* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Complex Networks
Passive optical network wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
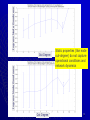
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
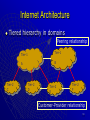
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
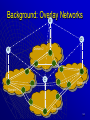
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Internet and Overlay Networks Ram Keralapura ECE Dept [email protected] Layered Architecture Five main layers • Application layer • Transport layer • Network (IP) layer • Link layer • Physical/Optical layer Applications/Computers Application layer links Routers Virtual IP links Optical switches Optical fibers 2 Introduction Internet Routing Infrastructure • Intra-domain routing (IGP) RIP, OSFP, ISIS, etc. Internet • Inter-domain routing BGP Domain or Autonomous System 3 Intra-domain Routing Links are assigned link costs/weights Path between two nodes inside a domain follows shortest path (least cost path) 4 B C 2 3 A 7 1 B 2 Dst D C A D 1 F 1 E F E 4 Network Properties Important properties of networks that service providers look for: • Connectivity • Performance • Resiliency • Robustness in functionality Service availability – delivering a given packet from source to destination 5 Characterizing Networks Main causes for concern – resiliency and robustness • How does the IGP protocol behave during network component failures? • How does the behavior impact the data that the network carries? 6 Characterizing Networks (cont’d) We have developed a model that captures the dynamic behavior of the network protocols during link failures [Keralapura et al, 2004] Protocol convergence depends on: • Topology – nodes and connectivity • Protocol timer settings • Number of entries to update in the forwarding tables 7 Characterizing Networks (cont’d) Metrics for service availability • Service disruption time • Traffic disruption Based on the above metrics we define “goodness factor” for the network 8 Ingress Node Goodness Results (cont’d) Ingress Node Goodness Out Degree Out Degree Static properties (like node out-degree) do not capture operational conditions and network dynamics 9 Network Goodness Network Diameter Similar results were also found in the paper “Layered Complex Networks” by Kurant and Thiran 10 Internet Architecture Tiered hierarchy in domains Peering relationship Tier-2 C Tier-1 Tier-1 A B Tier-2 D Tier-2 E Tier-2 F Customer-Provider relationship 11 Inter-domain routing Policy-based routing • Ad-hoc and can change with agreements with other domains Can we capture these policies? • Domains do not disclose their connectivity Policies can obstruct views and hinder domain-level topology discovery • Need multiple vantage points for more accurate topology information 12 Application Layer Networks Email Networks World Wide Web (WWW) Peer-to-Peer (p2p) Networks Several Content Delivery Networks (CDN) Overlay networks 13 Background: Overlay Networks B’ D’ Domain-2 A’ B Y X A D C’ Domain-4 Domain-1 C Domain-3 14 Interaction between networks Overlay networks compete with IP networks to provide routing service IP and overlay networks are unaware of key things happening at the other layer Multiple overlay networks co-exist and make independent decisions How does all this affect IP and overlay networks? 15 Interactions between Networks Identified some potential interactions [Keralapura et al, 2005] • Traffic engineering in IP networks Load balancing issues IP layer traffic matrix estimation • Coupling of multiple domains Defeats the objective of BGP • Multiple co-existing overlay networks Traffic oscillations Cascading reactions 16 Load Balancing and TM Estimation 5 H 5 5 G 5 8 M A 20 F N 5 8 5 E 5 5 B 5 5 D C 5 17 Coupling Multiple AS Domains F B X C A D Domain-1 G E H Domain-2 Defeats one of the objectives of BGP to decouple different domains 18 Traffic Oscillations Link Utilization Traffic Oscillations Time (ms) Failure of link 10-12 Failure of link 2-5 19 Open questions Interactions need to be understood better and we need to model them How to go about characterizing the robustness of a network after we model such interactions? Are there interactions between networks at other layers? • If yes, then how to we qualify, quantify, and model them? 20