* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Wide Area Networks
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Synchronous optical networking wikipedia , lookup
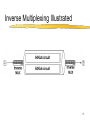
Wide Area Networks Computer Networks 1 Motivation Connect multiple sites Span geographic distances Cross public right-of-way streets buildings railroads 2 Building blocks Point-to-point long distance connections leased circuits provided by telecommunications companies Packet switches IP routers ATM switches many types... 3 Long-Distance Transmission Technology Lease transmission facilities from telecommunications companies Generally point-to-point NOT part of the conventional telephone system Copper, fiber, microwave or satellite Analog or digital 4 WAN Transmission Equipment Analog MODEM required at each end Digital CSU/DSU required at each end 5 CSU/DSUs Performs two functions, usually in a single box Needed because telecommunications digital encoding differs from computer industry digital encoding DSU translates between the two encodings CSU terminates line allows for maintenance 6 CSU/DSU Illustrated 7 Standards for WAN Circuits Specified by telephony industry in each region Can differ around the world North America and Japan examples DS0, DS1, DS3, T1, T3, Fractional T1 OC1, OC3, OC12, OC48, SONET Rest of the world examples E1, E2, E3 SDH 8 Inverse Multiplexing Recall multiplexing Instead of intertwining, you combine Combines two or more circuits Produces intermediate capacity circuit Special hardware required 9 Inverse Multiplexing Illustrated 10 Early WAN Technologies ARPANET historically important in packet switching fast when invented, slow by current standards precursor to today’s Internet X.25 protocol suite early commercial service still used more popular in Europe service by telecommunications companies 11 Recent WAN Technologies SMDS offered by telecommunications companies not as popular as frame relay Frame relay widely used commercial service offered by telecommunications companies ATM offered by telecommunications companies designed for both WAN and LAN 12 Future WAN Technologies Packet over SONET provided by telecommunications companies removes intermediate complexity Packet over DWDM provided by telecommunications companies and long haul fiber optic providers Ethernet? 13 Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) Connection oriented using virtual circuits Use of fixed sized packets called cells Defines service categories for QoS networking Operates on LANs using LAN Emulation (LANE) Usually used for high-speed WAN connectivity 14 Virtual Circuits Circuit ID instead of full host address pairs Switches swap IDs using translation tables Switch stores connection state for hosts 15 Cell Format 16 Service Types CBR VBR-NRT VBR-RT ABR UBR constant bit rate variable bit rate - non real time variable bit rate - real time available bit rate unspecified bit rate 17 LANE and MPOA Overview Backwards compatibility of ATM nodes with LANs such as Token Ring and Ethernet. Must support the broadcast nature of LANs with the virtual circuit nature of ATM. LAN Emulation Client (LEC) Provides abstraction for LAN protocols to ATM network LAN Emulation Server (LES) Manages and supports LECs LAN Emulation Configuration Server (LECS) Maintains emulated LANs (ELANs) and supports LECs Broadcast and Unknown Server (BUS) Distributes broadcasts/multicasts 18 How ATM is Used in a LAN 1. LEC - Implemented at each client (bridge listens to all) 2. LEC contacts LECS to going a ELAN via a pre-configured SVC or discovered dynamically via integrated local management interface (ILMI) 3. LECS assign LEC to a ELAN and direct them to a LES 4. LEC setups up connection to LES and registers addresses 5. LES assigns a BUS to the LEC 6. LEC queries LES for a MAC address to ATM address translation 7. LECS responds directly or forwards query to another LEC 8. MAC broadcasts are sent to BUS so that an associated ATM broadcast can be sent to all stations in the ELAN. 19 ATM Summary The aim was to combine the flexibility of packet data networks (e.g. Internet) with the per-user quality of service guarantees of a circuit switched network (e.g. telephone network). A monumental task! Although an important technology, it may follow the path of similar technologies (e.g. Token Ring). Stay tuned. 20 Final Thoughts Local loop ISDN Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) Cable modems Cellular CIR/CAR Everything over IP 21