* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electricity Practical
Commutator (electric) wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Overhead line wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
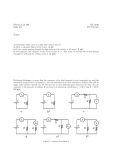
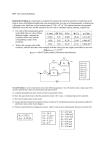
Topic 7 - Electricity • • • • • • • Charges Electrons Voltage Current Series Parallel Resistance The slides are designed to tie in with a set of worksheets, but could be adapted or serve as a template for other teachers Topic 7 page 1 4. I charged up a plastic comb by rubbing it with a duster/pulling it through my hair When I put the charged-up comb near some foil the foil jumped up to stick to the comb Item Topic 7 page 2 What it was rubbed on Plastic comb hair Plastic ruler hair Plastic bag cloth Wooden ruler cloth Plastic pen cloth Metal spatula cloth Did the bits of foil move? yes yes yes no yes no Topic 7 page 3 The electroscope Stop! Topic 7 page 4 Object Charged Plastic comb Plastic rod Plastic bag Plastic ruler Effect on Gold Leaf Rises Rises Rises Rises up up up up If an uncharged object is brought near an electroscope the gold leaf doesn’t move. If a charged object is brought near an electroscope the gold leaf rises up. Topic 7 page 6 Pulling and Pushing Charged object 1 Charged object 2 Comb Cling film Cling film Cling film Polythene rod Polythene rod Perspex rod What happened? Pull together Cling film Push apart Piece of record Pull together Polythene rod Push apart Perspex rod Pull together Perspex rod Push apart Topic 7 page 6 Is there a pattern? Charged object 1 Charged object 2 What happened? Cling film different Cling film Cling film same Cling film Piece of record different Polythene rodsame Polythene rod Polythene roddifferent Perspex rod Perspex rod same Perspex rod Pull together Push apart Pull together Push apart Pull together Push apart Comb Topic 7 page 6 5. If the charged objects are the same material then they will repel Topic 7 page 7 Where Does Charge Come From? Around the outside are the negative electrons The centre of the atom contains both yellow neutrons and green positive protons Topic 7 page 7 1. There are two kinds of electrical charge called positive and negative 2.a) To make an object positively charged you need to remove negative charges b) To make an object negatively charged you need to add negative charges 3. If a substance is neutral it means that the negative charges are exactly balanced by the positive charges Topic 7 page 8 4. Two charged polythene rods will repel because they have the same charge 5. A cleaned mirror will be dusty within 24hrs because the charge attracts dust 6. A woolen jersey could be attracted to a nylon shirt because they would have opposite charges which would attract Topic 7 page 10 1. A Van de Graff generator builds up and stores a negative charge 2. a) Your hair stands on end when you touch a Van de Graff generator because your hairs become negatively charged and repel each other b) Your hair goes down when you touch a water tap because the negative charges leave you flowing along the pipes to the ground and the hairs stop repelling Topic 7 page 11 When a current flows, charges are moving - Now fill the blanks Topic 7 page 12 Battery A Switch Bulb Ammeter Topic 7 page 13 Part of circuit Battery Statement measures current Bulb pushes the current Switch changes electrical energy to light Ammeter carries current round circuit Connecting wire turns the current on and off Topic 7 page 14 Dim bulb – small current Bright bulb - large current The brighter a bulb the bigger the current Topic 7 page 14 1. a) An electric circuit is a path that electricity can flow along b) A complete circuit has no gaps allowing electricity to flow along it 5. A 0.2A B 0.5A C 0.65A D 0.95A Topic 7 page 15 A. A A Topic 7 page 15 B. A A Topic 7 page 15 C. V V Topic 7 page 17 2a)The battery pushes the current through the wires b) The wires conduct the electricity c) The ammeter measures the current d) The switch opens and closes a gap 3a) The energy change in the bulb is Electrical energy Light energy b) The energy change in the battery is Chemical energy Electrical energy 4a) Electricians use symbols to make their diagrams clearer and tidier Topic 7 page 18 Z A X 0.2 Y A 0.2 A 0.2 Current at X Current at Y Current at Z 0.2 A 0.2 A 0.2 A In a series circuit the current is the same at all points in the circuit. Topic 7 page 19 A 0.4 Z A 0.2 A 0.2 Current at X Current at Y Current at Z 0.2 A 0.2 A 0.4 A X Y In a parallel circuit the current taken from the battery equals the sum of the currents through the two bulbs Topic 7 page 20 Q1. The two bulbs in circuit B make less light than the one bulb in circuit A because B shares the current between two (dim) bulbs Q2. No current flows in circuit C because one of the bulbs is blown creating a break in the circuit Q3. Q4. House lights are better wired in parallel than series; a) don’t dim b) Broken bulb doesn’t put whole house into darkness Using Voltmeters and Ammeters Voltmeter – connected in parallel V A Ammeter connected in series Correctly Wired? V No! The voltmeter has been connected in series – it should be parallel Correctly Wired? A No the Ammeter has been connected in parallel – it should have been series Correctly Wired? A Yes! This Ammeter has been connected correctly in series Correctly Wired? A Yes! This Ammeter has been connected correctly in series Correctly Wired? V Yes! The Voltmeter has been connected correctly in parallel Correctly Wired? A Yes! The Ammeter has been connected correctly in series Effects of Series? As more bulbs are added in series the bulbs grow dimmer Topic 7 page 23 Circuit Diagram Conductors Insulators Iron Brass Copper Steel Graphite Plastic Rubber Perspex Glass Wood Topic 7 page 25 Wire Observation Nichrome Glows red hot copper Tin-lead Use Electric fire Conducts Conducting doesn’t get wires hot Safety Heats up and fuse melts Topic 7 page 26, 27 Battery Battery voltage Bulb brightness 1. 1.5 V dim 2. 6 V brighter 3. 12 V bright When the voltage increases the current increases Topic 7 page 28 5. Write down your ideas. • The more batteries the brighter the bulb • This holds true as long as the batteries face the same way • If batteries are reversed they cancel each other out Elephant handout Topic 7 page 29 Text Animation 1 Topic 7 page 30 Title: Choosing the best type of cable Aim:To compare copper/nichrome, thick/thin, long/short wires and find the best Method: Test thick and thin wires in a circuit and measure how it affects the current using an ammeter. Then test copper/nichrome and long/short wires. Topic 7 page 30 Diagram: Results: Wire long short copper nichrome thick thin Current A bulb may be used instead of an ammeter A Topic 7 page 30 Conclusion: • Short wires are better than long wires. • Copper wires are better than nichrome wires. • Thick wires are better than thin wires. Topic 7 page 31 Copper has a lower resistance than nichrome Thin wires have higher resistance than thick ones Longer wires have higher resistance than short ones Topic 7 page 32 The variable resistor 4. Write down what you found out. The longer the wire (coil) the dimmer the bulb, the shorter the wire the brighter the bulb. Topic 7 page 33 The variable resistor Write down what you found out. The longer the wire (coil) the smaller the current and the dimmer the bulb. The longer wire has a higher resistance. Topic 7 page 35 1. A long thin nichrome wire has a higher resistance because thick has a lower resistance, as does copper and short wires. 2. a) Thick copper wires are good for carrying current because copper is a good conductor and thick wires have low resistance b) Long thin coils of nichrome are used in electric fires because nichrome has a high resistance causing it to heat up without melting Topic 7 page 35 3. A variable resistor is used to increase and decrease the current by changing the length of a resistance wire 4. When the volume on a radio is turned Down the resistance wire is lengthened, causing a reduction in the current. 5. Cookers need thick cabling because they use much more current than lamps Topic 7 page 36 The purpose of a fuse is to protect you from a short circuit - safety Not to make the device work Circuit Symbols (components used in slides) A V You can find more downloads and help at www.lab6.co.uk