* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Analytic Geometry Review Notes Create a booklet with the students
Survey
Document related concepts
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Four color theorem wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
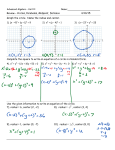
Analytic Geometry Review Notes Create a booklet with the students using these key concepts. The review is organized into sections, probability, coordinate geometry, quadratics, numbers, circles, and triangles and theorems. The review is set up to go from the newest material to the oldest, so the first semester stuff should be fresh in the students’ minds for the EOCT. Try to spend some class time creating the review booklet and some class time letting students work through and go over the corresponding EOCT review questions. Make sure every student has a copy of the EOCT formula sheet (the back page of the review packet) and that they use it during the review. Probability Union 𝐴 ∪ 𝐵 Intersection 𝐴∩𝐵 Complement A or A’ Compound Probability o or addition + o and multiplication x o mutually exclusive P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) o not mutually exclusive or overlapping P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) – P(𝐴 ∩ 𝐵) o Conditional Probability P( A B) o o Independent Dependent P( A B) P( A) P(A and B) = P(A) x P(B) P(A and B) = P(A) x P(B given A) Coordinate Geometry – Conics and Parabolas Circles o standard form (x-h)2 + (y-k)2 = r2 (h, k) center o convert to standard with completing the square o find intersection of circle with line o show a given point is on a circle Parabola o terms- focus, directrix, axis of symmetry o vertical equation o o yk 1 ( x h) 2 4p (h, k) vertex (h, k+p) focus x=h axis of symmetry y = k – p equation of directrix p > 0 opens up p < 0 opens down horizontal equation xh 1 ( y k)2 4p (h, k) vertex (h+p, k) focus y = k axis of symmetry x = h – p equation of directrix p > 0 opens right Prove theorems midpoint formula distance formula slope formula p < 0 opens left r = radius Quadratics factoring solving by quadratic formula completing the square solving using square roots Characteristics o zeros (solving) o shandard form f(x) = ax2 + bx + c o vertex form f(x) = a(x – h)2 + k o min/max (vertex) o x and y intercepts o increase, decrease o end behavior o domain o rate of change Comparing/transformations o shifts, stretches, shrinks, reflections b , 2a vertex vertex (h, k) Number System Rational Exponents Radical Expressions Rational vs Irrational numbers Polynomials o add, subtract o distribute, double distribute FOIL o perimeter, area Imaginary Numbers o simplify exponents, add, subtract, multiply Circles Vocab – diameter, radius, tangent, arc Angles o central angle o inscribed o angles inside the circle o angles outside the circle Segments o intersection inside the circle o intersection outside the circle Sectors o arc length o sector area Volumes – cylinder, cone, pyramid, sphere b f 2a Right Triangles Sin, Cos, Tangent Angle of Elevation, depression Triangles, Lines, and Proofs transformations – rigid transformations and dilations Similar Triangles o AA~ o similar triangles proportional sides Congruent Triangles o SSS, SAS, ASA, AAS, HL Proofs o vertical angles o alt interior angles o corresponding angles o Pythagorean theorem o triangle sum theorem o isosceles triangle theorem o triangle midsegment theorem Constructions o angle bisector o perpendicular lines o circumscribed triangle, square, hexagon