* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction of two new anaesthetic agents
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
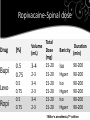
INTRODUCTION OF TWO NEW ANESTHETIC AGENTS Dr.G.k.kumar Ropivacaine Dexmeditomedine Ropivacaine Ropivacaine • New local anesthetic agent • Introduced in 1996. • In India 2009. Ropivacaine • Lower systemic toxicity • Safest long acting local anesthetic agent. * Groban et al. Anesth Analg, 2001. Ohmura et al. Anesth Analg, 2001. Santos et al. Anesthesiology, 2001. Ropivacaine -Pharmacology Ropivacaine-Pharmacology • Long acting LA agent. • Aminio amide. • Pure enantiomer -S isomer. Ropivacaine-Pharmacology • Greater selectivity for sensory blockade -binds selectively to Na⁺channels 1.7 • Shorter motor block *Liu BG et al, AnesAnalg.2000May. Simpsons D et al,2005 Ropivacaine-Pharmacology •Ropivacaine is less lipid soluble. •A smaller volume of distribution. •Greater clearance. •Shorter elimination half-life than bupivacaine. -Shorter duration of action esp motor blockade – early recovery. Ropivacaine-Pharmacology •Ropivacaine undergoes hepatic biotransformation and renal excretion •Excreted 86% as metobolites •Safe in CESLD & CESRD *Jokinen MJ et al, Anesthesiology,2007Jan. Jokinen MJ et al,Clinical Anesthesiology,2005 Ropivacaine-Pharmacology • The specific gravity of Ropivacaine Injection -from 1.002 to 1.005 at 25°C. -Isobaric Ropivacine-Safe Dose • 3-5mg /kg. • Pediatric-1-2mg/kg Ropivacaine-Epidural dose Drug Conc% Volume Dose mg 15-30 40-225 15-20 180-350 LEVO 0.25-0.75 15-30 40-250 15-20 180-350 ROPI 0.25-0.75 15-30 40-250 15-20 180-350 BUPI 0.25-0.5 Onset Duration *Miller’s anesthesia,7th edition Ropivacaine-Spinal dose Drug (%) Bupi 0.5 0.75 Levo Ropi 0.5 0.75 0.5 0.75 Total Volume Dose (mL) (mg) 15-20 3-4 2-3 15-20 3-4 15-20 2-3 15-20 3-4 15-20 2-3 15-20 Duration Baricity (min) Iso Hyper Iso Hyper Iso Hyper 90-200 90-200 90-200 90-200 90-200 90-200 *Miller’s anesthesia,7th edition Ropivacaine – clinical efficacy • When used for spinal anesthesia, 0.75% ropivacaine produces less intense sensory and motor block than 0.5% bupivacaine. • Equipotent to bupivacaine when used for lumbar epidural labor analgesia and C-section. Ropivacaine – clinical efficacy • In epidural and other blocks bupivacaine and ropivacaine demonstrate similar intensity of sensory anesthesia. Ropivacaine – clinical efficacy • Ropivacaine motor block -delayed in onset. -less intense. -shorter in duration. Toxicity • Ropivacaine < Levobupivacaine < Bupivacaine • Even at 50% higher dosage!!! *Dony et al. Anesth Analg, 2000 Toxicity • Tolerated blood conc. level [ROP] >> [BUP] = [LBUP] • Mortality: BUP (50%) > LBUP (30%) > ROP (10%) • • • * Groban et al. Anesth Analg, 2001. Ohmura et al. Anesth Analg, 2001. Santos et al. Anesthesiology, 2001. Ropivacine-Why Safer Than Bupivacaine? • Bupivacaine is a 50:50 racemic mixture of the S- and Renantiomers. • The R isomer has greater affinity and binding time for voltagegated sodium channels, and so cardiotoxicity. Ropivacine-Why Safer Than Bupivacaine? • R-bupivacaine is also more arrhythmogenic. • Slows ventricular conduction 4.6 times as much as Sbupivacaine. Ropivacine-Why Safer Than Bupivacaine? • The Ropivacaine is the pure S-enantiomer so decreased cardiotoxicity . Ropivacine-Why Safer Than Bupivacaine? • Cumulative doses up to 770 mg over 24 hours (intraoperative block plus postoperative infusion) • Continuous epidural infusion at rates up to 28 mg per hour for 72 hours have been well tolerated in adults, ie, 2016 mg plus surgical dose of approximately 100-150 mg as top-up. *www.fda druginformation.com Ropivacine-Why Safer Than Bupivacaine? • Ropivacaine has a larger therapeutic index • 70% less likely to cause severe cardiac dysarrhythmias • Greater CNS tolerance • The improved safety profile is due to a lower lipid solubility Ropivacaine HYPE? HOPE? LA toxicity more in • Heart block, HT, structural heart disease. • >65yr,<12yr. • Pregnancy. • Acidosis. • Liver dysfunction. • Acutely ill and debilitated. Role of Ropivacaine • • • • • • SAFE PRACTICE Pediatric patients. Geriatric patients. Continuous infusions. For labour analgesia. Rescue spinal anesthesia. Ropivacaine LA toxicity treatment • Supportive care: intubation, vasopressors, appropriate defibrillation, fluids, stop injection of LA. • Intralipid…Bolus 1cc/kg of 20% intralipid, 0.25cc/kg/min of 20% intralipid for 10 minutes • Bolus can be repeated every 5 minutes up to a maximum of 8cc/kg of 20% intralipid LA toxicity treatment • Cardiac support should be continued as ACLS dictates • Adrenaline and vasopressin are usefull. Ropivacaine








































![[ PDF ] - journal of evidence based medicine and](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007849467_1-90a7ae804bfc22844c15e13beda59f60-150x150.png)


