* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Ms. Rixie`s Website
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
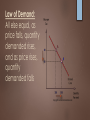
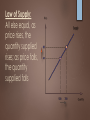
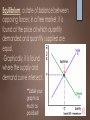
Demand, Supply, & Market Equilibrium UNIT 1 DAY 5 & 6 RIXIE Two major concepts: Demand: concerns consumers – deals with how much of something they are willing and able to buy at a series of prices Supply: concerns producers– deals with how much of something they are willing and able to make available at a series of prices Law of Demand: All else equal, as price falls, quantity demanded rises, and as price rises, quantity demanded falls Law of Supply: All else equal, as price rises, the quantity supplied rises; as price falls, the quantity supplied falls Movement along the Curves Movement from one point to another along a demand curve demonstrates a change in quantity demanded, as a result of a change in price. Movement from one point to another along a supply curve demonstrates a change in quantity supplied, as a result of a change in price. Using the correct terminology is very important!!! Shifting the Curves When the “other things equal” situation changes, it can cause the demand or supply curve to shift. Situations that cause this are called determinants. When the demand curve shifts left or right, we refer to this as a decrease or an increase in demand. When the supply curve shifts left or right, we refer to this as a decrease or an increase in supply. Determinants of Demand Change in: Consumer tastes # of buyers Consumer income Price of a complimentary or substitute goods Consumer expectations Determinants of Supply Change in: Resource or input price Technology Taxes or subsidies Price of other goods Producer expectations # of suppliers Types of Goods Normal v. Inferior Normal goods are things you buy more of when you have more $ (electronics / nice clothes) Inferior goods are things you buy less of when you have more $ (Ramen noodles) Types of Goods Substitute v. Complimentary A substitute good can be used in place of another good (Nikes & Reeboks) A complimentary good is one that is used together with another good (movies & popcorn) Equilibrium: a state of balance between opposing forces; in a free market, it is found at the price at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. -Graphically, it is found where the supply and demand curve intersect. **Label your graphs as much as possible!!! Watch this video (from the beginning to 2:36) and answer the following questions: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7eZcPs9z9OA What is a surplus? What is a shortage? Explain how market forces tend to push toward equilibrium price over time. Complex cases When both supply and demand change, it is not always possible to predict how equilibrium price and quantity will change. You can determine how one of the variables (price or quantity) will change, but the other will be indeterminate. For example, if supply increases and demand decreases: Both of these changes result in a decrease in equilibrium price. But what about quantity? Increase in supply increases equilibrium quantity, but decrease in demand decreases equilibrium quantity. So the change in quantity is indeterminate.