* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Trigonometric Functions of Acute Angles
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
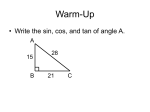
Trigonometry Unit 2 Note Packet Name____________________Hr___ Trigonometric Functions of Acute Angles EXAMPLE 1: Fill in the blanks with . Special Right Triangles 30°- 60°- 90° Triangle 2 45°- 45°- 90° Triangle 1 45° 45° √3 θ (Degrees) sin θ cos θ tan θ csc θ 30° 45° 60° Special Right Triangle Practice sec θ cot θ Trigonometry Unit 2 Note Packet EXAMPLE 2: Let ABC be a right triangle with side lengths a, b, c. Find the values of the six trigonometric functions for angle B. a) b) Trig Functions of Non-Acute Angles Reference Angles: The ______________ acute angle made by the terminal side of the angle and the _____________. EXAMPLE 1: Find the reference angle: a) 135° b) 370° c) -120° EXAMPLE 2: Find the six values of the trigonometric functions for 210°. d) -35° Trigonometry Unit 2 Note Packet EXAMPLE 3: Find the exact value of each expression. a) b) c) Evaluating Trig function values EXAMPLE 4 (WORKING BACKWARD): Find all values of θ between [0°, 360°). a) sin 3 2 b) cos 1 2 c) cot 1 Finding Trigonometric Function Values Using a Calculator EXAMPLE 1: Approximate the following values. a) b) c) d) e) f) Trigonometry Unit 2 Note Packet EXAMPLE 2 (WORKING BACKWARD): Find the acute angle that satisfies the condition. a) b) c) d) e) f) Solving Right Triangles EXAMPLE 1: Solve the right triangle using the Pythagoream Thm and trig ratios: cm EXAMPLE 2: Find all unknown values: Trigonometry Unit 2 Note Packet The Skateboarding Triangle (Round answers to the nearest tenth of a foot if needed.) Herman has taken up the sport of skateboarding and has built a ramp in his driveway. The triangular ramp reaches a maximum height of three feet over a horizontal distance of six feet. 1. Label the diagram below showing the maximum height and horizontal length of 2. Find the length of the skateboarding surface of Herman's ramp. the ramp. 3. Find the angle of inclination of the ramp. 4. If Herman builds another ramp and increases the angle of inclination by 5º but keeps the maximum height at three feet, will the length of the skateboarding surface increase or decrease? Find the amount of increase or decrease in this length. Trigonometry Unit 2 Note Packet 5. After watching Herman fall several times, his father tells him that he must make the original ramp safer. His father suggests that he either decrease the height of the original ramp by one foot, or increase the horizontal distance of the original ramp by two feet. a) State the angle of inclination of each of these new ramps. Which ramp has the smallest angle of inclination? b) State the length of each skateboarding surface of these new ramps. Which ramp has the least change in the length of the skateboarding surface when compared to Herman’s original ramp? c) Which ramp do you think Herman will prefer to build and why? Trigonometry Unit 2 Note Packet Applications Example 1: An airplane is flying 10, 500 ft above the level ground. The angle of depression from the plane to the base of a tree is 13°50’. How far horizontally must the plane fly to be directly over the tree? When a vehicle travels uphill or downhill, it experiences a force due to __________. This is called grade resistance and is modeled by the equation ____________________, where θ is the grade and W is the weight of the vehicle. Uphill: Downhill: Example 3: Calculate F for a 2500-lb car traveling an uphill grade with Bearing and Navigation Bearing: measured in a clockwise direction from due ______________ Illustrations- . Trigonometry Unit 2 Note Packet Example 1: Radar stations A and B are located on an east-west line, 3.7 km apart. Station A detects a plane at C, on a bearing of 61°. Station B simultaneously detects the same plane, on a bearing of 331°. Find the distance from A to C. Example 2: The bearing from A to C is S 52° E. The bearing from A to B is N 84° E. The bearing from B to C is S 38° W. A plane flying at 250 mph takes 2.4 hr to go from A to B. Find the distance from A to C. Trigonometry Unit 2 Note Packet PRACTICE (NO Calculators): Draw a picture and find the unknown side length using the Pythagorean Theorem. Then find the values of the six trigonometric functions for angle B. 1. Fill in the blanks with 2. . 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Give the exact value for each expression: 9. 10. 11. 12. Find the exact values of the following trig functions. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. Trigonometry Unit 2 Note Packet Find all values of θ between [0°, 360°) that has the following function values. 20. 19. √ 21. √ Use a calculator to find a decimal approximation for each value. Round to the nearest thousandth. 22. 23. 25. 26. 24. 27. 1 sec14.8 PRACTICE (Calculators ALLOWED): Use a calculator to decide whether each statement is TRUE or FALSE. 28. 29. 30. 31. Calculate F for a 5000-lb truck traveling a downhill grade with 32. What is the grade resistance of a 3600-lb car traveling on a uphill grade? Trigonometry Unit 2 Note Packet Solve the unknown parts of the right triangles. 33. 35. yd, cm 34. yd 36. in 37. Can a right triangle be solved with the following given information? Explain. a. Two acute angles and no side lengths b. One side and one acute angle c. Two side lengths and no angles 38. The length of the base of an isosceles triangle is 42.26 in. Each base angle is 38.12°. Find the length of each of the two equal sides of the triangle. Trigonometry Unit 2 Note Packet 39. You are at the hospital recovering from an injury due to a math-induced explosion. (You tried to divide by zero.) You look out the window from your hospital room and see Bill Snyder Family Stadium. You are 100 ft above the ground and you notice that the angle of elevation to the top of the stadium across the street is 50° and the angle of depression to the base of the stadium is 20°. Find the height of the stadium. 50° 20° 30ft BILL SNYDER FAMILY STADIUM 40. Suppose you are walking on a warm summer day. The angle of elevation of the sun is 23.4° and you are 5.75 feet tall. How long is your shadow at this time of day? 41. Find the distance across the lake if RT 53.1 meters, S R T and . Trigonometry Unit 2 Note Packet 42. Go to the website: http://www.proprofs.com/quiz-school/story.php?title=trigonometry-bearings_1 Answer questions 1, 2, 3, 5, 7 1) 2) 3) 5) 7) 43. A plane flies 1.3 hours at 110 mph on a bearing of 40°. Then it turns and flies 1.5 hours at the same speed on a bearing of 130°. How far is the plane from its staring point? EXPANSION: 44. Think about it: What angle does the line 45. Let a) tan 2 √ make with the positive x-axis? . Find the exact values: b) (cos )2 c) sin 2 d) 2sin 46. Find the coordinates of P on the circumference of the circle. 225° P . 10 Trigonometry Unit 2 Note Packet 47. If aerodynamic resistance is ignored, the braking distance D (in feet) for an automobile to change its velocity from V1 to V2 (in ft/sec) can be modeled by the equation: D 1.05(V12 V2 2 ) 64.4( K1 K 2 sin ) K1 is a constant determined by the efficiency of the brakes and tires, K 2 is a constant determined by the rolling resistance of the automobile, and θ is the grade of the highway. a) Compute the number of feet required to slow a car from 55mph (81 ft/sec) to 30 mph (44ft/sec) while traveling uphill with a grade of . Let K1 0.4 and K 2 0.02 . (Be sure to change mph to ft/sec.) b) How is braking distance affected by grade θ ? Does this agree with your driving experience? 48. Solve the right triangle: Trigonometry Unit 2 Note Packet Names: ___________________ Hr ___ Partner Activity: Choose one topic from the first column and two concepts from the second column. Use these ideas to compose a real life problem and solve this application. Topics Basketball MHS Topography Construction Weather Concepts Sine Cosine Tangent Angle of Elevation/Depression Pythagorean Theorem Trigonometry Unit 2 Note Packet Unit 2 Wrap-Up Know Special Right Triangles (NO Calculators!) Examples: Find the exact values of all six trig. functions for an angle of 480°. Find the reference angle and the exact value of the trigonometric function: Be able to work backward to find the angle θ given a trig ratio: cos 1 2 csc 2 sin 1 Be able use a calculator to find decimal approximations for non-special angles. Example: Be able to work backward to find the angle given a trig value: Find the missing pieces of right triangles using trig relationships. Examples: B 68.5142° 3579.42 m a C b A Trigonometry Unit 2 Note Packet To find the distance (RS) across a lake, a surveyor lays out and angle , with angle . Find length RS. S R T Use angles of elevation and depression to solve right triangles. Example: The angle of depression of a television tower to a point on the ground 36 meters from the bottom of the tower is 29.5°. Find the height of the tower. Use bearing to solve right triangles. Example: Two ships leave a port at the same time. The first ship sails on a bearing of 40° at 18 knots (nautical miles per hour) and the second at a bearing of 130° at 26 knots. How far apart are they after 1.5 hours?