* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 5 Similarity and Triangles
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
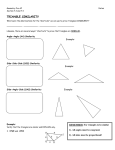
Geometry Unit 5: Similarity and Right Triangle Similarity Enduring understanding (Big Idea): Students will be able to apply their previous knowledge of transformations to determine similarity. They will focus on proving and using the AA similarity theorem and will apply all information to solve problems, which include finding angle measures and side lengths. Essential Questions: 1. How can you determine whether two figures are similar using similarity transformations, angle measures, and side lengths? 2. What is the AA Similarity theorem and why does it sufficiently determine whether two triangles are similar or not? 3. How can you prove that a line parallel to one side of a triangle divides the other two sides proportionally? How can this information be used to solve problems? Please note that the following objective is covered in 8th grade. 8.G.4 – Understand that a two-dimensional figure is similar to another if the second can be obtained from the first by a sequence of rotations, reflections, translations, and dilations; given two similar two-dimensional figures, describe a sequence that exhibits the similarity between them 8.G.5 – Use informal arguments to establish the … angle-angle criterion for similarity of triangles BY THE END OF THIS UNIT: Students will know… Students will be able to… AA Similarity Theorem A line parallel to one side of a triangle divides the other two proportionally, and conversely Vocabulary: Similarity, similar triangles, AA Similarity theorem, transformation, corresponding angles, corresponding sides (corresponding parts), proportion Unit Resources Learning Task: 1. 7.2 Think About a Plan; 2. 7.3 Think About a Plan *Both located at www.pearsonsuccessnet.com * Performance Task: Ch 7 Performance Tasks: Mathematical Practices in Focus: www.pearsonsuccessnet.com Project: Visit link below. Note: This project will need to be edited and personalized before implementation. Prove the AA Similarity Theorem Determine whether two figures and/or triangles are similar using similarity transformations Apply knowledge of similar triangles to solve problems, which include setting up proportions, and finding angle measures & side lengths. 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively 3. Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others 6. Attend to precision https://vasicek.wikispaces.com/file/view/The+Similar+Triangles+Project.pdf Standards on successive pages were unpacked by Utah State Office of Education, CMS-district specific modifications and resources for this unit were created by CMS teacher leaders. Standards are listed in alphabetical /numerical order not suggested teaching order. PLC’s must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes. Geometry Unit 5: Similarity and Right Triangle Similarity CORE CONTENT Cluster Title: Understand similarity in terms of similarity transformations Standard: G-SRT.2 – Given two figures, use the definition of similarity in terms of similarity transformations to decide if they are similar; explain using similarity transformations the meaning of similarity for triangles as the equality of all corresponding pairs of angles and the proportionality of all corresponding pairs of sides. Concepts and Skills to Master Determine if two figures are similar using properties of transformations Determine if two triangles are similar, given their angle measures and side lengths Given angle measures and side lengths, determine if two triangles are similar SUPPORTS FOR TEACHERS Critical Background Knowledge 8.G.4 – Understand similarity as a sequence of transformations Knowledge of the different types of transformations (rotations, reflections, translations, and dilations). Academic Vocabulary Similarity, Transformation, Congruence, Corresponding Parts Suggested Instructional Strategies Resources 1. Textbook Correlation: Give students pairs of triangles, some of which are similar o 7.2 Similar Polygons and some of which are not. Have students verify or disprove similarity using transformations and the definition of similarity. Use geometry software and patty paper to explore properties of similarity. Sample Formative Assessment Tasks Skill-based task Problem Task 1. Jan uses an overhead projector to enlarge a picture 5 in. high 1. http://illustrativemathematics.org/illustrations/603 – “Are and 7 in. wide. She projects the picture on a blackboard 4 ft they similar” activity 2 in. high and 12 ft wide. What are the dimensions of the 2. Under what conditions do two lines intersected by two largest picture that can be projected on the blackboard? transversals form similar triangles? Standards on successive pages were unpacked by Utah State Office of Education, CMS-district specific modifications and resources for this unit were created by CMS teacher leaders. Standards are listed in alphabetical /numerical order not suggested teaching order. PLC’s must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes. Geometry Unit 5: Similarity and Right Triangle Similarity Teacher Created Argumentation Tasks (W1-MP3&6) Your classmate provides the following solutions to the problems below. In complete sentences, identify and explain the error in each explanation, and tell me how you would help your classmate reach an accurate conclusion. (From www.pearsonsuccessnet.com – Chapter 7: Find the Errors! for sections 7.2-7.3) Standards on successive pages were unpacked by Utah State Office of Education, CMS-district specific modifications and resources for this unit were created by CMS teacher leaders. Standards are listed in alphabetical /numerical order not suggested teaching order. PLC’s must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes. Geometry Unit 5: Similarity and Right Triangle Similarity CORE CONTENT Cluster Title: Understand similarity in terms of similarity transformations Standard: G-SRT.3 – Use the properties of similarity transformations to establish the AA criterion for two triangles to be similar. Concepts and Skills to Master Prove using the properties of similarity transformations that if two angles of one triangle are congruent to two angles of another triangle, the triangles are similar (AA). SUPPORTS FOR TEACHERS Critical Background Knowledge 8.G.4 – Understand similarity as a sequence of transformations 8.G.5 – Use informal arguments to establish facts about the angle sum…of triangles and…the angle-angle criterion for similarity of triangles Knowledge of the different types of transformations (rotations, reflections, translations, and dilations). If two angles of a triangle are congruent to two corresponding angles of a second triangle, then the third pair of corresponding angles must be congruent. Academic Vocabulary Similarity, Transformation, Angle-Angle Similarity Theorem Suggested Instructional Strategies Resources 1. Textbook Correlation Review the Triangle Angle Sum Theorem and angle a. 7.3 Proving Triangles are Similar relationships with parallel lines prior to addressing this 2. Puzzle: Similarity Search standard. a. Located at www.pearsonsuccessnet.com under the “Activities, Games, and Puzzle” link for section 7.3 Standards on successive pages were unpacked by Utah State Office of Education, CMS-district specific modifications and resources for this unit were created by CMS teacher leaders. Standards are listed in alphabetical /numerical order not suggested teaching order. PLC’s must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes. Geometry Unit 5: Similarity and Right Triangle Similarity Sample Formative Assessment Tasks Skill-based task 1. Determine whether the two triangles are similar. Justify your conclusion. Problem Task 1. Given two different-sized triangle cutouts with two corresponding angles congruent, allow the students to show that the third angle is congruent, and find a dilation that produced the two triangles. Teacher Created Argumentation Tasks (W1-MP3&6) 1. Write a proof to justify why the AA similarity theorem guarantees similarity for two triangles. 2. Explain why there is an AA Similarity Postulate, but not an AA Congruence Postulate. Standards on successive pages were unpacked by Utah State Office of Education, CMS-district specific modifications and resources for this unit were created by CMS teacher leaders. Standards are listed in alphabetical /numerical order not suggested teaching order. PLC’s must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes. Geometry Unit 5: Similarity and Right Triangle Similarity CORE CONTENT Cluster Title: Prove theorems involving similarity Standard: G-SRT.4 – Prove theorems about triangles. Theorems include: A line parallel to one side of a triangle divides the other two proportionally, and conversely; the Pythagorean Theorem proved using triangle similarity. Concepts and Skills to Master Prove that if a line intersecting a triangle is parallel to one of the sides, then it divides the other two sides of that triangle proportionally. Prove that if a line divides two sides of a triangle proportionally, then it is parallel to the third side. SUPPORTS FOR TEACHERS Critical Background Knowledge Understand Angle-Angle Similarity Ability to set up and solve proportions Academic Vocabulary Parallel Lines, Similar triangles, Angle-Angle Similarity, Proportion Suggested Instructional Strategies Resources Help students understand that the sides are Textbook Correlation: proportional for any segment parallel to the o 7.3 Proving Triangles are Similar base, not just the midsegment. o 7.4 Similarity in Right Triangles o 7.5 Proportions in Triangles 7.5 Enrichment located at www.pearsonsuccessnet.com Section B: Right Triangles, Altitudes, the Pythagorean Theorem, and You (Located at www.discoveryeducation.com) http://player.discoveryeducation.com/index.cfm?guidAssetId=A42740C77915-4A90-A1CB-DD891170FFF5 Sample Formative Assessment Tasks Standards on successive pages were unpacked by Utah State Office of Education, CMS-district specific modifications and resources for this unit were created by CMS teacher leaders. Standards are listed in alphabetical /numerical order not suggested teaching order. PLC’s must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes. Geometry Unit 5: Similarity and Right Triangle Similarity Skill-based task 1. Is segment SU parallel to segment RV? Explain why or why not. Problem Task 1. Given: T is the midpoint of is the midpoint of RS . Prove: ∆QRS ~ ∆VUT QR , U is the midpoint of QS , and V *This problem found at www.pearsonsuccessnet.com under the Enrichment task for section 7.3* Standards on successive pages were unpacked by Utah State Office of Education, CMS-district specific modifications and resources for this unit were created by CMS teacher leaders. Standards are listed in alphabetical /numerical order not suggested teaching order. PLC’s must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes. Geometry Unit 5: Similarity and Right Triangle Similarity CORE CONTENT Cluster Title: Prove theorems involving similarity Standard: G-SRT.5 – Use congruence and similarity criteria for triangles to solve problems and to prove relationships in geometric figures. Concepts and Skills to Master Apply knowledge of congruent and/or similar triangles to find scale factor, angle measures, side lengths, and other measurements such as perimeter and area. Apply knowledge of congruent and/or similar triangles to determine the similarity of triangles based on various given information. SUPPORTS FOR TEACHERS Critical Background Knowledge Students should be able to identify corresponding parts of triangles Set up and solve proportions Understand that similar figures have congruent corresponding angles and proportional corresponding sides Academic Vocabulary Similar triangles, proportions, scale factor Suggested Instructional Strategies Resources Challenge students to find real-world Textbook Correlation: examples of similar triangles on their o 7.3 Proving Triangles are Similar own. Encourage them to prove how o 7.4 Similarity in Right Triangles they were able to conclude that the Videos: triangles were similar. o “Section A: Proving the Similarity of Triangles” located at www.discoveryeducation.com http://player.discoveryeducation.com/index.cfm?guidAssetId=F6D5649D-C54840B4-9546-DB85CA892F02&blnFromSearch=1&productcode=US Standards on successive pages were unpacked by Utah State Office of Education, CMS-district specific modifications and resources for this unit were created by CMS teacher leaders. Standards are listed in alphabetical /numerical order not suggested teaching order. PLC’s must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes. Geometry Unit 5: Similarity and Right Triangle Similarity Sample Formative Assessment Tasks Skill-based task 1. Solve for x in the diagram below. Problem Task 1. At 4:00 pm, Karl stands next to his house and measures his shadow and the house’s shadow. Karl’s shadow is 8 ft. long and the house’s shadow is 48 ft. long. If Karl is 6 ft tall, how tall is his house? 2. From www.pearsonsuccessnet.com, 7.4 Enrichment assignment (specifically #6-7) Standards on successive pages were unpacked by Utah State Office of Education, CMS-district specific modifications and resources for this unit were created by CMS teacher leaders. Standards are listed in alphabetical /numerical order not suggested teaching order. PLC’s must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes.