* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 6: The Humoral Immune Response
Survey
Document related concepts
Duffy antigen system wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
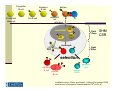
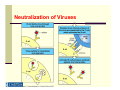
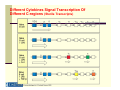
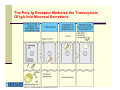
Lecture 6: The Humoral Immune Response (based on lecture by Dr. Matthew Scharff, Einstein) Progenitor B cell Pluripotent stem cell Immature B cell antigen mature B B cell activation Pre-B cell centroblast AID Th AID Dark Zone AID centrocyte SHM CSR Light Zone FDC selection memory B cell apoptotic cell plasma B cell anergic B cell modified from Luo, Ronai, and Scharff. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004 and Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine 16th ed Ch. 97. Questions to Consider How can we make antibody to every possible pathogen-i.e. Diversity How do we avoid making autoantibodies-i.e. Specificity How do we rapidly increase amount of antibody-i.e. Mobilization How do we switch from making IgM to IgG- i.e. Isotype Switching How do we increase the the affinity of antibody-i.e. Affinity maturation How do we generate memory Humoral Immune Response Class Switch Recombination IgM IgG / IgE / IgA Antigen-binding site Effector arm Somatic Hypermutation Low affinity high affinity Janeway and Travers, Immunobiology Antibody Mediated Functions IgM is Polymeric Which Increases Its Avidity Neutralization of Viruses Antibodies Neutralize Toxins Binding of Antigen to Surface Ig Triggers The Proliferation And Differentiation of B Cells Generation of Antibodies To Polysaccharides by Conjugation to Proteins (Glycoconjugate Vaccines) Circulating Antibodies Reflect Somatic Mutation And Isotype Switching HaveAre Different C Region Structures Ig Isotypes Isotype Encoded by Unique Constant Regions Isotypes Mediate Different Effector Functions Ig Isotypes Have Different Functions Due to Their Unique Constant Regions IgM And IgA Are Polymeric Which Increases Their Avidity Binding of Antigen to Surface Ig Triggers The Proliferation And Differentiation of B Cells Different Cytokines Secreted By T Cells Induce Switching To Different Isotypes Different Cytokines Signal Transcription Of Different C-regions (Sterile Transcripts) Activation-induced Cytidine Deaminase (AID) NLS N alpha helix Deficiency causes Hyper IgM type II F15X NES active site PS CSR C H56Y W68X C87R L106P C147X R174S R24W M139V L59F W80R W84X R112C F151S L181 R112H P182 C U G Luo, Ronai, and Scharff. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004 • AID is a cytidine deaminase whose in vitro substrate is ssDNA • AID may associate with RPA, RNAP II &? others • Transcription is required for somatic SHM and CSR R190X Activation-induced Cytidine Deaminase (AID) Mediates Class Switching Isotype Switching Requires Recombination Between Different Switch Regions The Poly-Ig Receptor Mediates the Transcytosis Of IgA Into Mucosal Secretions Cells Express Multiple Fc Receptors With Unique Functions Antibody Complexed To Antigen Binds to FcR’s and Activates Macrophages Antibody Complexed To Tumor Cells Targeting Their Killing by NK Cells Through FcRs IgE Complexed To Antigen Binds to FcR’s on Mast Cells and Mediates The Release Of Granules Questions to Consider How can we make antibody to every possible pathogen-i.e. Diversity How do we avoid making autoantibodies-i.e. Specificity How do we rapidly increase amount of antibody-i.e. Mobilization How do we switch from making IgM to IgG- i.e. Isotype Switching How do we increase the the affinity of antibody-i.e. Affinity maturation How do we generate memory





































![Anti-PCB antibody [3H2AD9] ab110314 Product datasheet 3 Images Overview](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000076345_1-acbfa58e194757c519d151062b812354-150x150.png)




