but at times the disorder can carry through to adulthood. • 4 types of Errors: • Additions - adding sounds to a word – “Buhlue” rather than “Blue” • Substitutions – Substituting one sound for another – “Tat” for Cat” • Omissions – Omitting a sound from a word – “_at” for “cat” • Distortions – One sound is distorted and may not sound like the correct one. DYSARTHRIA • Dysarthria is a motor speech disorder that affects the muscles that are used for speech production such as the lips ,tongue, vocal folds, and/or diaphragm. • Dysarthria can occur throughout the lifespan, but is more common in adults. • Signs/Symptoms: • Slow rate of speech • Slurred speech • Limited articulator movement • Causes of Dysarthria: • Stroke • Brain Injury • Tumor • Parkinson’s Disease • Multiple Sclerosis STUTTERING • Stuttering affects the fluency of speech. • As of now, the cause of stuttering is unknown. • 3 Main Types: • Sound Prolongations – A sound is held longer than normal “S-SS-She is going to the store” • Part Word Repetition – Part of a word is repeated multiple times “The he-he-he-heater is not working” • Interjections- The use of filler words in order to prevent a stutter –”I’ll um um um meet you are the store” • Block – no words are repeated or said, there is a long “pause” or “block” in the sentence. APHASIA • • • Aphasia is a loss of language. 2 Types of Aphasia • Broca’s Aphasia – struggle with expressive language, but receptive language is intact • Wernicke’s Aphasia – struggle with receptive language, but expressive language is intact Aphasia is mainly caused by a stroke in the left hemisphere. VOICE DISORDERS • Vocal cord nodules • Nodules are growths on the vocal cords • These growths are non cancerous, but effect the quality of voice • The number one cause of vocal nodules is vocal abuse • Vocal Cord Paralysis • Paralysis occurs when one or both vocal cords are unable move or are paralyzed • 2 Types • Bilateral – both vocal cords are involved • Unilateral – only one vocal cord is involved • Spasmodic Dysphonia • Spasmodic Dysphonia is an abnormal movement of the vocal cords • Speech may be very jerky and quivery, making it hard to understand • This occurs more in adults between the ages of 30 – 50 years old APRAXIA – CHILDHOOD APRAXIA • Apraxia is a motor speech disorder in adults, that affects the connection between the brain and the actual movement of the articulators • This disorder is not related to muscle weakness, but can occur in combination with dysarthria and aphasia. • Causes: • Stroke • Traumatic Brain Injury • Dementia • Childhood Apraxia of Speech is a motor speech disorder occurring in children. • Children have trouble saying specific sounds, syllables, and words but this is not due to muscle weakness. • This disorder is neurological and has nothing to due with the articulators. HEARING DISORDERS • Conductive Hearing Loss – damage in the outer or middle ear • Causes • Fluid in the ear • Ear infection • Allergies • Sensorineural Hearing Loss – damage in the inner ear where the cochlea resides • Causes • Illnesses (Meningitis) • Aging • Head Trauma • Mixed Hearing Loss – Damage in the outer or middle ear in combination with inner ear damage. (Conductive + Sensorineural) BALANCE DISORDERS • A common balance disorder is called Vertigo. • Vertigo makes a person feel like their head is constantly moving or spinning, causing them to feel off balanced. • A common cause of vertigo is Meniere’s Disease, which is a build up of fluid in the • Fullness in the ear • Dizziness • Ringing in the ear MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION What type of stuttering would a person have if he/she said this sentence? “F F F F Frankie is the boy who is sitting in his chair with his head down.” Please click the answer to see if you are correct. A. Block Stuttering B. Sound Repetition Stuttering C. Partial Word Repetition Stuttering D. Interjection Stuttering BLOCK STUTTERING I’m sorry…This answer is incorrect. An example of block stuttering would be “I _____________________ need to go to the bathroom.” There is a long pause in the middle of a sentence. SOUND REPETITION STUTTERING CORRECT! This example is a person who repeats individual sounds when stuttering. PARTIAL WORD REPETITION STUTTERING I’m sorry, this answer is incorrect. An example of partial word repetition would be “Re Re Re Reading is a lot of fun.” INTERJECTION STUTTERING I’m sorry…This answer is incorrect. An example of interjection stuttering is “She went to the um um um um bathroom.” Please go back and try again. END OF LESSON You have now completed this lesson. Please press the home button to return home for the next student participating in the interactive power point assignment.