* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Administration Side Effects Preparations available Drug Interactions
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
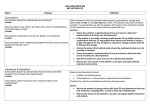
SHARED CARE PROTOCOL for SOUTH EAST ESSEX Drug Name METHOTREXATE Clinical Indication: Rheumatoid Arthritis and Psoriasis; psoriatic arthritis, connective tissue diseases, juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Date approved: December 2014 Due for review: December 2016 Author(s)/Originator(s): Esther Trillo-Gallo / Dr W M Wong Administration Side Effects Oral or parenteral Methotrexate is available as 2.5mg and 10mg tablets. Care needs to be taken if switching between 10mg and 2.5mg tablets. Subcutaneous injection is preferred route in children. Consider sc injection in adults with inefficacy or intolerance of the oral preparation. Folic acid supplementation should be co-prescribed. Local recommendation is folic acid 5mg/day on 6 days per week. Nausea, alopecia, skin rash & diarrhoea. May resolve with reduction in the dose or increasing the dose of folic acid. Stop the treatment if does not resolve and inform the specialist team. Pulmonary Symptoms: A small minority of patients develop symptoms of interstitial pneumonitis soon after starting treatment indicated by persistent dry coughs /shortness of breath. Stop the methotrexate and refer to the specialist team or Casualty urgently. Significant reduction in cellular count in blood (Cytopaenia): Withdraw methotrexate and inform the specialist team or a haematologist. Consider Folinic acid rescue. Preparations available Methotrexate tablets 2.5mg and 10mg. Metoject pre-filled PENs 50mg/ml, 0.15ml (7.5mg); 0.2ml (10mg); 0.25ml (12.5mg); 0.3ml (15mg); 0.35ml (17.5mg); 0.4ml (20mg); 0.45ml (22.5mg); 0.5ml (25mg); 0.55ml (27.5mg); 0.6ml (30mg). Drug Interactions For full information on Drug Interactions, go to Methotrexate List of Drug Interactions Reduced excretion with NSAIDs and salicylates (at the doses of methotrexate used these interactions are not clinically significant). Increased toxicity with cyclosporin. Bone marrow depression with trimethoprim and co-trimoxazole. Probenecid increases serum methotrexate levels and dose reduction is needed. Contra-indications Hepatic impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, active infection and immune deficiency syndromes. Precautions Blood disorders, renal impairment, peptic ulceration, ulcerative stomatitis. Alcohol: Generally advised to stay well within national limits, 21 Units/week for men, 14 Units/week for women. Pregnancy & Breast Feeding: Men & Women of childbearing age should not plan to conceive whilst on methotrexate. All female patients should be advised against conception and pregnancy. A reliable form of contraception should be advised to all patients during methotrexate therapy as well as for at least 3 months after discontinuation of treatment. In case of accidental pregnancy stop methotrexate and discuss with the specialist team. Elective Surgery: Drug can be continued (stop if any active infection, consider withdrawal with GU or lower GI surgery). Immunisations: All live immunisations should be avoided. Pneumococcal vaccination is recommended, revaccination is not recommended (see BNF). Flu vaccines should be given annually. Passive immunisation should be carried out using VZIg in non-immune patents if exposed to Chicken pox or shingles, 1 gram im (adults 15+ yr) as soon as possible after exposure, and within 10 days. Patient Information Patients should report all symptoms and signs suggestive of infection, especially sore throat Aspirin and NSAID: Patients should be advised to avoid self-medication with over-the-counter aspirin or ibuprofen. Methotrexate. For full prescribing information refer to the latest BNF and SPC 1 Criteria for shared care. Prescribing responsibility will only be transferred when: Treatment is for a specified indication. Treatment has been initiated and established by the secondary care specialist. The patient’s initial reaction to and progress on the drug is satisfactory. The patient’s general physical, mental and social circumstances are such that he/she would benefit from shared care arrangements. Responsibilities of initiating specialist Initiation of treatment 3 month worth of treatment will be supplied or until patient is stable and does not require blood tests for three months. Monitor tests as required before and during treatment as agreed in Summary of Monitoring and Responsibilities document. Discussion with the patient regarding benefits and side effects of treatment Prompt communication with the GP of any changes in treatment (including dose adjustments) and assessments of adverse events Advice to GPs about all aspects of treatment Report adverse events to the CSM Ensure clear arrangements for back-up, advice and support. Responsibilities of the GP To prescribe on going therapy to patients after treatment has been established in Secondary Care, usually three months. To report any adverse events to the consultant. Prompt referral to specialist if there is any change in patient’s status. Reporting to and seeking advice from the specialist on any aspect of patient care which is of concern to the GP and may affect treatment. To monitor overall health and wellbeing of the patient. To review that blood tests are performed within the last 3 months before issuing a new prescription. For best practice it is recommended that GPs check that blood tests’ results are in range and contact specialist as detailed in Summary of Monitoring and Responsibilities document or as below. Results that require specialist team input: Liver enzymes elevated or transaminase WCC Significant reduction in renal function MCV Increased > 105 > 2 times upper normal limit 9 < 3.5 x 10 /l Neutrophils Platelets 9 < 2 x 10 /l 9 < 100 x 10 /l Check for other causes (B12, folate and alcohol consumption). A high MCV is not an indication to stop treatment. Flu-like symptoms, sore throat, infection, rash, ulceration, bruising Secondary Care contact information If stopping medication or needing advice please contact: Dr / nurse Contact number: Department Patient’s named Consultant or Clinical Nurse Specialist team in Rheumatology 01702 385128 Nurse specialist live telephone service Mon, Tues, Wed, Fri 9am – 11am. . Alternatively Rheumatology secretaries on 01702 435555, extension numbers 5616 or 6721 or Email: [email protected]. Rheumatology Methotrexate. For full prescribing information refer to the latest BNF and SPC 2