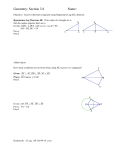
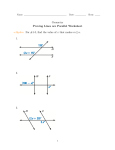
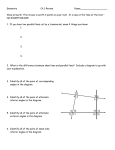
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MCA-I Semester Regular Examinations, 2013
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
MCA-I Semester Regular Examinations, 2013-2014 Probability and statistical Applications Unit – I PROBABILITY THEORY 1(a) Find the probability that in a random arrangement of the letters of the word “ASSASSINATION”, THE FOUR S’s come consequently. (b) A box of 100 gaskets contains 10 gaskets with type A defects, 5 gaskets with type B defects and 2 gaskets with both types of defects. Find the probability that (i) a gasket to be drawn has a type B defects under the condition that it has type A defect. (ii) a gasket to be drawn has no type B defect under the condition that it has no type A defect. [6+6] (OR) (c ) State and prove Baye’s theorem. (d) In a railway reservation office , two clerks are engaged in checking reservation forms on an average, the first clerk checks 55% of the forms, while the second does the remaining. The first clerk has an error rate of 0.03 and second has an error rate of 0.02. A reservation form is selected at random from the total number of forms checked during a day and is found to have an error. Find the probability that it was checked (i) by the first (ii) by second clerk. [6+6] 2(a) Define terms Probability, Event and state and prove addition theorem of probability for “N” events. (b) Three groups of children contain respectively 3 girls, 1 boy; 2 girls, 2 boys ; and 1 girl, 3 boys; one child is selected at random from each group. Find the probability that the 3 selected consist of 1 girl and 2 boys. [6+6] (OR) (c ) State and prove Boole’s theorem of probability. (d) A machine part is produced by three factories A, B and C. Their proportional production is 25, 35 and 40% respectively. Also the % defectives manufactured by three factories are 5, 4 and 3 respectively. A part is taken at random and is found to be defective. The probability that selected part belongs to factory B is. [6+6] 3(a) In a referendum submitted to the students body at a university, 850 men and 566 women voted. 530 of the men and 304 of the women voted YES. Does this indicate a significance difference of opinion on the material at 1% level, between men and women students? (b) In a city 60% read newspaper A, 40% read newspaper B and 30% read newspaper C, 20 % read A and B, 30% read A and C, 10% read B and C. Also 15% read papers A, B and C. The % of people who don’t read any of these newspapers is. [6+6] (OR) (c) Define axioms of probability, sample space, sample points and state and prove two simple theorems of probability. (d) A sample of 400 individuals is found to have a mean height of 67.47 inches. Can it be reasonably regarded as a sample from a large population with mean height of 67.39 inches and standard deviation 1.30 inches. Also obtain the 95% confidence limits for the population mean height. [6+6] 4(a) Define the terms experiment, trial, and event and mention types of events. Prove that Probability of the Impossible even is zero and If A B the P(A) P(B). (b) Mr X is selected for interview for 3 posts. For the first post there are 5 persons, for the second post there are 4, for third there are 6. If the selection of each candidate is equally likely find the probability that Mr X will be selected for at least one post? [6+6] (OR) (c) Define Probability, event and state the axioms of probability. Prove that (i) If A is an event in the finite sample space S, then P(A) equals the sum of the probabilities of the individuals outcomes comprising A. (ii) If A B= then show that P(A) P(B). (d) Define the terms exclusive event, exhaustive event, independent event and mutually exclusive event by giving an example. Prove that If B A then P(A B) = P(A) – P(B). [6+6] 5(a) Define mathematical definition of Probability. State and prove the addition theorem of probability for two and three events. (b) Three machines A,B,C with capacities proportional to 2 : 3 : 4 are producing bullets. The probabilities that the machines produce defectives are 0.1, 0.2 and 0.1 respectively. A bullet is taken from a day’s production and found to be defective. What is the probability that it came from (i) Machine A and (ii) Machine C. [6+6] (OR) ( c) Define conditional probability and conditions for mutual independence of “n” events. State and prove General Multiplication Theorem. ( d) Suppose that one of three men, a politician, a businessman, an educator will be appointed as the Chancellor of a university. The respective probabilities of their appointments are 0.50, 0.30, 0.20. The Probabilities that research activities will be promoted by these people if they are appointed are 0.30, 0.70, 0.80 respectively. What is the probability that the research will be promoted by the new Chancellor. [6+6]