* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Infection Control measures of Leprosy
Survey
Document related concepts
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Common cold wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
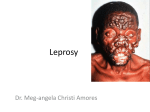
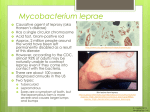
Infection Control measures of Leprosy Period of communicability Leprosy is not usually infectious after three months of continuous treatment with dapsone or clofazimine, or after two to three weeks of treatment with rifampicin. Control measures Preventive measures BCG vaccination has some protective efficacy and is recommended for neonates born to a person diagnosed with leprosy. Control of case Isolation of tuberculoid cases is unnecessary. Isolation of lepromatous cases is indicated until treatment is initiated, particularly if nasal smears are positive. Nasal discharges of infectious patients should be disinfected or disposed of as infectious waste. Rifampicin is the key to early control of disease and rapid elimination of the risk of further transmission of infection to contacts. Control of contacts Investigation of contacts (annual examinations for five years after last contact with the infected person) and early detection and treatment of new cases is required. Prophylactic BCG has resulted in a considerable reduction in the incidence of tuberculoid leprosy among contacts in some trials. Using a single dose of rifampicin as prophylaxis following leprosy exposure. Head of microbiology diagnostic infection control unit Prof. Mohammad Abou-El-Ela Done by Doaa Tawfik Masallat