* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Old Sample Exam #2
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Nebular hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
History of supernova observation wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
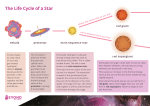
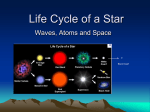
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical naming conventions wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
NAME:_______________________ SECOND EXAM ASTR 1020 SECTION 001 MARCH 16, 2010 DO ALL 19 PROBLEMS. MARK YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS SHEET AND TURN IT IN. Each answer worth 5 points except last which is worth 10 points. All constants in mks units unless otherwise specified: c=3x108 G=6.7x10-11 h=6.6x10-34 =5.7x10-8 REarth=6400km 16 1pc=3x10 m 1AU=1.5x1011m M=2x1030kg R=7x108m 4 7 L AT T 3 x10 F=ma x=vt c E h 3 r 2 r 2 GM v P 2 P v GM v r c 0 v=at _____ 1) How big is a red supergiant? As big as: a) a comet b) the Sun c) Mars orbit d) Jupiter e) Earth _____ 2) What is the luminosity of a white dwarf with surface temperature equal to the Sun? (in solar luminosities) a) 104 b) 102 c) 1 d) 10-2 e) 10-4 _____ 3) How long can a star run on gravity without nuclear fusion? (in years) a) 1031 b) 1012 c) 1010 d) 107 e) 100 _____ 4) What element cannot be nuclear burned to release energy? a) oxygen b) iron c) hydrogen d) uranium e) helium _____ 5) Planetary nebulae are often shaped like a(n) a) hourglass b) Frisbee c) basketball d) coke can e) ice cream cone _____ 6) How long will Prox Centauri (M5 dwarf) spend on the main sequence? (years) a) 1000 b) 106 c) 109 d) 1012 e) 1015 _____ 7) A White Dwarf star is comparable in size to a) a comet b) the Sun c) Mars orbit d) Jupiter e) Earth _____ 8) What is the density of a neutron star compared to that of water? a) .001x b) 1x (comparable) c) 103x d) 106x e) 109x _____ 9) How long will a neutron star survive if left alone? (years) a) thousand b) million c) billion d) trillion e) forever _____ 10) What carries the bulk of the energy out of a type II supernova explosion? a) photons b) neutrinos c) blast wave d) gravity waves e) wires 1 11.When a star becomes a giant it gets redder. Why? 12. What is the Helium Flash? 13. What is the fate of the Earth as the Sun ages? 14. What is electron degeneracy? 15. What is a Nova? 16 What is an Accretion Disk? 17 What is the difference between a Type I and Type II Supernova? 18. What is a Pulsar? 2 3 19 (10 Points) Draw an HR Diagram. Label both axes. Draw the Main Sequence and show the position of the Sun. Show the path that a two solar mass star follows from proto-star to final resting point. Label what the star is called in each of its major stages. 4