* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 5 - life.illinois.edu
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Coevolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
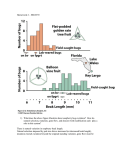
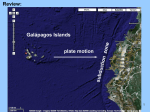
Coyne – Chapter 5. Hornets versus European honey bees – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6fTrSOFyfxs Hornets versus Japanese honey bees – http://video.nationalgeographic.com/video/bees_vs_hornet?source=relatedvideo Unparasitized Ant Parasitized Ant Parasitized ant Among the Berries Cryptic Katydids Cryptic Katydid Flower mimicking bee to attract males What has to happen for evolution via natural selection to occur? Why do we say that mutations are random? In what sense are mutations not random? Is evolution random? Coyne puts up some pretty big demands on natural selection. What are they? MISCONCEPTION: Natural selection acts for the good of the species. MISCONCEPTION: Natural selection involves organisms trying to adapt. What is genetic drift? How does drift compare to natural selection? In what ways are artificial selection (i.e. domestication of dogs, breeding of crops for particular traits) alike? In what ways are they different? What are the lessons to be had from humans selecting on dogs, corn, wheat, rice, cows, etc.? Evolution, HIV, and AZT Geospiza fortis and Daphne Major – Darwin's Finches in the Galapagos Islands Beak depth is variable within populations. Beak depth is heritable. In 1977, there was a huge draught and lots of birds died due to lack of food. The abundance of seeds declined. The few seeds that were left were large and hard. If we compare the original birds with the survivors, we see that the survivors had deeper beaks. The offspring of the survivors had larger beaks (like their parents) compared to finches hatched before the draught. draught Another depiction of how beak size, beak shape, and body size changed with the draught. draught draught Geospiza fortis and Daphne Major – Darwin's Finches in the Galapagos Islands Soapberry Bugs Soapberry bugs in Florida Example of rapid evolution due to natural selection: Soapberry bugs Soapberry bugs have long, needlelike beaks, the they use to penetrate the fruits of plants and consume seeds. They liquefy the contents and then suck them back up. Native plantBugs have long mouthpart Introduced plantBugs have short mouthpart Soapberry Nativebugs plantBugs have long mouthpart Introduced plantBugs have short mouthpart Soapberry bugs (Jadera haematoloma) and their native and introduced host plants in Texas and Florida, drawn to scale Native Host Plant Introduced Host Plant The Evolution of Complex Biochemical Pathways Has there been enough time for evolution to have produced all of the biological diversity that we see today? MISCONCEPTION: Natural selection gives organisms what they need. MISCONCEPTION: All traits of organisms are adaptations.