* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PARTS OF THE CELL CELL ORGANELLES
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
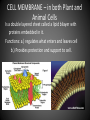
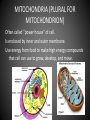
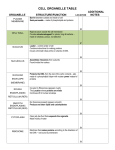
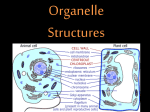
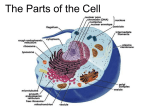
PARTS OF THE CELL FUNCTIONS OF CELL ORGANELLES NUCLEUS: controls most cell processes and contains DNA (code for all proteins and other molecules made by cells) CELL MEMBRANE – in both Plant and Animal Cells Is a double layered sheet called a lipid bilayer with proteins embedded in it. Functions: a.) regulates what enters and leaves cell b.) Provides protection and support to cell. RIBOSOMES • Organelle that produces proteins by following coded instructions received from the nucleus’ DNA. • Some ribosomes move freely in the cell. • Other ribosomes are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM Two types: Rough E.R. and Smooth E.R. Function is to assemble components of the cell membrane. rE.R. has ribosomes on its surface and makes proteins sE.R. has enzymes that synthesize (make) lipids (fats) GOLGI APPARATUS Proteins made by rE.R. move into a stack of Golgi apparatus to be stored. Enzymes in the Golgi apparatus attach carbohydrates and lipids to proteins. LYSOSOMES This tiny organelle is filled with enzymes. a.) Function is to break down lipids(fats), carbohydrates, & proteins into particles usable by rest of cell. b.) Also function to break down organelles that have outlived their usefulness. This helps prevent “junk” from cluttering up cell. VACUOLES Sacs that store water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates. Plant cells have larger vacuoles than animal cells. In plant cells, vacuoles provide pressure to support heavy leaves, stems and flowers. MITOCHONDRIA (PLURAL FOR MITOCHONDRION) Often called “power house” of cell. Is enclosed by inner and outer membrane. Use energy from food to make high energy compounds that cell can use to grow, develop, and move. CHLOROPLASTS Found in plant cells only. Use light energy (Sun) to make glucose sugar molecules by process of photosynthesis. Contain chlorophyll, a green pigment. Is a double membraned organelle. CELL WALL – found only in plant cells • Functions to provide support and protection for the plant cell. • Made of cellulose (a carbohydrate) and protein. Cell Wall