* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Determination of Proteins
Structural alignment wikipedia , lookup
Implicit solvation wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation wikipedia , lookup
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
Alpha helix wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
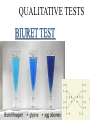
PROTEINS السالم عليكم ورحمة هللا وبركاته OBJECTIVES • Master how to determine the conc. of protein in serum/plasma. • Important of protein estimation in health and various diseases. • Understand the principles behind protein estimation. Introduction Proteins are polymers of amino acids linked covalently through peptide bonds. Proteins are large molecules and can be split into smaller units by hydrolysis-amino acids. Proteins: Classification Depending upon their solubility and physical properties , proteins are divided into three classes. 1- Simple proteins: Simple proteins are those which contain only amino acids. e.g. albumin and globulin 2- Conjugated proteins: Conjugated proteins are those which contain a non amino acid component in addition to the amino acids. e.g. lipoprotein , phosphoproteins etc. 3- Derived proteins: Derived from simple proteins (denaturation) e.g. peptones. Element Components of Proteins • Major elements C, H, O, N, S. • Trace elements P, Fe, Cu, Zn, I, … Properties of Proteins • Molecular weights range from 10000-several hundred thousand •Generally proteins are soluble in water, except the membrane proteins which are hydrophobic •Absorption maxima in the ultraviolet region •Proteins are charged molecules, but the charge depend on the pH of the buffer. •Move under an electric field and can be separated by electrophoresis Functions of Proteins 1. Proteins build new tissues of the body. 2. They maintain and replace damaged tissues. 3. They carry out regulating activities as enzymes and hormones. 4. They are protective as antibodies. 5. They help in other activities such as movement of skeletal muscles, transport of oxygen, pigmentation of skin etc. QUALITATIVE TESTS XANTHOPROTEIC TEST MILLONS TEST NINHYDRIN TEST METHODS OF PROTEIN ESTIMATION Biuret method Bradford method Folin- Lowry method Kjeldahl method Bicinchoninic method UV method Flourimetric method