* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hardy Weinberg Principle (equilibrium)
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
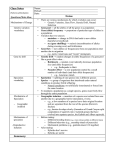
Allele frequencies will remain constant unless one If there is no change, there is no evolving. or more factors cause the frequencies to change. Natural selection acts on the range of phenotypes in a population. Evolution occurs as a population’s genes and their frequencies change over time. All of the alleles of a population’s genes together make up a gene pool. Allele frequency - % of any specific allele in the gene pool. Genetic equilibrium – a population in which the frequency of alleles remains the same over generations. Mutations are one cause of genetic change. Lethal mutations disappear quickly, but mutations that cause a useful variation become part of the gene pool Genetic drift – the alteration of allele frequencies by chance events. Gene flow – transport of genes into or out of a population by migrating individuals. Genetic drift, gene flow, and mutations can greatly affect small populations. Natural selection is usually the most significant cause of changes in any gene pool. Some variations increase or decrease an organism’s chance of survival in an environment. Variations are controlled by alleles. Allelic frequencies in a gene pool will change due to natural selection of variations. If conditions are not met the genetic equilibrium is disrupted – *population evolves and changes* If conditions are met the genetic equilibrium stays the same– *population does not evolve* Genotype proportions remain constant – calculated from allele frequencies P+Q = 1 or 100 percent (allele frequencies) P2 + 2PQ + Q2 = 1 or 100 percent (genotype frequencies) P = frequency of the dominant allele in the population Q = frequency of the recessive allele in the population P2 = percentage of homozygous dominant individuals Q2 = percentage of homozygous recessive individuals 2PQ = percentage of heterozygous individuals If 98 out of 200 individuals in a population express the recessive phenotype, what percent of the population are homozygous dominant?