* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Internal Resistance
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
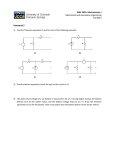
Internal Resistance Thus far we have referred to a battery as a source of voltage and we have made the assumption that the battery _________ battery would be able to is an ideal source. An ideal __________ maintain the same _______________ _____________ potential difference between its terminals regardless of the current drawn. Consider the following diagram: + r VT ε r Internal resistance of the real battery ε emf of the battery VT Terminal voltage of the battery (the actual voltage applied to the external circuit) Which value is larger ε or VT? Why emf is larger because VT is the voltage put out by the battery after some of the emf has been ‘lost’ to the internal resistance Derive an expression that relates ε and VT (assume a current flows through the internal resistance) ε = VT + Ir Would the value of the resistance connected across the terminals of the battery effect the emf of the battery? Explain. No; emf is determined by the electrochemical processes within the battery Would the value of the resistance connected across the terminals of the battery effect the terminal voltage of the battery? Explain. Yes; the bigger the resistance across the terminals of the battery, the smaller the current drawn and thus the bigger VT Would the value of the resistance connected across the terminals of the battery effect the internal resistance of the battery? Explain. No; internal resistance is determined by the makeup of the components of the battery Practice Exercise Suppose a battery has an emf of 15.0 V. When a resistance of 2.0 ohms is placed across the battery terminals, 72 Watts is dissipated in the 2 ohm resistor. Determine the internal resistance of the battery. Draw the circuit ε = 15.0 V Given: Since 72 watts is dissipated in the 2Ω resistor, we can easily determine the voltage across this resistor RL = 2Ω PL = 72 watts r ε 2Ω Find this value Real battery 2 2 72 = V V= 12 V 2 terminal _____________ voltage This is also the __________ of the battery. P= V R Use Ohm’s Law to determine the current through the circuit. VT = IT RT 12 = I (2) IT = 6 amps This is also the current flowing through the __________ internal resistance of the battery. _____________ Now that we know the emf, current, and terminal voltage, we can solve for the internal resistance of the battery. ε = VT + Ir 15 = 12 + (6)r r = 0.5Ω Now solve for the power dissipated in the battery. P = IV P = (6)(3) = 18 watts Current through internal resistance. Voltage across internal resistance.