* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 9 PP: Feudal Europe - Auburndale High School AP World
Survey
Document related concepts
Wales in the Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
History of Jerusalem during the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Post-classical history wikipedia , lookup
Medieval Inquisition wikipedia , lookup
Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
European science in the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Late Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Medieval technology wikipedia , lookup
Christianity in the 9th century wikipedia , lookup
Medievalism wikipedia , lookup
History of Christianity during the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
High Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
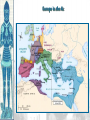
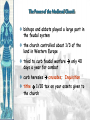
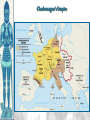
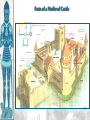
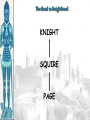
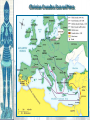
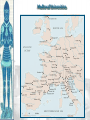
Unit 2, Chapter 9 Periodization Early Middle Ages: 500 – 1000 High Middle Ages: 1000 – 1250 Late Middle Ages: 1250 - 1500 Europe in the 6c Setting the Stage: Europe 600–1000 • Caliphates took Iberian peninsula • Carolingian Empire – Gaul, Germany, & Italy • Pope – southern Italy • Treaty of Verdun (843) – French speaking west – German speaking east • Vikings – Scandinavia • Celts & Saxons - Britain Vikings • Plundered the English & French coasts • Established settlements – Iceland – Greenland – Newfoundland • William the Conqueror (Normandy 1066) Politics & the Church • Relationship between kings & pope was tense • 800 – pope crowned Charlemagne first Holy Roman Emperor • Canon Law (Excommunication) • Jurisdiction • Who should appoint bishops? Investiture Controversy • Controversy between the church and lay lords over Bishop appointments • Also applies to conflict of popes and kings • Excommunication of Holy Roman Emperor, Henry IV • Led to Concordat of Worms in 1122 The Medieval Catholic Church filled the power vacuum left from the collapse of the classical world monasticism: St. Benedict – Benedictine Rule of poverty, chastity, and obedience provided schools for the children of the upper class inns, hospitals, refuge in times of war libraries & scriptoria to copy books and illuminate manuscripts monks missionaries to the barbarians. [St. Patrick, St. Boniface] The Power of the Medieval Church bishops and abbots played a large part in the feudal system the church controlled about 1/3 of the land in Western Europe tried to curb feudal warfare only 40 days a year for combat curb heresies crusades; Inquisition tithe 1/10 tax on your assets given to the church A Medieval Monk’s Day Charlemagne: 742 to 814 Charlemagne’s Empire Pope Crowned Charlemagne Holy Roman Emperor: Dec. 25, 800 Medieval Economy • • • • • • Switch to more agrarian Roman roads in disrepair Back to bartering Germanic lords focus on self-sufficiency Decline of literacy Rise of manors – Small farms given to large landowners in exchange for political & physical protection The Medieval Manor Life on the Medieval Manor Serfs at work Feudalism A political, economic, and social system based on loyalty and military service. Carcassonne: A Medieval Castle Parts of a Medieval Castle The Road to Knighthood KNIGHT SQUIRE PAGE Chivalry: A Code of Honor and Behavior Revival of Western Europe 1000-1200 • Growth in population and agricultural output • Reasons: – New technologies • Plow; draft harnesses, iron horseshoes, horse collar – Seaborne trade • Venice • Revival of coinage – Growth of cities • Esp. in Italy Coincided & contributed to the CRUSADES! The Crusades • Contributions – Reforming leaders of the Latin Church promoted the Truce of God – Ambitious rulers were looking for new lands to conquer – Italian merchants wanted to increase trade in the eastern Mediterranean and acquire posts in Muslim territory – Rivalry between popes and kings – Desire of church to demonstrate political authority over western Chrisiandom Focus on the Holy Land • Pious pilgrims often visited the relics of Rome or Constantinople • Some went to Antioch or Jerusalem • Pilgrims brought back tales from their trips • Battle of Manzikert – Seljuk Turks defeated Byzantines making pilgrimages difficult • Byzantine emperor asked both the Western Church for help to recapture the Kingdom of Heaven – “God wills it!” Pope Urban II: Preaching a Crusade Setting Out on Crusade The Crusades • • • • • 1st – captured Jerusalem 1099 Muslims retook the city in 1187 Many attempts to retake the city Defeated by Saladin Christians lost Constantinople in last Crusade Christian Crusades: East and West Impact of the Crusades • Exposure to Muslim culture & technology • Arabic translations on Greek philosophical & scientific works as well as Iranian & Arab original works stimulated European thought • Will lead into the Renaissance! Medieval Universities Oxford University Late Medieval Town Dwellings Medieval Trade Medieval Guilds Guild Hall Commercial Monopoly: Controlled membership apprentice journeyman master craftsman Controlled quality of the product [masterpiece]. Controlled prices