* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 7.1 Totalitarian Dictators
World War II and American animation wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Nazi views on Catholicism wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Post–World War II economic expansion wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Propaganda of Fascist Italy wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
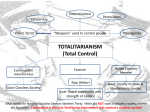
Totalitarian Regimes 7.1: Analyze the decision of the United States to enter World War II, including the nation’s movement from a policy of isolationism to international involvement and the japanese attack on Pearl Harbor Important Terms I. Communism A. Central Government control of property and resources B. Gov’t directs all political and economic decisions C. Control is typically through Communist Party committee D. II. Fascism A. Extreme nationalism B. One significant powerful figure as a leader C. Loss of individuality and creativity III. Nazism (shortened German word for National Socialism) A. Form of Fascism in Germany during Hitler’s rule B. Unite German people C. Elimination of Jews, gypsies, disabled, etc. Rise of Totalitarianism Great Depression was worldwide People blamed governments Totalitarian governments: restricted personal freedoms and prohibited political opposition - essentially kills off opposition Fascism is NOT Communism Joseph Stalin USSR (Russia) – Union of Soviet Socialist Republics Takes power in 1929 Name literally means “man of steel” responsible for 8 to 13 million deaths USSR becomes 2nd largest industrial power Benito Mussolini Seizes control of Italy in 1921 Fascism: the state more important than the individual, maintains control of the economy, suppresses opposition and is ruled by a dictator countries that have extreme nationalism fall victim very good orator, known for fluctuating voice and pounding speech - Dr. King studied him Adolf Hitler Germany had to pay for WWI; led to extreme resentment and embarrassment promised to restore country to glory went from 6 million unemployed to nearly nothing in a year, people built canals, roads and railroads Third Reich - “third rule” of 1000 years Very good orator - clearly could captivate people Hirohito and Tojo Hirohito was Democratic, but lost support when negotiations with US fail Japan has a ruling class, which was the Shogun or Samurai Warrior Class split country in two Democracy falls and Tojo Hideki rises to power over Hirohito Tojo primarily responsible for Pearl Harbor plan Totalitarian Dictators • Totalitarianism: State holds TOTAL authority in society and seeks to control all aspects of public and private life • Stalin: Communist in Soviet Union • Mussolini: Fascist in Italy • Hitler: Nazi (National Socialist) in Germany • Tojo: Military leader in Japan • All provided hope for a better future but restricted personal liberties for the “betterment” of their countries Mussolini, Hitler and Tojo Mussolini expands borders into Ethiopia 1935 Hitler annexed Rhineland, Austria and Sudetenland 1936-38 Tojo invaded Manchuria 1931 Appeasement: Idea of ignoring a problem and just letting it continue to happen because of not wanting to get involved United States Great Depression passed Neutrality Act of 1935: Prohibited the sale of weapons to warring nations - this is what brought the US into WWI Quarantine Speech: economic and diplomatic sanctions against aggressor nations; specifically Japan Japan saw as threatening: US would not trade oil Europe War 1939: Hitler Invaded Poland Blitzkrieg - lightning war Russia was ally to Poland Britain and France declare war on Germany Germany defeated France in under 9 months, wanted to humiliate France so they made de Gaulle sign armistice in same train car as Germany had 30 years prior US involvement Neutrality Cash and Carry- will trade goods to countries that will pay in cash and transport them Destroyers for Bases- US exchanged ships for base rights on British possessions Lend-Lease Act- “Loaned” Allied Countries weapons- ended Neutrality Because we shipped the material, Germany opened fire - US Navy protected shipments in a state of undeclared war Japan the US was providing aid (oil) to Allied countries (China) Japan, an island with limited resources, needed lots of oil to power their large military Quarantine Speech was one of last straws due to economic sanctionsembargo against aggressive countries, no more oil to Japan Japan Attacks: fears US power in the Pacific and upset over embargo Dec 7, 1941-Pearl Harbor: “Day that will live in infamy” US declares war on Japan