* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PPT of Network Topology
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
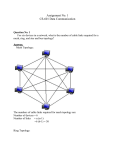
Created by- AMRITANSHU KUMAR Network Topology • Network Topology refers to layout of a network and how different nodes in a network are connected to each other and how they communicate. • Topologies are either physical (the physical layout of devices on a network) or logical (the way that the signals act on the network media, or the way that the data passes through the network from one device to the next). Types of Network Topology • There are five types of Network Topology 1. Mesh Topology 2. Star Topology 3. Bus Topology 4. Ring Topology 5. Tree Topology 1. Mesh Topology • In a mesh network, devices are connected with many redundant interconnections between network nodes. In a true mesh topology every node has a connection to every other node in the network. • There are two types of mesh topologies:I. Full mesh topology II. Partial mesh topology 2. Star Topology • In a star network devices are connected to a central computer, called a hub. Nodes communicate across the network by passing data through the hub. Main Advantage: In a star network, one malfunctioning node doesn't affect the rest of the network. Main Disadvantage: If the central computer fails, the entire network becomes unusable. 3. Bus Topology • In networking a bus is the central cable -- the main wire -- that connects all devices on a local-area network (LAN). It is also called the backbone. This is often used to describe the main network connections composing the Internet. Bus networks are relatively inexpensive and easy to install for small networks. Ethernet systems use a bus topology. Main Advantage: It's easy to connect a computer or device and typically it requires less cable than a star topology. Main Disadvantage: The entire network shuts down if there is a break in the main wire and it can be difficult to identify the problem if the network shuts down. 4. Ring Topology • A local-area network (LAN) whose topology is a ring. That is, all of the nodes are connected in a closed loop. Messages travel around the ring, with each node reading those messages addressed to it. Main Advantage: One main advantage to a ring network is that it can span larger distances than other types of networks, such as bus networks, because each node regenerates messages as they pass through it. 5. Tree Topology • This is a "hybrid" topology that combines characteristics of linear bus and star topologies. In a tree network, groups of starconfigured networks are connected to a linear bus backbone cable. Main Advantage: A Tree topology is a good choice for large computer networks as the tree topology "divides" the whole network into parts that are more easily manageable. Main Disadvantage: The entire network depends on a central hub and a failure of the central hub can cripple the whole network. Multiplexer networks • A Multiplexer is a device that allows one of several analog or digital input signals which are to be selected and transmits the input that is selected into a single medium. Multiplexer is also known as Data Selector. A multiplexer of 2n inputs has n select lines that will be used to select input line to send to the output. Multiplexer is abbreviated as Mux. MUX sends digital or analog signals at higher speed on a single line in one shared device. It recovers the separate signals at the receiving end. The Multiplexer boosts or amplifies the information that later transferred over network within a particular bandwidth and time. Demultiplexer • The process of getting information from one input and transmitting the same over one of many outputs is called demultiplexing. A demultiplexer is a combinational logic circuit that receives the information on a single input and transmits the same information over one of 2n possible output lines. • The bit combinations of the select lines control the selection of specific output line to be connected to the input at given instant. The below figure illustrates the basic idea of demultiplexer , in which the switching of the input to any one of the four outputs is possible at a given instant. Thank you… Click here YouTube , Twitter , My Website , Facebook .