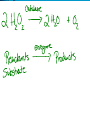* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemical Reactions and Enzymes What is a chemical reaction?
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fusion wikipedia , lookup
Artificial photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Chemical equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Chemical biology wikipedia , lookup
Chemical industry wikipedia , lookup
Process chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Photoredox catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen-bond catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Restriction enzyme wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis of doxorubicin wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Lewis acid catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Bioorthogonal chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Supramolecular catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme kinetics wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
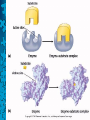
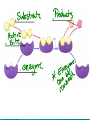
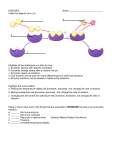
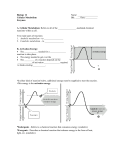
Chemical Reactions and Enzymes What is a chemical reaction? • Changes or transforms chemicals into other chemicals • Ex: Iron + Oxygen Iron Oxide (rust) • What is the product? • What are the reactants? Energy Is Required • Energy can be either given off or absorbed for a chemical reaction to occur • Identify the type of reaction as either endothermic or exothermic by the graphs to the right: Activation Energy • • Energy needed to start a reaction Identify the activation energy supplied for the following chemical reactions 1) Building a Fire 2) Turning on a Light 3) Starting a Car Catalyst • Any substance that lowers the activation energy needed to start a reaction. Enzymes Baby!!!!!! • Describe what enzymes “do” using the graph below: Enzymes • Enzymes are proteins made by the cell to speed up the chemical reactions. Properties of Enzymes 1. Lowers activation energy 2. Speeds up a reaction 3. Can be used repeatedly 4. Shape specific (substrate)* *If shape is altered, enzyme cannot function Animations Factors That Affect Enzyme Activity • High Temperature (boiling ) • Extreme pH – (acid/base) • Changes enzyme shape Denaturing an Enzyme • A change in the shape of the active site on the enzyme What life molecule are enzymes a part of??? PROTEINS! • Enzymes = speed up reactions (to break down substances) • Substrate= a molecule which is acted upon by an enzyme (the reactant) “ase” • Enzymes have an ending “ase” • It helps you identify which one is the enzyme and which one is the substrate.