* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Microevolution is a change in a population*s gene pool
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
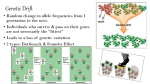
Microevolution is a change in a population’s gene pool Ch. 14.4 Populations and Their Gene Pools Population is a local group of individuals belonging to the same species Natural selection becomes clear when an ENTIRE population is tracked over time GENE POOL consists of all the alleles in all the individuals that make up a population – Think of it as the reservoir for the next generation to gather it’s genes Where genetic variation is stored Changes in Gene Pools Causes of genetic variation mutuations and sexual recombination (random occurrences) Natural selection is NOT random – Environment favors genetic combinations that CONTRIBUTE to survival/reproductive success Mendel’s and Darwin’s work combined lead us to MICROEVOLUTION a generation to generation change in the frequencies of alleles within a population Genetic Drift A change in the gene pool of a population due to chance GENETIC DRIFT ALL populations are subject to genetic drift – Smaller pop; more impact genetic drift has on that pop. The smaller the sample, the greater the chance that the results will differ from an expected result – Ex: coin tossed 10 times vs. 1,000 times Gene Flow and Mutation Exchange of genes with another pop. GENE FLOW – Fertile individuals or their gametes migrate btwn pops. Change in organism’s DNA MUTATION Mutations are esp. important as a source of variation in asexually reproducing organisms that clone themselves rapidly Natural Selection and Fitness Natural selection is a BLEND of CHANCE and SORTING FITNESS contribution that an individual makes to the gene pool of the next generation compared to other individuals



















![Microevolution is a change in population`s gene pool [1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000926710_1-bb56556ff16eaa56e5fbaa116b073962-150x150.png)