* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Final Exam Review - Hicksville Public Schools / Homepage
Survey
Document related concepts
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Lake ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Coevolution wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
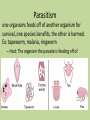
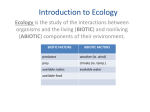
Final Exam Review Unit 3- Ecology Environment Every living and nonliving thing that surrounds an organism Biotic Factors • Living Factors • ex: plants, prey, predators, bacteria, fungus Abiotic Factors • Nonliving Factors • ex: water, temperature, sunlight, soil, Population A group of one species living in an area Community All of the different populations living in an area Ecosystem All of the living and nonliving things and how they interact in an area Biome Group of ecosystems that have the same climate and community Habitat Where an organism lives Trophic Levels Autotrophs Organisms that produce their own food for energy, photosynthesis Ex: Producers: make their own food, through the process of photosynthesis, ex: plants, algae Heterotrophs Organisms that cannot produce their own food for energy Consumers: Organisms that eat/consume other organisms • • • • • Herbivore Carnivore Omnivore Scavenger Decomposer Herbivore eats plants, primary consumers, ex: deer, cow Carnivore eats meat/other consumers, ex: lion, tiger Omnivore eats both plants and animals, ex: humans, raccoons, bears Scavenger eats dead animals, ex: vultures Decomposer breaks down dead matter and recycles the nutrients back to the soil, ex: fungus, bacteria Food Chain shows the flow of energy in an ecosystem, simple Food Web • many food chains interconnected • complex Ecological Pyramids • • • • Energy Biomass Numbers decreases as you move up the pyramid, • producers are always the largest and on the bottom. Biological Magnification • The concentration of a toxin increases as is moves through the food chain, highest concentrations at the top of the food chain, ex: • DDT in bald eagles Biodiversity The number of different species in an area, more biodiversity=more stable Niche an organisms role/job in its environment, two species cannot occupy the same niche Competitive Exclusion When two organisms try to occupy the same niche, they will compete. One will stay in that niche and the other will either die or have to occupy a different niche Fundamental Niche The niche a species can ideally have, can be larger than the realized niche Realized Niche The niche a species actually occupies, can be smaller than the fundamental niche Niche Diversity the number of different niches in an ecosystem due to abiotic factors • fluctuating abiotic factors many niches (desert) • constant abiotic factors=few niches (marsh) Evolution a slow gradual change in a species over time Adaptation A trait that an organism has that allows it to survive in a changing environment Specialized species Generalized species • A species with a small niche, only one food source. • Ex: koala bear and panda bear • A species with a large niche, many food sources. • Ex: mice, roaches Convergent evolution two species evolve separately to have similar traits because they have similar niches. Coevolution • When two species evolve to rely on each other for survival, mutualism • ex: acacia tree and stinging ants Predator-Prey predator- the hunter prey-the hunted Parasitism one organisms feeds off of another organism for survival, one species benefits, the other is harmed. Ex: tapeworm, malaria, ringworm – Host: The organism the parasite is feeding off of Mutualism • two species rely on each other for survival, both benefit • ex: Egyptian Plover and Nile Croccodile Commensalism One species benefits, the other isn’t harmed or helped, ex: barnacles on a whale Invasive Species A non-native species that causes harm to the environment • Why are they dangerous? – They outcompete with native species for essential resources • How do they get here? – Accidental (in wood), boats (mass transportation), intentional release (pets that get too big), tropical plants for garden Endangered Species A species that is close to extinction Main reason for species endangerment? • Habitat destruction