* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2.1 Use Inductive Reasoning
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
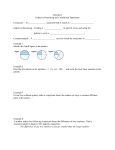
Geometry Chapter 2: Reasoning and Proof Section 2.1-‐ Use Inductive Reasoning SWBAT: describe patterns and use inductive reasoning. Common Core: • G.CO.9. Prove theorems about lines and angles. Vocabulary: conjecture, inductive reasoning, and counterexample Example 1: Describe a visual pattern Example 2: Describe a number pattern Describe the pattern in the numbers 1000, 500, 250, 125, … and write the next three numbers in the pattern. Geometry Chapter 2: Reasoning and Proof Example 3: Make a Conjecture Given the pattern of triangles below, make a conjecture about the number of segments in a similar diagram of 5 triangles. Example 4: Make and test a Conjecture Numbers such as 3, 11, 15, and 29 are odd numbers. Make and test conjecture about the product of any two odd numbers. v Disproving Conjectures: To show that a conjecture is true, you must show that it is true for all cases. However, you can show that a conjecture is false by finding one case where the conjecture doesn’t work. A ______________________________________________ is a specific case for which the conjecture is false. Geometry Chapter 2: Reasoning and Proof Example 5: Find a counterexample to disprove the conjecture: Supplementary angles are always adjacent. Example 6: Standardized Test Practice Homework: Handout 2.1 Practice B