* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Wavelength
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
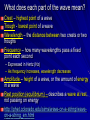
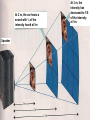
Parts of a Wave Frequency = 2 waves per second Crest Wavelength Normal Rest Position Trough Wavelength What does each part of the wave mean? Crest – highest point of a wave Trough - lowest point of a wave Wavelength – the distance between two crests or two troughs Frequency – how many wavelengths pass a fixed point each second – Expressed in Hertz (Hz) – As frequency increases, wavelength decreases Amplitude – height of a wave, or the amount of energy in a wave Rest position (equilibrium) – describes a wave at rest, not passing on energy http://phet.colorado.edu/sims/wave-on-a-string/waveon-a-string_en.html Properties of Sound Loudness is an important property of sound Loudness refers to your perception of the energy of a sound Loudness of a sound depends on two factors: – The amount of energy it takes to make the sound – The distance from the source of the sound In general, the greater the energy used to make a sound, the louder the sound Ex: the harder you pluck the strings of a guitar, the louder the sound Intensity The more energy used to pluck the string, the greater the amplitude of the wave, and the more intense the sound Recall that amplitude is the height of a wave; and the amount of energy in a wave Intensity is the amount of energy in a sound, or loudness – As amplitude increases, intensity increases – As amplitude decreases, intensity decreases Loudness in Decibels (db) The loudness of different sounds is compared using a unit called the decibel (db) The greater the intensity of a sound, the higher the decibels (db The loudness of a sound you can barely hear is about 10 db Each 10-db increase in loudness represents a tenfold increase in the intensity of the sound For example, soft music at 30 db sounds ten times louder than a 20-db whisper The 30-db music is 100 times louder than the 10-db sound of rustling leaves Sounds louder than 100 db can cause damage to your ears, especially if you listen to those sounds for long periods of time 120 db is the loudness level that can actually cause pain to your ears Intensity vs. Distance from the Source Because sound waves spread out in all directions, intensity decreases as the distance between you an the source increases A sound wave of greater intensity sounds louder As you move away from the source, loudness decreases because the intensity decreases 3 m, the At 2 m, the ear hears a sound with ¼At of the intensity has decreased to 1/9 intensity At 2 m, the ear hears a heard at 1m of the intensity sound with ¼ of the at 1m. At 3m, the intensity has decreased to 1/9 intensity heard at 1m. of the intensity at 1m Speaker