* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organic Molecules - Mr. Swords` Classes
Survey
Document related concepts
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
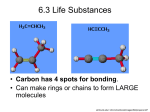
Also called Biomolecules or Organic Molecules Most “life” molecules have a backbone of carbon. Carbon can form 4 bonds so many atoms can bond and branch off. Many molecules are composed mostly of carbon & hydrogen = Hydrocarbons Biomolecules may be made of hundreds to millions of atoms! Large molecules are built from smaller, repeating units. Monomer = Small molecular units that make up a polymer. Polymer = Long chains of monomers. Classified into four main groups Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids STRUCTURE: -Made of: Monosaccharides These are simple sugars. -When you put monosaccharides together, you get: Polysaccharide - A key source of energy for the body. -They turn into energy for all cells. Examples of Carbohydrates: Starch – stored energy in plants Glycogen – stored energy in animals Cellulose – structural support in plants Monomers: Glycerol & Fatty Acids Polymers: Fat Energy Storage Hydrophobic: ◦ “Water Fearing” ◦ Saturated Fat – all fatty acid chains contain max of hydrogen atoms (all single bonds). ◦ Solid at room temperature. ◦ Contribute to an unhealthy diet. Unsaturated Fats – contain less than the maximum number of hydrogen atoms in the fatty acid chains. Liquid at room temp. Healthier choice. Carbon skeleton forms four fused rings. Chemical Message Example: ◦ Testosterone (male hormone) ◦ Estrogen (female hormone) ◦ Cholesterol Monomer: Amino Acid Polymer: Polypeptide Examples & Uses: ◦ Body Structures: Hair, Fur, Nails, Muscle. ◦ Long Term Nutrient Storage. ◦ Body Defense – Receptors on Cells ◦ Control Chemical Reactions Watch enzyme animations: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XTUm75-PL4&feature=related Used to speed up chemical reactions in a cell. (lowers the amount of energy needed) End in “ase” ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Protease breaks down proteins Lipase breaks down fats Enzymes are catalysts: Speeds up reaction, can be used over and over again. The reaction does not change it (like a key!) Acts on a substrate: The substance that is changed during the reaction. An enzyme lowers the energy needed so that the reaction can work at normal cell temperatures How an Enzyme Works: Shape of an enzyme only fits particular molecules (substrate) Active site → where the substrate fits Proteins are made of chains of amino acids twisted, folded and coiled into a unique shape. Analogy: ◦ Yarn = string of amino acids ◦ Sweater= protein with a purpose! The “folds” determine the function. Denaturation: When proteins are affected and lose their shape. Ex: Frying an Egg