* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
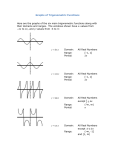
Download c. pulse-modulated signals
Chirp spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Chirp compression wikipedia , lookup
Time-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic range compression wikipedia , lookup
Spectral density wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
1. What operation produces a pulse-modulated signal? a. converting the message signal to a digital code b. passing the message signal through a high-pass filter c. sampling the amplitude of the message signal d. sampling the message signal's frequency 2. What are PAM, PWM, and PPM signals? a. PLL-modulated signals b. 4-bit digital codes c. pulse-modulated signals d. 2-bit digital codes 3. What circuit demodulates a pulse-modulated signal? a. sampler b. comparator c. low-pass filter d. samplehold 4. What are pulse-modulated signals? a. pulses that represent amplitude samples of a message signal b. AM and FM analog signals c. digital codes for frequency samples of a message signal d. pulses that represent frequency samples of a message signal 5. How are PAM and PCM signals usually multiplexed? a. JK multiplexed (JKM) b. SCR multiplexed (SCRM) c. integrated digitally multiplexed (IDM) d. time-division multiplexed (TDM) 6. What circuit encodes analog message signals and decodes pulsecode modulated (PCM)signals? a. ramp generator b. digital sampler c. CODEC d. ring counter 7. A 1-bit delta modulation (DM) code is output by the digital sampler. What dos the DM coderepresent? a. an increase or decease in the message signal's amplitude b. an amplitude sample of the message signal c. a change in the message signal's frequency d. an increase or decrease in the message signal's phase 8. What PAM signal parameter varies with the message signal? a. pulse frequency b. pulse width c. pulse amplitude d. all of the above 9. What circuit demodulates a PAM signal? a. sampler b. low pass filter c. high pass filter d. samplehold 10. The power dissipated by a PAM signal is directly proportional to the value of what parameter? a. sample pulse's period (T) b. output impedance (Z) c. maximum message signal frequency (f m) d. PAM signal's duty cycle fraction (PWT) 11. What condition(s) must exist to reconstruct a clear message signal from a PAM signal? a. The message signal is limited to a maximum of f m. b. f sis greater than twice f m(the Nyquist rate). c. The low pass filter cutoff frequency is between f mand the lowest frequency (f s- f m)in the first replica. d. all of the above 12. What condition causes aliasing in a PAM signal? a. The first replica frequency (f s- f m) is less than f m. b. The amplitude of each PAM pulse is constant. c. The amplitude of each PAM pulse varies. d. f sis 3 times f m. 13. What are PAM-TDM signals? a. frames and time slots b. PAM pulses sent in different time slots on the same channel c. signals sent with a timing clock on the same channel d. synchronization pulses 14. What is time-division multiplexing? a. A method of transmission that uses transmitters and receivers. b. The use of sampler circuits. c. A method of transmission that provides a common path with separate frequency bandsassigned to each of several signals. d. A method of transmission that provides a common path with separate intervalsassigned to each of several signals. 15. What is the function of the slot counter in a PAM-TDM transmitter? a. divides each frame into time slots b. sums the PAM signals to form the PAM-TDM signal c. ensures no two frames have the same number of slots d. samples the message signal 16. What is the overall purpose of the PAM-TDM transmitter? a. adding message signals, synchronization, and clocks b. multiplexing messages c. demultiplexing message signals d. interleaving synchronization and clocks 17. What are the FILTER circuits used for in a PAM-TDM transmitter? a. amplifying the message signals b. demultiplexing the message signals c. increasing the message signal bandwidth d. reconstructing the message signals 18. What is the function of the SAMPLE HOLD circuits in a PAM-TDM circuit? a. interleave message signals b. sample the synchronization time slot c. hold the timing clock d. demultiplex message signals 19. What parameter of a PPM signal varies in direct proportion to the message signal amplitude? a. the average frequency of the PPM pulses b. the distance between the PPM pulses c. the amplitude of the PPM pulses d. the width of the PPM pulses 20. What is the function of the prefilter in a PTM modulation circuit? a. completely removes frequencies greater than 8 kHz b. completely removes the PTM signal's first replica frequencies c. filters the message signal d. partially reconstructs and amplifies the message signal 21. What PWM parameter varies directly with the message signal's amplitude? a. amplitude b. frequency c. pulse width d. pulse position 22. What PPM parameter varies directly with the message signal's amplitude? a. amplitude b. frequency c. pulse position d. pulse width 23. What advantage does a PPM signal have over a PWM signal? a. can be used for message signals greater than 5kHz b. requires lower sampling frequency c. easier to demodulate d. requires less transmission power 24. What circuit demodulates a PTM signal? a. adder and comparator b. limiter c. low-pass filter d. ramp generator and samplehold 25. Why does PTM require a higher sampling frequency than PAM? a. The amplitude of PTM signals is constant. b. There are more sidebands in the first replica of a PTM signal than in a PAM signal. c. A samplehold circuit requires a higher sampling frequency. d. There are fewer sidebands in the first replica of a PTM signal than in a PAM signal. 26. Why does PPM signal demodulation require two stages (prefilter and filter) of filtering? a. The power of a PPM signal is low. b. The pulses in a PPM signal change position. c. A PPM signal contains high-frequency sidebands that must be removed. d. The frequency of PPM pulses is high. 27. How is PCM different from PAM, PWM, and PPM? a. In PCM, the pulse amplitude varies with the message signal's amplitude. b. In PCM, the pulse width varies with the message signal's amplitude. c. In PCM, the binary code represents the amplitude sample of the message signal. d. In PCM, the pulse position varies with the message signal's amplitude. 28. What device converts analog signals to digital codes for transmission and converts digitalcodes that are received to analog signals? a. comparator b. filter c. register d. CODEC 29. To improve the overall signal-to-noise ratio, a CODEC uses what process? a. companding b. quantization c. sampling d. ADC and DAC 30. What process is used to carry many digital communications channels on the sametransmission line? a. PCM b. TDM c. AMd. FM 31. When PCM signals are time-division multiplexed, what is the period of time called for onePCM channel? a. frame b. multiplexed channel c. clock pulse d. time slot 32. What type of modulation converts a message signal sample to an 8-bit code? a. TDM b. PPM c. PCM d. PTM 33. In PCM, what does the quantization process accomplish? a. The overall signal-to-noise ratio is improved. b. An amplitude sample is converted to one of 256 quantum values. c. The message signal's frequency is limited. d. A higher digital transmission frequency can be used. 34. In PCM, what does companding accomplish? a. A higher digital transmission frequency can be used. b. An amplitude sample is converted to one of 256 quantum values. c. The message signal's frequency is limited. d. The overall signal-to-noise ratio is improve 35. What is a group of repeating time slots called? a. channel b. frame c. multiplexed group d. full duplex transmission 36. How does a DM signal indicate an increase or decrease in the message signal's amplitude? a. with a 1-bit code b. with a series of logic 1s c. with a 2-bit code d. with a series of logic 0s 37. What causes slope overload? a. The low-pass filter's cutoff is too high. b. The message signal's slope is less than the slope of the integrated signal. c. The message signal slope is greater than the slope of the integrated signal. d. The quantization voltage is too small. 38. Delta modulation (DM) encodes what parameter of the message signal? a. amplitude b. amplitude increase or decrease c. frequency change d. frequency and phase change 39. DM uses how many bit(s) to encode a message signal? a. 8 b. 4 c. 1 d. 0 40. A digital sampler that outputs a DM signal contains what components? a. comparator and D-type flip flop b. samplehold and limiter c. integrator and filter d. ramp generator and adder 41. What does a continuously variable slope delta (CVSD) modulation system change to reduce errors in the recovered message signal? a. sampling rate b. clock signal c. feedback integrator's reference voltage d. slope of the integrator's signal 42. Limiting a channel's bandwidth a. decreases the rise and fall times of a pulse. b. limits how rapidly a signal can change. c. increases the range of frequencies that can be transmitted. d. all of the above 43. For a pulse to retain most of its amplitude, its a. rise time must be greater than its pulse width. b. period must be less than the rise time. c. period must be twice the pulse width. d. pulse width must be greater than its rise time. 44. To increase the message capacity of a channel its a. bandwidth must be increased. b. bandwidth must be decreased. c. ringing must be increased. d. passband must be narrowed. 45. Which of the following can increase distortion in the recovered message signal? a. Increasing the receiver bandwidth. b. Increasing signal-to-noise ratio. c. Increasing signal amplitude. d. all of the above SNR(dB) = 20 x log(VsVn) 46. When calculating the signal-to-noise ratio, Vs and Vnare a. root-mean-square voltages. b. peak voltages. c. peak-to-peak voltages. d. the peak voltage times 0.707. 47. When channel bandwidth is increased: a. the noise power decreases. b. the rise times increase. c. the fall times increase. d. the message capacity increases. 48. Why do transmitters often shape or filter pulses? a. To increase the signal bandwidth. b. To increase the pulse amplitudes. c. To increase rise times. d. To reduce ringing. 49. What will minimize the effect of the channel's noise? a. Increasing the receiver's bandwidth. b. Increasing the pulse amplitudes. c. Increasing the signal-to-noise ratio. d. Decreasing the signal power. 50. Why is PCM preferable to PAM transmission? a. PAM reconstruction requires a filter. b. PAM cannot be used for analog messages. c. PCM requires less bandwidth. d. The digital PCM signals are less susceptible to noise.