* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download spelling
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
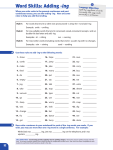
Tips to help you become a better speller 1 Introduction Spelling can be complex. For example, there are eleven different ways of representing the sh sound: shoe, sugar, ocean, issue, nation, schist, suspicion, conscious, nauseous, mansion, and fuchsia. 2 Remember that the regularity in spelling relates not only to sound-letter connections but also to our stored visual memory of related words. We know that president is not spelled « presadent, » because we recognize its relation to the word preside. 3 Paying attention to guidelines of spelling can help you avoid spelling errors. 4 20 Most Commonly Misspelled Words A study revealed the following twenty words as being the most common misspelled words. Compare them to words you have trouble spelling correctly. 1. 3. 5. 7. 9. 11. 13. 15. 17. 19. their/there/they’re a lot receive/d/s you’re/your develop/s than/then occurred cannot success until 2. 4. 6. 8. 10. 12. 14. 16. 18. 20. too/to noticeable lose an/and definitely believe/d/s affect/s separate through where 5 Recognizing Homonyms Definition: Words that sound alike but have different spelling and meaning. their (possessive form of they) there (in that place) they’re ( contraction of they are) to (in the direction of) too (in addition; excessive) two (number between one and three) 6 Homonyns (continued) your (possessive form of you) you’re (contraction of you are) affect (to have an influence) effect (noun: result, verb: to cause to happen) accept (to take or receive) except (to leave out) who’s (contraction of who is or who has) whose (possessive form of who) its (possessive form of it) it’s (contraction of it is or it has) 7 Spelling Rules i before e except after c or when pronounced « ay » as in neighbor or weigh or in weird exceptions like either i BEFORE e achieve believe brief chief experience friend field piece relieve thief EXCEPT AFTER c ceiling conceive deceive receive perceive 8 OR WHEN PRONOUNCED « AY » neighbor freight weigh reign eighth sleigh OR IN WEIRD EXCEPTIONS weird either neither leisure seize foreign height caffeine protein 9 Adding Prefixes Prefixes-letters placed at the beginning of words to add to or qualify their meaning. The prefix re-, for example, adds repetition to the meaning of a word: reappear means« appear again. » Prefixes do not change the spelling of the words they are added to, even when the last letter of the prefix and the first letter of the word it is added to are the same. In such cases, keep both letters. Example next page . . . 10 dis + service = disservice over + rate = overrate *Some prefixes require the use of hyphens. When in doubt, check the dictionary. . 11 Adding Suffixes Suffixes – letters placed at the end of words in to form related words. For example, we can build on basic word short to get the following words: shortage shorten shortly shortness shorter 12 Dropping the final e For words ending in an unpronounced e (receive, lose, definite), you must decide whether or not to drop the e when adding a suffix. In general, if the suffix starts with a vowel, drop the e. explore + -ation=exploration imagine + -able=imaginable continue + -ous=continuous future + -ism futurism exercise + ing= exercising productive + ity productivity 13 Exceptions •To distinguish homonyms or potentially confusing words dye + -ing = dyeing (not dying) singe + -ing = singeing (not singing) •To clarify pronunciation be + -ing = being (not bing) shoe + -ing = shoeing (not shoing) 14 More exceptions . . . To keep the sound of C or G soft notice + -able = noticeable marriage + -able = marriageable salvage + -able = salvagable courage + -ous = courageous peace + -able = peaceable 15 Keeping the final e If the suffix starts starts with a consonant, keep the e. force + -ful = forceful excite + -ment = excitement state + -ly = stately same + - ness = sameness Exceptions argue + -ment = argument true + -ly = truly whole + -ly – wholly nine + -th = ninth 16 Exercise Combine each of the following words and suffixes, dropping the unpronounced e when necessary. 1. future + -ism 2. hope + -ful 3. lone + -ly 4. malice + -ous 5. outrage + -ous 6. exercise + -ing 17 Using –ally Using –ally Use –ally if the base word ends in ic. Examples: drastic + -ally = drastically basic + -ally = basically, characteristic + -ally = characteristically, dramatic + -ally = dramatically **Exception: public + -ly = publicly Using –ly Use –ly if the base word does not end in ic. Examples: apparent + -ly = apparently conscious + -ly = consciously supposed + -ly = supposedly certain + -ly = certainly quick + -ly = quickly 18 Doubling the final consonant When a word ends in a consonant, the consonant is sometimes doubled when a suffix is added. If the word ends in consonant-vowel-consonant, the suffix begins with a vowel, and the word contains only one syllable or ends in an accented syllable, double the final consonant. stop + -ing = stopping hot + -est = hottest begin + -ing = beginning occur + -ence = occurence slap + -ed = slapped run + -er = runner refer + -ing = referring 19 EXCEPTION Double the final l even in words that do not end in an accented syllable. counsel + -or = counsellor travel + -ed = travelled label + -ing = labelling 20 DO NOT DOUBLE THE CONSONANT If it is preceded by more than one vowel or by another consonant bait + -ing = baiting fight + -er = fighter sleep + -ing = sleeping start + -ed = started If the suffix begins with a consonant ship + -ment = shipment fit + -ness = fitness If the word is not accented on the last syllable benefit + -ing = benefiting fasten + -er = fastener 21 If the accent shifts from the last to the first syllable when the suffix is added. infer + -ence = inference prefer + -ence = preference **If the last letter of the word and the first letter of the suffix are the same, keep both letters: mortal+ -ly = mortally room + -mate =roommate rotten + -ness = rottenness usual + -ly = usually 22