* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reproduction: Asexual vs
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Parental investment wikipedia , lookup
Parthenogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Animal sexual behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
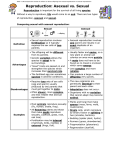
TEKS 7.14B compare the results of uniform or divers offspring from sexual reproduction or asexual reproduction Reproduction: Asexual vs. Sexual Reproduction is important for the survival of all living species. Without a way to reproduce, life would come to an end. There are two types of reproduction, asexual and sexual. Comparing sexual with asexual reproduction: Sexual Asexual Sexual reproduction involves fertilization so it typically requires the sex cells of two parents. Asexual reproduction involves one parent and results in an exact duplicate of an organism. Advantages The offspring will be different from its parents. Genetic variation allows the species to adapt to its surroundings. “Good” traits are passed on and strengthen the species which increases their survival rate. The fertilized egg can sometimes survive in adverse conditions. Usually faster and easier, so a new plant or animal can colonize an area more quickly. A mate does not have to be found so no travel is involved which saves energy. Less complex and more reliable. Can produce a large number of offspring very quickly. Disadvantages Requires two sets of sex cells (egg and sperm) usually produced by two parents that must get together to mate. Often slower, more complex, and less reliable that asexual reproduction. The new organisms are genetically identical to their parent and each other. Adaptation does not occur. Organisms with no variation that cannot adapt may become extinct. Examples Most animals reproduce sexually (fly, human, snake, frog). All flowering plants and those that make seeds reproduce sexually. (daffodil, grass, rose, oak tree). Fertilization may be internal (mammals, birds, reptiles) or external (frogs, fish). Plants and fungi that make spores (moss, ferns, mold, mushrooms). Single cells, which reproduce by binary fission or splitting in two (amoeba, bacteria). Budding (spider plant, hydra). Runners (grass, strawberries). Fragmentation (planarians). Regeneration (starfish). Definition TEKS 7.14B compare the results of uniform or divers offspring from sexual reproduction or asexual reproduction Reproduction: Asexual vs. Sexual ____________________ is important for the survival of all living _______________. Without a way to reproduce, __________ would come to an _________. There are two types of reproduction, _______________and _______________. Comparing sexual with asexual reproduction: Sexual Sexual reproduction involves Definition parent and results in an ___________ requires the sex cells of ______ parents. duplicate of an organism. from its parents. Genetic ___________ allows the species to ____________ to its surroundings. “Good” traits are passed on and strengthen the species which increases their _______________ __________. The fertilized egg can sometimes _______________ in adverse conditions. Requires _____ sets of sex cells (egg and Disadvantages Asexual reproduction involves ______ ____________________ so it typically The offspring will be _______________ Advantages Asexual Usually faster and _______________, so a new plant or animal can colonize an area more _______________. A __________ does not have to be found so no travel is involved which saves _______________. Less _______________ and more _______________. Can produce a large number of _______________ very quickly. The new organisms are genetically sperm) usually produced by two parents _______________ to their parent and that must get together to each other. _______________. Often _______________, more _______________ does not occur. Organisms with no _______________ _______________, and less reliable that that cannot adapt may become asexual reproduction. _______________. Plants and fungi that make Most _______________ reproduce sexually (fly, human, snake, frog). All _______________ plants and those Examples that make _______________ reproduce sexually. (daffodil, grass, rose, oak tree). Fertilization may be _______________ (mammals, birds, reptiles) or _______________ (frogs, fish). _______________ (moss, ferns, mold, mushrooms). _______________ cells, which reproduce by binary fission or _______________ in two (amoeba, bacteria). Budding (spider plant, hydra). Runners (grass, strawberries). Fragmentation (planarians). Regeneration (starfish).