* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Microarray Technology
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
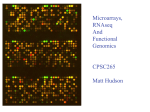
Microarray Technology • Introduction – Microarrays are extremely powerful ways to analyze gene expression. – Using a microarray, it is possible to examine the expression level of thousands of genes in one experiment – Microarrays can be used to compare the expression of many genes under different conditions (cancer cells vs. normal cells, skin cells vs. organ cells, rapidly growing cells vs. quiescent cells, etc.) • Types of Microarrays – Microarrays can be classified into two general types. • cDNA arrays consist of cDNA copies of mRNA spotted onto a glass slide. • oligo arrays consist of strands of oligonucleotides either spotted onto a glass slide or lithographed onto a solid surface. • Oligonucleotide Array • Microarray experiments – A typical microarray experiment consists of extracting RNA from the cells or tissue being examined, converting the RNA to cDNA, labelling the cDNA with fluorescent dyes and allowing the labelled cDNA to hybridize with the material (cDNA or oligonucleotide) on the microarray slide. – In some experiments, the control and subject RNAs are synthesized with different fluorescent dyes and mixed on the same slide. Other protocols use separate slides for the subject and control RNAs. • Microarray experiments – After hybridization, the slides are scanned using a laser device to determine the amount of fluorescent label that is attached to each cDNA on the slide. – The amount of fluorescence is displayed as a spot on a matrix corresponding to the original slide. – The intensity images are colored according to a standard where a higher level of fluorescent label in the subject (enhanced gene expression) is colored red. A lower level (repressed level of gene expression) is colored green. Equal levels are yellow. • Microarray experiments – Follow the link to see a realistic animation of a cDNA experiment. Microarray animation – The next step is analyzing the data. See the Microarray Data Analysis presentation.