* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
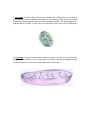
Download The cell wall is found in plant cells, but not in animal cells
Survey
Document related concepts
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
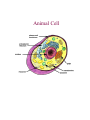
The cell wall is found in plant cells, but not in animal cells. This is the outermost layer in the plant cell. It is stiff, rigid, nonliving, and made of cellulose. It provides support so that the plant can grow tall and protection. Some materials like water, oxygen, and carbon dioxide can pass through it. The cytoplasm is a thick, jellylike substance found in both plant and animal cells filling the space between the nucleus and the cell membrane. It contains and supports the cell organelles. The cytoplasm is constantly in motion. The cell membrane is found in both plant and animal cells. It is the outermost layer in the animal cell and is found just inside the cell wall in the plant cell. The animal cell membrane contains cholesterol, but the plant cell does not. It has pores and is selectively permeable allowing the movement of certain substances into and out of the cell. This helps maintain homeostasis in the cell. The cell membrane also protects and supports the cell. The nucleus is a large, oval structure found in both plant and animal cells. It controls and regulates all cell activities. It contains genetic material. The mitochondrion is a bean-shaped structure found in both plant and animal cells. The mitochondria (plural) break down sugars and release energy for use by the cell. It has inner membranes or cristae. Cells with high activity levels contain more mitochondria, such as muscle cells. The vacuole is a round, fluid-filled sac found in both plant and animal cells. Plants usually have a few large vacuoles, while animal cells have smaller vacuoles, if any. It stores food, water, and other materials for use by the cell. Wastes may also be stored in vacuoles. A chloroplast is found in plant cells, but not in animal cells. Chloroplasts are oval-shaped, green structures usually containing chlorophyll, a green pigment. They use the sun's energy to make food for the plant through a process called photosynthesis. The photograph at the right was taken of Elodea, a water plant. All of the darker spots in the cell are chloroplasts! The lysosome is a small, round structure common in animal cells, but not usually found in plant cells. The lysosome is involved in digestive activities, including breaking down large food molecules into smaller ones and the digestion of old cell parts. The nuclear membrane is a selectively permeable membrane that is found in both plant and animal cells. It surrounds the nucleus and controls movement of materials into and out of the nucleus. The ribosomes are structures found in both plant and animal cells. They are small bodies that are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum or free bodies. Ribosome produces proteins. The endoplasmic reticulum (E. R.) is found in both plant and animal cells. It is a network of tubes or membranes that carries materials though the cell. Animal Cell Cell Organelles