* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Weld Control Cabinet 7_6_95.FM5
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Hendrik Wade Bode wikipedia , lookup
Fire-control system wikipedia , lookup
Control theory wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Distributed control system wikipedia , lookup
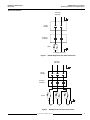
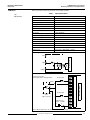
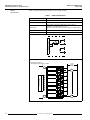
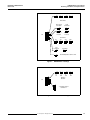
Bulletin No. 50006-524-01A March 1996 Raleigh, NC, USA Instruction Bulletin Replaces 50006-524-01 dated July 1995 EQ5300 Weld Control Cabinet Receiving, Installation, and Specifications © 1995 Square D All Rights Reserved EQ5300 Weld Control Cabinet Receiving, Installation, and Specifications Bulletin No. 50006-524-01A March 1996 !! DANGER HAZARD OF ELECTRICAL SHOCK, BURN OR EXPLOSION. • Read and understand this bulletin in its entirety before installing or operating EQ5300 weld controls. Installation, adjustment, repair and maintenance of these weld controls must be performed by qualified personnel. • DO NOT short across capacitors or touch unshielded components or terminal strip screw connections with voltage present. • Install all covers and close door before applying power or operating the weld control. • User is responsible for conforming to all applicable code requirements with respect to grounding all equipment. • Many parts in this weld control, including printed wiring boards, operate at line voltage. DO NOT TOUCH. Use only electrically insulated tools. • Power is applied to the weld control for some corrective action procedures. Use extreme caution. • Before servicing weld control: — Disconnect all power. — Place a “DO NOT TURN ON” label on weld control disconnect. — Lock disconnect in open position. Failure to observe these precautions will cause death, personal injury, or electrical shock. The EQ5300 Weld Control is manufactured under one or more of the following United States Letters Patents: 4104724, 4251764, 4254466, 4282417, 4289948, 4289951, 4301351, 4388515, 4399511, 4456809, 4459456, 4459457, 4463244, 4516008, 4910659, 4945210, other patents pending. © 1995 Square D. All rights reserved. This document may not be copied in whole or in part, or transferred to any other media, without the written permission of Square D. © 1995 Square D All Rights Reserved Bulletin No. 50006-524-01A March 1996 Table of Contents SCOPE OF MANUAL .......................................................................................................... 2 INSTALLATION .................................................................................................................. 2 Handling & Inspection .................................................................................................. 2 Hoisting......................................................................................................................... 3 Mechanical Installation ................................................................................................ 4 Water Connections ...................................................................................................... 4 Electrical Installation .................................................................................................... 5 Line-side Fuses .................................................................................................... 6 Input Power Connections ...................................................................................... 6 Output Power Connections ................................................................................... 6 Separation of Circuits ........................................................................................... 6 User I/O ................................................................................................................ 7 Weld Control Communications ............................................................................. 7 Operator Interface ................................................................................................. 7 WELD CONTROL COMPONENTS .................................................................................... 8 System Overview ......................................................................................................... 8 Circuit Breaker ............................................................................................................. 8 Isolation Contactor ....................................................................................................... 8 Weld Control Module ................................................................................................... 9 Input and Output Modules ........................................................................................... 9 WRIM Module .............................................................................................................. 9 Control Transformer ..................................................................................................... 9 Firing Board ................................................................................................................. 9 SCR/Power Assembly .................................................................................................. 9 TECHNICAL INFORMATION ........................................................................................... 10 Weld Control Cabinet ................................................................................................. 10 Circuit Breaker ........................................................................................................... 10 Isolation Contactor ..................................................................................................... 10 I/O Modules ............................................................................................................... 11 Input Specifications ............................................................................................ 11 Output Specifications .......................................................................................... 12 WRIM module ............................................................................................................ 13 Introduction ......................................................................................................... 13 Switch Settings ................................................................................................... 14 LED Indicators .................................................................................................... 16 Watchdog Circuitry ............................................................................................. 16 Operation ............................................................................................................ 17 Adjustments ........................................................................................................ 18 User Connections ............................................................................................... 18 Hardware Connections ....................................................................................... 18 Specifications ..................................................................................................... 20 Alarm Detection and Correction ......................................................................... 21 © 1995 Square D All Rights Reserved 1 EQ5300 Weld Control Cabinet Receiving, Installation, and Specifications SCOPE OF MANUAL Bulletin No. 50006-524-01A March 1996 This manual contains receiving, installation and technical information for the EQ5300 weld control cabinet. A set of schematics and parts lists containing configuration-specific information is packaged with this manual. The following EQ5300 weld control manuals are also available: INSTALLATION • EQ5300 Weld Control Module Functions and Specifications, Instruction Bulletin No. 50006-524-02 • EQ5300 Weld Control Module Quick Start Guide, Instruction Bulletin No. 50006524-03 • EQ5300/SFW WELD Quick Reference Guide, Instruction Bulletin No. 50006524-04 The nameplate on the front of the weld control provides the part number and serial number of the weld control. This part number is referenced on the drawings and part ordering information that are applicable to your weld control. Use it to locate relevant information in the schematics package that accompanies this manual. The weld control module inside the cabinet contains nameplate information for the processor itself. This weld control is designed to be programmed by the C600 handheld programmer, the C1600 data entry panel, or a computer with DOS based SFW WELD programming software. The data entry device provides the number and revision level of the software that is currently in use. Handling & Inspection The weld control must be thoroughly inspected before installation: 1. Do not remove the weld control from the shipping pallet until it is at the final installation site. The pallet protects the weld control and prevents damage to its exterior. Handle carefully to avoid damage to the internal components, frame and enclosure. When handling the weld control enclosure, balance it carefully to keep it from tipping. 2. Remove the weld control from its packaging and visually inspect enclosure for shipping damage. 3. Make sure weld control nameplate conforms to the packing slip and corresponding purchase order. 4. Open weld control door. 5. Verify that all components are properly seated, securely fastened and undamaged. 6. Verify that all internal wiring connections are tight and connectors are not damaged. 7. Close and secure the weld control door. 8. If any shipping damage is found, notify the carrier and your Square D representative. ! WARNING INSTALLATION HAZARD. Do not operate or install any weld control that appears damaged! Failure to observe this precaution can cause death, severe personal injury, or equipment damage. 2 © 1995 Square D All Rights Reserved Bulletin No. 50006-524-01A March 1996 EQ5300 Weld Control Cabinet Receiving, Installation, and Specifications Hoisting ! WARNING HANDLING AND LIFTING HAZARD. Keep area below and around any equipment being lifted clear of all personnel and property. Use lifting method shown in Figure 1. Failure to observe this precaution can cause death, severe personal injury, or equipment damage. Eyebolts are provided on the top of the enclosure to facilitate handling with hoisting equipment. Use a spreader bar as illustrated in Figure 1. Figure 1 © 1995 Square D All Rights Reserved Hoisting the Weld Control 3 EQ5300 Weld Control Cabinet Receiving, Installation, and Specifications Mechanical Installation Bulletin No. 50006-524-01A March 1996 Follow these guidelines when installing the weld control: • Choose an installation location which is compatible with the weld control’s environmental rating. Refer to Table 1 on page 10 for enclosure environmental ratings. • The weld control should be mounted in a location that minimizes the external heat load on the enclosure from radiative or convective heat sources. • Allow sufficient space in front of and clearance around the weld control to allow for door swing and ventilation. Refer to Figure 2 for door clearance. Refer to the appropriate cabinet drawing for dimensions. Figure 2 Door Clearance • Mount the weld control vertically on a surface capable of supporting its weight. Use mounting hardware compatible with the application. Refer to the appropriate cabinet drawing for mounting information. • When selecting the weld control mounting height from the floor, personnel access to the weld control disconnect handle and flange mounted operator controls should be considered. Be sure to follow applicable code requirements. For dimensions, refer to the appropriate cabinet drawing. Water Connections ! CAUTION OVERHEATING HAZARD. • Proper flow of cooling water to the SCR/power assembly must be maintained during operation of the weld control. • Keep water hose free of kinks. Failure to provide the proper flow of cooling water can cause equipment damage. The SCR/power assembly requires cooling water for proper operation. Refer to the appropriate cabinet drawing for location and size of the water fittings, and for allowable water inlet temperature, flow rate, and pressure requirements. 4 © 1995 Square D All Rights Reserved Bulletin No. 50006-524-01A March 1996 EQ5300 Weld Control Cabinet Receiving, Installation, and Specifications Electrical Installation Incoming 480 VAC Circuit Breaker Isolation Contactor SCR To Weld Transformer Figure 3 EQ5300 Single Pack User Power Connection Incoming 480 VAC Circuit Breaker Isolation Contactor SCRs XFMR A Figure 4 XFMR B XFMR C EQ5300 3-Pack User Power Connections © 1995 Square D All Rights Reserved 5 EQ5300 Weld Control Cabinet Receiving, Installation, and Specifications Line-side Fuses Bulletin No. 50006-524-01A March 1996 All weld controls must have fuses installed in the line-side power wiring. Proper fuse selection is shown on the safety label reproduced below. ! DANGER FAULT PROTECTION HAZARD. • No internal fault protection. Controller must always have fuses installed externally on line side of circuit breaker. • Approved fuses: Bussman FRS-400 Fusetron, Bussman 68400 Welder Limiter, Gould-Shawmut A4BX400 Type 150 Form 480 Welder Protector Amp-Trap, Gould-Shawmut ATS-DE-400 Amp-Trap and Gould-Shawmut TRS-400 TRIONIC. • Do not substitute fuses. Failure to observe this precaution will cause death, severe personal injury, or equipment damage. Input Power Connections Route incoming weld bus power cabling through the cutouts on the top of the weld control enclosure. Connect power cabling to L1 and L2 at the top of the circuit breaker. Use proper bushing or strain relief. The current ratings of all branch circuit components and equipment (such as bus taps, disconnect devices, fuses and feeder cables) are based upon the following criteria: • Maximum 400 A continuous RMS current • Weld control application • Expected duty cycle of the application • Allowable voltage drop of the feeder system Generally, the conductor ampacity necessary to limit the voltage drop within acceptable limits is greater than the required ampacity to prevent conductor overheating. Torque all power connections to the circuit breaker to 300 in-lbs (25 ft-lbs). Output Power Connections Connect the weld transformer cable to U1 of the SCR/power assembly and to V1 of the circuit breaker or the isolation contactor. Weld transformer cabling exits the enclosure through cutouts on the bottom of the enclosure. Use proper bushing or strain relief. Separation of Circuits Good wiring practice requires the separation of control, communication and power wiring. This separation reduces the possibility of coupling electrical transients from one circuit type to another. Follow these practices when wiring weld controls: 6 • Power wiring can be run in metallic conduit or metallic cable trays. Metallic conduit is preferred, although metallic cable trays are acceptable. • Do not run power, communications or control wiring in the same conduit or cable tray. • Metallic conduits or metallic cable trays carrying control or communications wiring should be separated by at least 4 inches (10 cm). • Metallic conduits or metallic cable trays carrying power should be separated from control and communications wiring by at least 18 inches (45.5 cm). • Whenever power, communications or control wiring cross, the metallic conduits or trays should cross at right angles. © 1995 Square D All Rights Reserved Bulletin No. 50006-524-01A March 1996 EQ5300 Weld Control Cabinet Receiving, Installation, and Specifications • Do not make ground connection to the bus duct case. The ground connection must be made to building steel. The voltage and frequency specifications of the input line must match the weld control configuration. Refer to Table 1 on page 10. User I/O Several configurations are available for user I/O wiring. Refer to the appropriate ordering information for I/O wiring configurations. Refer to the appropriate electrical schematic for connection and wiring information. Weld Control Communications Refer to the appropriate cabinet drawing for specific wiring information. An EQ5300 communications network is comprised of a physical network similar to RS485 using a proprietary half duplex (two-wire) communication protocol. Other Square D devices or third party devices are not compatible with this network and should not be used without the expressed written consent of Square D Company. This network allows many ways to interconnect weld controls to a variety of operator interfaces (C600 Hand Held, C1600 Data Entry Panel, SFW WELD programming software) as well as plant network gateways. Please refer to the EQ5300 Weld Control Communications document for complete details. Operator Interface A single, 1/4-turn lock connects the cable to the operator interface. This can be either a C600 Hand Held Programmer, or a C1600 Data Entry Panel. Refer to “Cable Ordering Information” for cable selection. © 1995 Square D All Rights Reserved 7 EQ5300 Weld Control Cabinet Receiving, Installation, and Specifications Bulletin No. 50006-524-01A March 1996 WELD CONTROL COMPONENTS System Overview The EQ5300 weld control is comprised of several components. Incoming 480 VAC weld bus power is routed through a circuit breaker, an isolation contactor, and SCR/power assembly before connecting to the weld transformer. Power is supplied to the internal components via a control transformer connected to the 480 VAC bus. If required, a 24 VDC power supply driven by the control transformer is also utilized. The weld control module interfaces to the circuit breaker and isolation contactor via I/O modules. User I/O can be interfaced via discrete I/O modules and/or a welder remote interface module (WRIM). The weld control module interfaces with the SCR/power assembly via a firing board. Control Transformer Inputs Outputs Inputs Outputs Power Supply Circuit Breaker Weld Control Module Isolation Contactor MemPack Firing Board SCR Assembly Figure 5 EQ5300 Weld Control Cabinet Circuit Breaker The circuit breaker provides power disconnect and magnetic overload protection for the weld control power circuit. Isolation Contactor The isolation contactor is an electromechanical switch that interrupts weld bus power to the SCR/power assembly. Optional. 8 © 1995 Square D All Rights Reserved Bulletin No. 50006-524-01A March 1996 Weld Control Module EQ5300 Weld Control Cabinet Receiving, Installation, and Specifications The EQ5300 weld control module is comprised of a power supply, microprocessor board, analog board (interface to firing board) and MemPack. Programming the weld control module allows it to perform weld control functions such as: • Fault monitoring • Input/output activity • SCR firing See Instruction Bulletin 50006-524-02, EQ5300 Weld Control Module Functions and Specifications, for the complete description of the weld control module. Note: Do not store the weld control module with the MemPack installed. This will cause undue draining of the MemPack battery. Input and Output Modules The weld control cabinet can contain several configurations of I/O modules: 24 VDC, 110 VAC, relay or solid state outputs, and/or a welder remote interface module (WRIM). Please refer to the Order Information/Configuration section at the end of this document and the appropriate configuration schematics for details. WRIM Module The welder remote interface module (WRIM) is a Square D manufactured module that provides the translation between the EQ5300 I/O bus and the Allen-Bradley remote I/O network. Control Transformer The control transformer steps the 480 VAC weld bus voltage down to 120 VAC. This voltage is for use as an internal power source for power supplies, inputs/outputs and the weld control module. Firing Board The firing board, sometimes referred to as the contactor interface, resides on the SCR power assembly and controls the interface between the weld control module and the SCR. SCR/Power Assembly The SCR/power assembly controls the flow of current to the weld transformer and reads voltage, current, and chill plate temperature. It is comprised of the firing board, a chill plate mounted SCR (silicon controlled rectifier), snubber assembly, current transformer, and load resistors. © 1995 Square D All Rights Reserved 9 EQ5300 Weld Control Cabinet Receiving, Installation, and Specifications Bulletin No. 50006-524-01A March 1996 TECHNICAL INFORMATION Weld Control Cabinet Table 1 Equipment Specifications Supply Voltage 480 VAC ±20%, 60 HZ Temperature Operating Ambient Storage 0 to 60 °C (32 to 140 °F) 0 to 70 °C (32 to 158 °F) Humidity Operating Relative Operating Absolute 5 to 95% non condensing 1 to 29 g/m3 Circuit Breaker Refer to Square D Instruction Bulletin 48049-034-02 for installation information. Isolation Contactor Refer to Telemecanique Instruction Bulletin W9 135 5817 01 21 for LC1F15 . . . F630 Contactors for complete information. 10 © 1995 Square D All Rights Reserved Bulletin No. 50006-524-01A March 1996 Table 2 provides technical specifications for the input modules. Table 2 Input Specifications Unit name 8 Function DC Input Module (Sink type) Type No. DN-108 Rated input 24 VDC Input voltage range 10 V to 30 VDC No. of inputs 8 points/module (one common connection per 8 points) Input current 10 mA/point (at 24 VDC) Input impedance 2.3 k¾ Turn on time 7 msec maximum Turn off time 11 msec maximum Must turn on voltage 10 VDC Must turn off voltage 3 VDC Must turn on current 4.10 mA at 10 VDC Must turn off current 0.98 mA at 3 VDC Input indication LED indication Common polarity Common terminal . . . . . (-) Internal current draw 20 mA maximum Isolation mode Photocoupler (1,500 V RMS / 1 minute) Circuit configuration IN7 Internal Circuit IN0 COM(-) Contact input (+) 4 (-) Contact input 1 2 Transistor output device (Open collector) DC Input (Sink) 5 No-contact input 3 (OUT) 6 7 Terminal screw: M3.5 Unit weight: Approx. 120 g (0.26 lbs) NC External wiring example External power supply 24 VDC (+) (-) 0 Input Specifications COM(-) I/O Modules EQ5300 Weld Control Cabinet Receiving, Installation, and Specifications Note: NC (No Connection) - Do not connect input and other wiring. © 1995 Square D All Rights Reserved 11 EQ5300 Weld Control Cabinet Receiving, Installation, and Specifications Output Specifications Bulletin No. 50006-524-01A March 1996 Table 3 provides technical specifications for the output modules. Table 3 Output Specifications Unit name 8 Function Relay Output Module Type No. RT-108 No. of outputs 8 points/module Output signal Relay output, Independent 1NO. Relay can be replaced. 120 VAC, 4.5 A (240 VAC, 2 A) cos φ = 1 (Each relay unit can be replaced with a transistor or SSR output.) Output indication LED indication Internal current draw 150 mA Internal Circuit Circuit configuration Ry Ry External wiring example Terminal screw: M3.5 Unit weight: Approx. 250 g (.55 lbs.) Load power supply c c a 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Relay Output a L L 12 © 1995 Square D All Rights Reserved Bulletin No. 50006-524-01A March 1996 EQ5300 Weld Control Cabinet Receiving, Installation, and Specifications WRIM module Introduction The welder remote interface module (WRIM) is compatible with the Allen-Bradley 1771 remote I/O link. It allows the EQ5300 weld control module to communicate with various Allen-Bradley programmable logic controllers. When using the WRIM with an Allen-Bradley 1771 remote I/O link, only one cable is required. The WRIM maps the weld control module inputs and outputs to the PLC without racks, I/O modules, or other adapters. All Allen-Bradley remote I/O standards are supported: • 1/4, 1/2, 3/4 or full rack simulation • Communication at 57.6 KBaud, 115.2 KBaud, and 230.4 KBaud • Rack addressing is switch selectable • Hold last state • Processor restart lockout • Green status LED The WRIM interfaces with the I/O bus of the EQ5300 weld control module and converts it to an Allen-Bradley remote interface (“blue hose”). To the Allen-Bradley PLC, the WRIM is functionally identical to two 16-bit output cards and two 16-bit input cards. Up to three host weld control modules can be supported by a single WRIM. To each of the host weld control modules, the WRIM is functionally identical to two 8-bit output modules and two 8-bit input modules. The WRIM performs three primary functions: • Allows an Allen-Bradley PLC to provide logical control signals to each weld control module and to receive logical status information from each weld control module without the use of discrete I/O. The I/O mapping between the two interfaces is fixed. • Provides logical interpretation and support for auxiliary I/O, also known as local I/O. • Sources the cabinet keep-alive strobe signal through the local output module. The WRIM also supports an RS485 service port, to be used only by Square D authorized personnel. J4 - Local I/O J8 - Service Port S2 - Switch 2 WRIM Welder Remote Interface Module Assembly 52045-042 S1 - Switch 1 LED Indicators J6 - Weld Control Module C S3 - Service Port Terminator J7 - User Connections J5 - Weld Control Module B J3 - Weld Control Module A Figure 6 Switch Settings Welder Remote Interface Module Communication Rate (S2 - #7, #8) © 1995 Square D All Rights Reserved The proper settings for the WRIM communication data rate are determined by the PLC network configuration. 13 EQ5300 Weld Control Cabinet Receiving, Installation, and Specifications 14 Bulletin No. 50006-524-01A March 1996 Hold Last State (S2 - #6) This is used in conjunction with Processor Restart Lockout to determine the outputs’ state at the time of losing communications with the PLC, or when the WRIM has been disabled by the PLC. To have the outputs hold the last data processed before the loss of communication, turn Hold Last State ON. To have the WRIM outputs disabled, turn Hold Last State OFF. Processor Restart Lockout (S2 - #5) This is used with Hold Last State to establish the restart criteria when the PLC stops communicating with the WRIM, or the WRIM has been disabled by the PLC. To have the PLC automatically re-establish communications, turn Processor Restart Lockout OFF. To require the control to be power cycled, turn Processor Restart Lockout ON. I/O Rack Size (S2 - #3, #4) This determines the size of the rack that is emulated by the WRIM. Last Rack (S2 - #2) (PLC2 only) Turn ON to indicate the WRIM is the last rack in the drop. I/O Rack Number (S1 - #1 TO #6) These settings determine the I/O rack number for the WRIM interface and are dependent on the PLC that is used. Service Port Enable (S2 - #1) This is used to enable or disable the service port and should be in the OFF position for normal operation. Starting Quarter (S1 - #7, #8) The proper settings for the starting quarter (S1 - #7, #8) are determined by the PLC physical installation. © 1995 Square D All Rights Reserved Bulletin No. 50006-524-01A March 1996 EQ5300 Weld Control Cabinet Receiving, Installation, and Specifications OFF 7 57.6K 8 ON OFF 8 OFF 7 OFF 8 ON 8 7 ON 7 ON 115.2K 230.4K 230.4K Data Rate Hold Last State Don’t Hold Last State OFF 6 S2 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 OFF 5 ON OFF 3 ON 4 3 ON 3 Last Rack 2 ON Normal Operation Service Port WRIM Switch 2 Settings OFF 8 OFF 7 0 1st 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 ON 8 OFF 7 2 2nd OFF 8 ON 8 7 ON 7 ON 4 3rd 6 4th Starting Quarter 1 2 4 8 16 32 © 1995 Square D All Rights Reserved Full OFF 4 ON OFF 3 OFF 2 Figure 8 5 4 Not Last Rack S1 ON Rack Size 1/2 3/4 1/4 OFF 4 Figure 7 6 Processor Lockout Processor Restart OFF 1 ON 1 - 6 Binary Select I/O Rack # WRIM Switch 1 Settings 15 EQ5300 Weld Control Cabinet Receiving, Installation, and Specifications LED Indicators Bulletin No. 50006-524-01A March 1996 WRIM Processor Status GREEN RI/O Status OFF - no communication ON - communications established Flashing - commands being received in program mode Indicates the state of the WRIM processor. RED Watchdog Circuitry Indicates the state of the PLC remote I/O communications link. Off - Normal operating mode ON - WRIM processor error Flicker - service port in use The WRIM controls the isolation contactor and circuit breaker shunt trip through the local I/O. The WRIM receives power and timing signals from weld control module A (see Figure 8). If weld control module A fails, the WRIM would fail to monitor the state of the isolation contactor and provide a shunt trip. Because of this, weld control module A provides a keepalive signal by toggling a local I/O point to an Underspeed Control Relay. The weld control cabinet’s Underspeed Control Relay has a built-in watchdog function, which causes the relay to trip the circuit breaker if the keep-alive signal falls below a certain adjustable frequency. If the relay fails to receive the keep-alive strobe, the relay de-energizes. The delay between the time that power is applied to the Underspeed Control Relay and the time that the relay is energized is measured to be 17.15 ms worst-case. An ON-Delay relay is employed in series with the Underspeed Control Relay to guarantee that weld control module A is providing the keep-alive signal before energizing. Figure 9 illustrates the configuration of the cabinet watchdog function. 16 © 1995 Square D All Rights Reserved Bulletin No. 50006-524-01A March 1996 EQ5300 Weld Control Cabinet Receiving, Installation, and Specifications EQ5300 Weld Control Module “A” WRIM STROBE 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 CLOCK DATA INPUTS DATA ENABLE DATA DATA 12 V OUTPUTS 12 V RTN 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Underspeed Control Relay Sense Input 120 V Input +24 VDC Supply + L1 24 V Input 120 VAC - L2 “Cabinet keep alive” signal ON-Delay Relay 120 V Input Circuit Breaker SHUNT TRIP Figure 9 Operation Cabinet Watchdog Function This configuration requires that the following circuitry MUST be fully operational for the cabinet to remain powered up: • IDEC interface of weld control module A • 12 V supply of weld control module A • Local I/O interface of WRIM • Processor of WRIM • Relay #4 of the local I/O block If, at any time, any of these functions fail, the Underspeed Control Relay causes the circuit breaker to be shunt tripped. If a mechanical relay output block is used, a constant clicking will be heard with a frequency of 1 Hz (one second) from inside the cabinet during normal operation. This noise is the cycling of relay #4 of the local I/O modules as it is used to toggle the sense input of the Underspeed Control Relay. © 1995 Square D All Rights Reserved 17 EQ5300 Weld Control Cabinet Receiving, Installation, and Specifications Bulletin No. 50006-524-01A March 1996 Adjustments No user adjustments are required. These are all set at the factory. User Connections The Allen-Bradley remote I/O connections are made at connector J7 of the WRIM: J7 Pin Connection 8 Blue 9 Shield 10 Clear A termination resistor should be installed on the WRIM if it is the last remote I/O drop on the physical communications cable. It is connected across pins 6 and 7 of J7. The value of the resistor should be as follows: Hardware Connections Comm Rate J7 - 6, 7 Resistor value 57.6 KBaud 150 Ohm 115.2 KBaud 150 Ohm 230.4 KBaud 82 Ohm Table 4 Pin Connector J7 - 10-PIN Phoenix (User Connections) Connection 1 24 V Return 2 +24 VDC 3 Chassis/Earth Ground 4 5 6 Termination Resistor-Allen-Bradley interface 7 Termination Resistor-Allen-Bradley interface 8 “Blue” lead of 1771 interface 9 “Shield” lead of 1771 interface 10 “Clear” lead of 1771 interface Table 5 Pin 18 Connector J8 - 5-PIN Phoenix (Service Port) Connection 1 RS422 2 RS422 3 Shield 4 RS422/485 5 RS422/485 © 1995 Square D All Rights Reserved Bulletin No. 50006-524-01A March 1996 EQ5300 Weld Control Cabinet Receiving, Installation, and Specifications Table 6 Pin Connector J3 - Weld Control Module A Connection 1 12 V Return 2 Data Clock from weld control module 3 12 VDC Return 4 Strobe Signal 5 12 VDC Supply 6 Enable Signal 7 12 VDC Supply 8 Data Output 9 Chassis Ground 10 Data Output Table 7 Pin Connection 1 Data Output 2 Chassis Ground 3 Data Input 4 12 VDC Supply 5 Enable Signal 6 12 VDC Supply 7 Strobe Signal 8 12 VDC Return 9 Data Clock 10 12 VDC Return Table 8 Pin Connector J4 - Local I/O Connector J5 - Weld Control Module B Connection 1 12 V Return 2 Data Clock from weld control module 3 12 VDC Return 4 Strobe Signal 5 12 VDC Supply 6 Enable Signal 7 12 VDC Supply 8 Data Output 9 Chassis Ground 10 Data Input © 1995 Square D All Rights Reserved 19 EQ5300 Weld Control Cabinet Receiving, Installation, and Specifications Bulletin No. 50006-524-01A March 1996 Table 9 Pin Connector J6 - Weld Control Module C Connection 1 12 V Return 2 Data Clock from weld control module 3 12 VDC Return 4 Strobe Signal 5 12 VDC Supply 6 Enable Signal 7 12 VDC Supply 8 Data Output 9 Chassis Ground 10 Data Input Specifications Table 10 Parameter Specifications Spec Min Typ Notes Max Units Deg. C Size 4.1" x 8.54" Operating Temp 0 60 32 140 Deg. F Storage Temp -40 80 Deg. C -40 20 176 Deg. F Input Voltage 19 24 30 VDC Input Current 50 150 1000 mA © 1995 Square D All Rights Reserved Depending on accessory board and peripherals used Bulletin No. 50006-524-01A March 1996 Alarm Detection and Correction EQ5300 Weld Control Cabinet Receiving, Installation, and Specifications If problems arise while using the WRIM, one of the following errors may have occurred. Follow the steps outlined on the following pages to isolate and solve the problem. Problem: No RI/O communications Symptoms: Green LED always OFF 1. Probable Cause: Reversed connection on connector J7 of the WRIM. Recommended Solution: Make sure the cable is connected with the blue lead on pin 8, the shield on pin 9, and clear lead on pin 10. 2. Probable Cause: Incorrect Data Rate setting. Recommended Solution: Make sure that the settings of S2 - 7, 8 match the Data Rate setting on the PLC. 3. Probable Cause: Incorrect First I/O Group setting. Recommended Solution: Make sure that S2 - 7, 8 are set properly as determined by the PLC configuration. 4. Probable Cause: Incorrect I/O Rack Number setting. Recommended Solution: Make sure that S1- 1 to 6 are set properly. 5. Probable Cause: Incorrect setting of the switches for Last Rack and Rack Size. Recommended Solution: Check the settings of S2 - 2, 3, 4. Problem: Synchronization difficulty. Symptom: Green LED intermittently ON. 1. Probable Cause: Missing termination resistor. Recommended Solution: Check J7 for the presence of the termination resistor. Make sure it is in the correct position. 2. Probable Cause: Incorrect termination resistor value. Recommended Solution: Make sure that the termination resistor being used matches the requirements. © 1995 Square D All Rights Reserved 21 EQ5300 Weld Control Cabinet Receiving, Installation, and Specifications Bulletin No. 50006-524-01A March 1996 Problem: Unintelligible transmit data. Symptom: Green LED flashing. 1. Probable Cause: PLC is in program mode. Recommended Solution: Check the PLC to make sure it is in the correct operating mode. 2. Probable Cause: Reversed connection on connector J7 of the WRIM. Recommended Solution: Make sure that the cable is connected with the blue lead on pin 8, the shield on pin 9, and clear lead on pin 10. Problem: WRIM Error. Symptom: Red LED ON. 1. Probable Cause: WRIM is in test or service mode. Recommended Solution: Ensure that S2-1 is in the OFF position, then cycle power to the EQ5300 cabinet. 22 © 1995 Square D All Rights Reserved Bulletin No. 50006-524-01A March 1996 EQ5300 Weld Control Cabinet Receiving, Installation, and Specifications © 1995 Square D All Rights Reserved 23 EQ5300 Weld Control Cabinet Receiving, Installation, and Specifications Bulletin No. 50006-524-01A March 1996 Electrical equipment should be serviced only by qualified electrical maintenance personnel. No responsibility is assumed by Square D for any consequences arising out of the use of this material. © 1995 Square D All Rights Reserved